Question: I need help with part C b) (6) Because absorbance for a given solution containing FeSCN2+ is proportional to molar concentration of FeSCN (as per

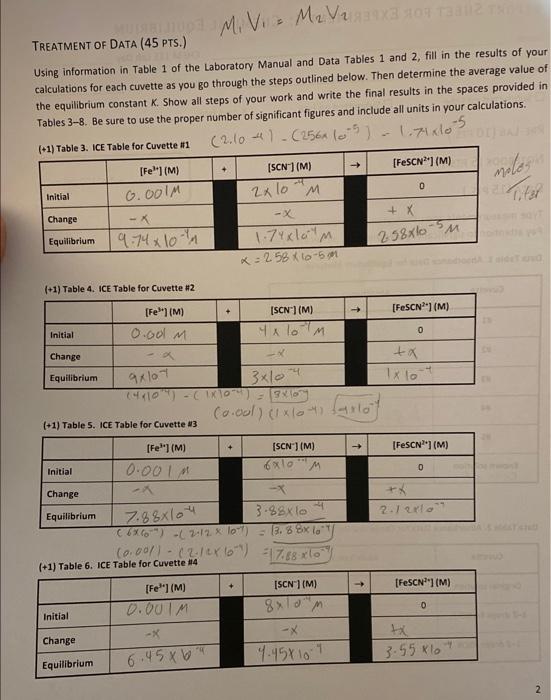
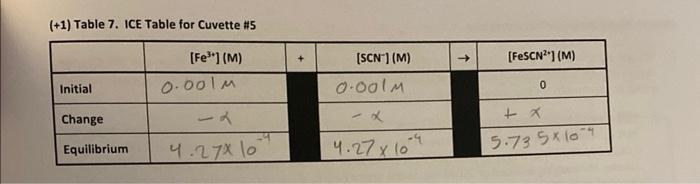
b) (6) Because absorbance for a given solution containing FeSCN2+ is proportional to molar concentration of FeSCN (as per Beer's Law), use a simple proportionality equation (shown below) to solve for the Equilibrium concentration of FeSCN 2+ in each cuvette. Show your work for cuvette H1 in the space below, and put in the Equilibrium values for [FeSCN2] in each cuvette into the respective ICE table. A=bC where A is the measured absorbance (this is a unitless quantity) the product b is a constant composed of two separate constants called the molar absorptivity ( ) and the thickness of the absorbing medium (b) C is the molar concentration of the absorbing species \[ \frac{\left[\mathrm{FeSCN}^{2+} ight]_{\perp}}{A_{H}}=\frac{\left[\mathrm{FeSCN}^{2+} ight]_{\text {STD }}}{A_{S T D}} \] where [FeSCN2+], is the molar concentration of FeSCN2+ in a particular cuvette Aa is the measured absorbance for the solution in a particular cuvette [FeSCN2+] Asro is the measured absorbance of the known standard solution [3CC2+]=2.0104 c) (3) Note that the concentrations that you just calculated are the equilibrium concentrations for FeSCN2+ for each cuvette. Examine the last column in your ICE tables and notice that this concentration also represents the Change in FeSCN" molar concentration, x. Now, enter in the Change in molarities of FeSCN2,Fe3+ and SCN into the ICE table for each cuvette (Tables 3-7). Be sure to indicate the sign of the individual values. TREATMENT OF DATA ( 45 PTS.) M1V1=M2V2 Using information in Table 1 of the Laboratory Manual and Data Tables 1 and 2, fill in the results of your calculations for each cuvette as you go through the steps outlined below. Then determine the average value of the equilibrium constant K. Show all steps of your work and write the final results in the spaces provided in Tables 3-8. Be sure to use the proper number of significant figures and include all units in your calculations. (2.104)(256(05)1.7105 (+1) Table 5. IcE Table for Cuvette 13 (t+11 Table 6. Ice Table for Cuvette "14 (+1) Table 7. ICE Table for Cuvette \#5 b) (6) Because absorbance for a given solution containing FeSCN2+ is proportional to molar concentration of FeSCN (as per Beer's Law), use a simple proportionality equation (shown below) to solve for the Equilibrium concentration of FeSCN 2+ in each cuvette. Show your work for cuvette H1 in the space below, and put in the Equilibrium values for [FeSCN2] in each cuvette into the respective ICE table. A=bC where A is the measured absorbance (this is a unitless quantity) the product b is a constant composed of two separate constants called the molar absorptivity ( ) and the thickness of the absorbing medium (b) C is the molar concentration of the absorbing species \[ \frac{\left[\mathrm{FeSCN}^{2+} ight]_{\perp}}{A_{H}}=\frac{\left[\mathrm{FeSCN}^{2+} ight]_{\text {STD }}}{A_{S T D}} \] where [FeSCN2+], is the molar concentration of FeSCN2+ in a particular cuvette Aa is the measured absorbance for the solution in a particular cuvette [FeSCN2+] Asro is the measured absorbance of the known standard solution [3CC2+]=2.0104 c) (3) Note that the concentrations that you just calculated are the equilibrium concentrations for FeSCN2+ for each cuvette. Examine the last column in your ICE tables and notice that this concentration also represents the Change in FeSCN" molar concentration, x. Now, enter in the Change in molarities of FeSCN2,Fe3+ and SCN into the ICE table for each cuvette (Tables 3-7). Be sure to indicate the sign of the individual values. TREATMENT OF DATA ( 45 PTS.) M1V1=M2V2 Using information in Table 1 of the Laboratory Manual and Data Tables 1 and 2, fill in the results of your calculations for each cuvette as you go through the steps outlined below. Then determine the average value of the equilibrium constant K. Show all steps of your work and write the final results in the spaces provided in Tables 3-8. Be sure to use the proper number of significant figures and include all units in your calculations. (2.104)(256(05)1.7105 (+1) Table 5. IcE Table for Cuvette 13 (t+11 Table 6. Ice Table for Cuvette "14 (+1) Table 7. ICE Table for Cuvette \#5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


