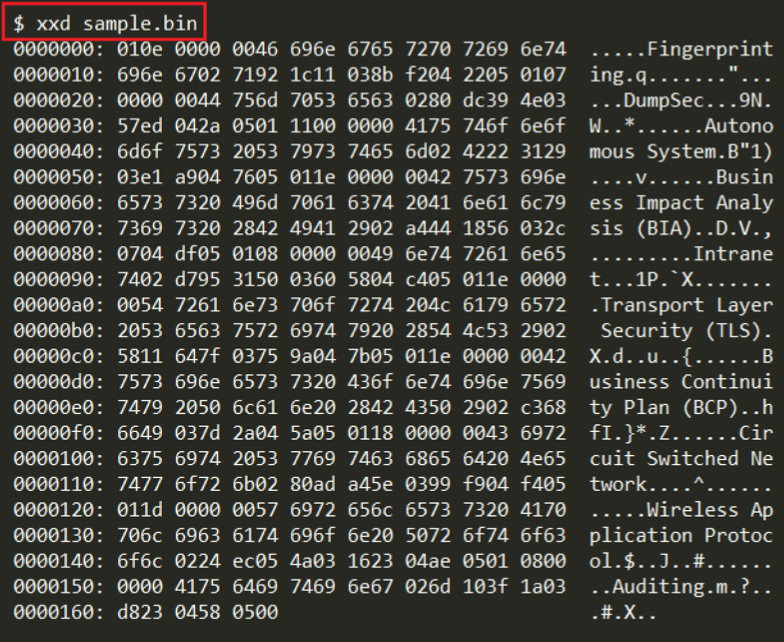
Question: I need some help with my C code, so basically the code is supposed to take sample.bin which looks like below and everytime it reaches
I need some help with my C code, so basically the code is supposed to take sample.bin which looks like below and everytime it reaches a tag it would look at the table and follow the corresposing rule, My code is not working:
#include
int main ()
{
/*-------------- read the file -------------------------------------*/
fptr = fopen ("sample.bin", "r");
str1 = fgetc(fptr);
while (str1 != EOF)
{
printf ("%c", str1);
str1 = fgetc(fptr);
}
printf(" ");
fclose (fptr);
fprintf( ptrFile, " "); fprintf( ptrFile, "
" ); fprintf( ptrFile, " "); fprintf( ptrFile, "
This file was created from a C program
");
for( i = 0; i%d. line
", i); }
fprintf( ptrFile, " "); fprintf( ptrFile, ""); fclose( ptrFile ); return 1;
} FILE * fptr;
int i,n;
char str[100];
char fname[100]="sample.txt";
char str1;
FILE *ptrFile = fopen( "sample.html", "w");
fptr = fopen ("sample.bin","w");
for(i = 0; i
{
fgets(str, sizeof str, stdin);
fputs(str, fptr);
}
fclose (fptr);
Sample HTML :
This is a table
Sample.bin
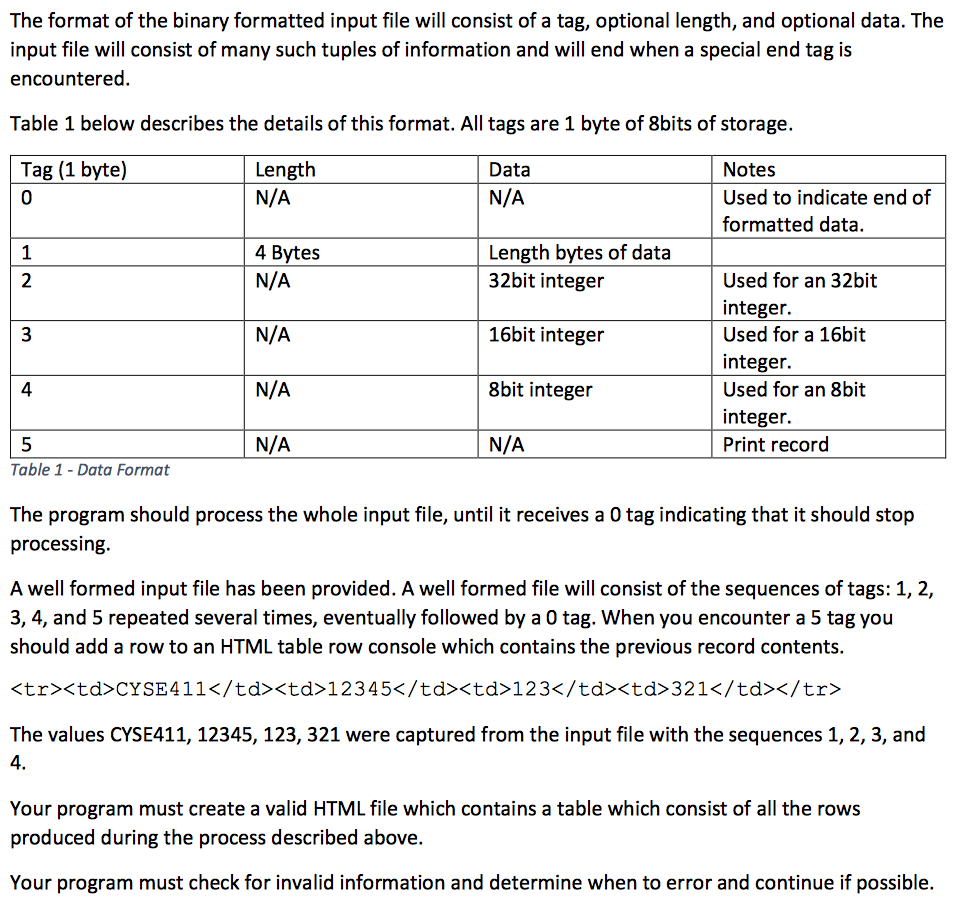
The format of the binary formatted input file will consist of a tag, optional length, and optional data. The input file will consist of many such tuples of information and will end when a special end tag is encountered. Table 1 below describes the details of this format. All tags are 1 byte of 8bits of storage. Length Tag (1 byte) 0 Notes Used to indicate end of formatted data. Data N/A N/A 1 4 Bytes Length bytes of data N/A N/A N/A N/A 32bit integer 16bit integer 8bit integer N/A Used for an 32bit integer. Used for a 16bit integer. Used for an 8bit integer. Print record 4 Table 1 -Data Format The program should process the whole input file, until it receives a 0 tag indicating that it should stop processing A well formed input file has been provided. A well formed file will consist of the sequences of tags: 1,2, 3, 4, and 5 repeated several times, eventually followed by a 0 tag. When you encounter a 5 tag you should add a row to an HTML table row console which contains the previous record contents.
