Question: i need help with questions e to g, I've put what i think some of the reasons could be but please help with anymore suggestions

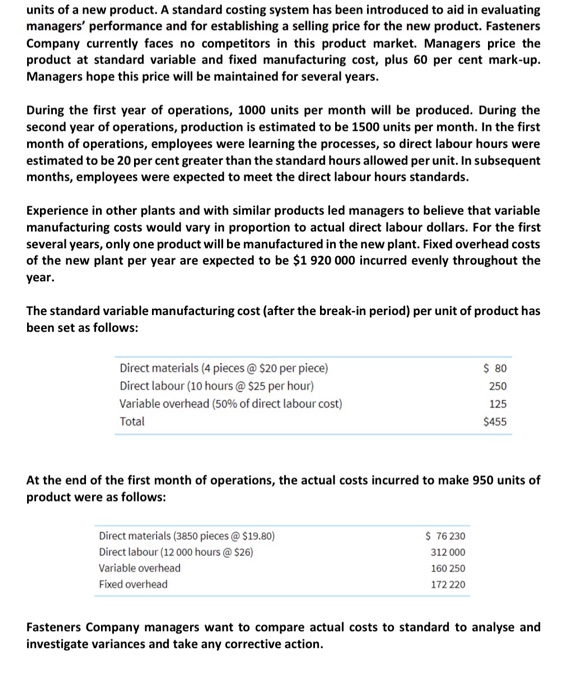

e) Explanations for each of the following variances: direct labour price variance - Minimum wage goes up each year - Union parties convince for better pay for workers - Direct labour price variance can be caused by unexpected avertime hours Seconci, it can be caused by error in the accounting records for the actual cost of direct labour - It can also be the result of unreasonable standard of labour price (ii) direct labour efficiency variance Change in average labour time due to experience To start off with labour hours are lower because of inexperience - It can be caused by fluctuating hours of labour worked - It can also be the consequence of unintentional or intentional over or under reporting of the total labour hours (iii) variable overhead spending variance - Unreasonable standard variable overhead allocation rate - Unexpected changes in the prices paid for variable overhead resources as a result of varying prices of supplies or indirect lahat and new labor or supplier contract - Erroneous accounting records for the actual costs of variable overheads Improved or out of control spending of variable overhead costs (iv) fixed overhead spending variance - Unreasonably estimated costs of fixed overhead Improved or cut-of-control efficiency in spending fixed overhead costs units of a new product. A standard costing system has been introduced to aid in evaluating managers' performance and for establishing a selling price for the new product. Fasteners Company currently faces no competitors in this product market. Managers price the product at standard variable and fixed manufacturing cost, plus 60 per cent mark-up. Managers hope this price will be maintained for several years. During the first year of operations, 1000 units per month will be produced. During the second year of operations, production is estimated to be 1500 units per month. In the first month of operations, employees were learning the processes, so direct labour hours were estimated to be 20 per cent greater than the standard hours allowed per unit. In subsequent months, employees were expected to meet the direct labour hours standards. Experience in other plants and with similar products led managers to believe that variable manufacturing costs would vary in proportion to actual direct labour dollars. For the first several years, only one product will be manufactured in the new plant. Fixed overhead costs of the new plant per year are expected to be $1 920 000 incurred evenly throughout the year. The standard variable manufacturing cost (after the break-in period) per unit of product has been set as follows: Direct materials (4 pieces @ $20 per piece) Direct labour (10 hours @ $25 per hour) Variable overhead (50% of direct labour cost) Total $ 80 250 125 $455 At the end of the first month of operations, the actual costs incurred to make 950 units of product were as follows: Direct materials (3850 pieces @ $19.80) Direct labour (12 000 hours @ $26) Variable overhead Fixed overhead $ 76230 312 000 160 250 172 220 Fasteners Company managers want to compare actual costs to standard to analyse and investigate variances and take any corrective action. (e) Provide at least two possible explanations for each of the following variances: (i) direct labour price variance (ii) direct labour efficiency variance (iii) variable overhead spending variance (iv) fixed overhead spending variance The reasons for variances must be identified before conclusions and actions are decided upon. For two of the variance explanations you provided in part (e), explain what action(s) managers would most likely take. Would it most likely be easier or more difficult to analyse the variances at the new plant compared to Fasteners Company's other plants? Explain. (f) (g) e) Explanations for each of the following variances: direct labour price variance - Minimum wage goes up each year - Union parties convince for better pay for workers - Direct labour price variance can be caused by unexpected avertime hours Seconci, it can be caused by error in the accounting records for the actual cost of direct labour - It can also be the result of unreasonable standard of labour price (ii) direct labour efficiency variance Change in average labour time due to experience To start off with labour hours are lower because of inexperience - It can be caused by fluctuating hours of labour worked - It can also be the consequence of unintentional or intentional over or under reporting of the total labour hours (iii) variable overhead spending variance - Unreasonable standard variable overhead allocation rate - Unexpected changes in the prices paid for variable overhead resources as a result of varying prices of supplies or indirect lahat and new labor or supplier contract - Erroneous accounting records for the actual costs of variable overheads Improved or out of control spending of variable overhead costs (iv) fixed overhead spending variance - Unreasonably estimated costs of fixed overhead Improved or cut-of-control efficiency in spending fixed overhead costs units of a new product. A standard costing system has been introduced to aid in evaluating managers' performance and for establishing a selling price for the new product. Fasteners Company currently faces no competitors in this product market. Managers price the product at standard variable and fixed manufacturing cost, plus 60 per cent mark-up. Managers hope this price will be maintained for several years. During the first year of operations, 1000 units per month will be produced. During the second year of operations, production is estimated to be 1500 units per month. In the first month of operations, employees were learning the processes, so direct labour hours were estimated to be 20 per cent greater than the standard hours allowed per unit. In subsequent months, employees were expected to meet the direct labour hours standards. Experience in other plants and with similar products led managers to believe that variable manufacturing costs would vary in proportion to actual direct labour dollars. For the first several years, only one product will be manufactured in the new plant. Fixed overhead costs of the new plant per year are expected to be $1 920 000 incurred evenly throughout the year. The standard variable manufacturing cost (after the break-in period) per unit of product has been set as follows: Direct materials (4 pieces @ $20 per piece) Direct labour (10 hours @ $25 per hour) Variable overhead (50% of direct labour cost) Total $ 80 250 125 $455 At the end of the first month of operations, the actual costs incurred to make 950 units of product were as follows: Direct materials (3850 pieces @ $19.80) Direct labour (12 000 hours @ $26) Variable overhead Fixed overhead $ 76230 312 000 160 250 172 220 Fasteners Company managers want to compare actual costs to standard to analyse and investigate variances and take any corrective action. (e) Provide at least two possible explanations for each of the following variances: (i) direct labour price variance (ii) direct labour efficiency variance (iii) variable overhead spending variance (iv) fixed overhead spending variance The reasons for variances must be identified before conclusions and actions are decided upon. For two of the variance explanations you provided in part (e), explain what action(s) managers would most likely take. Would it most likely be easier or more difficult to analyse the variances at the new plant compared to Fasteners Company's other plants? Explain. (f) (g)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


