Question: I need some help with this python coding problem in my computer science class. One of the simplest forms of encryption is the Caesar Cipher,
I need some help with this python coding problem in my computer science class.
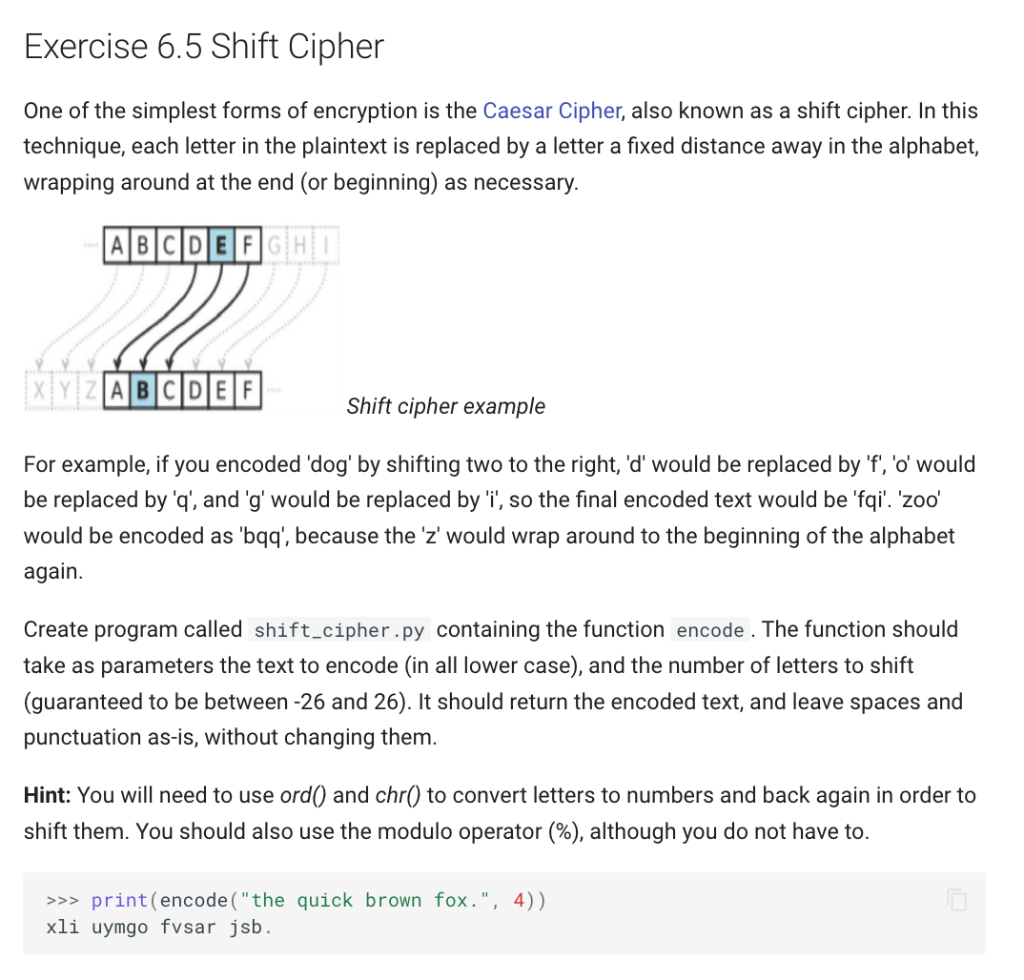
One of the simplest forms of encryption is the Caesar Cipher, also known as a shift cipher. In this technique, each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter a fixed distance away in the alphabet, wrapping around at the end (or beginning) as necessary. shift cipher example For example, if you encoded 'dog' by shifting two to the right, 'd' would be replaced by 'f', 'o' would be replaced by ' q ', and ' g ' would be replaced by 'i', so the final encoded text would be 'fqi'. 'zoo' would be encoded as 'bqq', because the 'z' would wrap around to the beginning of the alphabet again. Create program called shift_cipher.py containing the function encode. The function should take as parameters the text to encode (in all lower case), and the number of letters to shift (guaranteed to be between 26 and 26 ). It should return the encoded text, and leave spaces and punctuation as-is, without changing them. Hint: You will need to use ord() and chr() to convert letters to numbers and back again in order to shift them. You should also use the modulo operator (\%), although you do not have to. >> print(encode("the quick brown fox.", 4)) xli uymgo fvsar jsb
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