The values CYSE411, 12345, 123, 321 were captured from the input file with the sequences 1, 2, 3, and 4. Your program must create a valid HTML file which contains a table which consist of all the rows produced during the process described above. Your program must check for invalid information and determine when to error and continue if possible. The format of the binary formatted input file will consist of a tag, optional length, and optional data. The input file will consist of many such tuples of information and will end when a special end tag is encountered. Table 1 below describes the details of this format. All tags are 1 byte of 8bits of storage. Length Tag (1 byte) 0 Notes Used to indicate end of formatted data. Data N/A N/A 1 4 Bytes Length bytes of data N/A N/A N/A N/A 32bit integer 16bit integer 8bit integer N/A Used for an 32bit integer. Used for a 16bit integer. Used for an 8bit integer. Print record 4 Table 1 -Data Format The program should process the whole input file, until it receives a 0 tag indicating that it should stop processing A well formed input file has been provided. A well formed file will consist of the sequences of tags: 1,2, 3, 4, and 5 repeated several times, eventually followed by a 0 tag. When you encounter a 5 tag you should add a row to an HTML table row console which contains the previous record contents.
The values CYSE411, 12345, 123, 321 were captured from the input file with the sequences 1, 2, 3, and 4. Your program must create a valid HTML file which contains a table which consist of all the rows produced during the process described above. Your program must check for invalid information and determine when to error and continue if possible
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


