Question: I ONLY NEED PART B AND C FOR THIS PROBLEM!! Need help!! Please provide a step-by-step solution through the use of MALAB code along with
I ONLY NEED PART B AND C FOR THIS PROBLEM!!
Need help!! Please provide a step-by-step solution through the use of MALAB code along with a detailed explanation!!!! It is alright if you handwrite the step-by-step solution but I would prefer the solution to be shown in MATLAB code. This is very URGENT!!! PLEASE reply as soon as possible!! Thank you!!
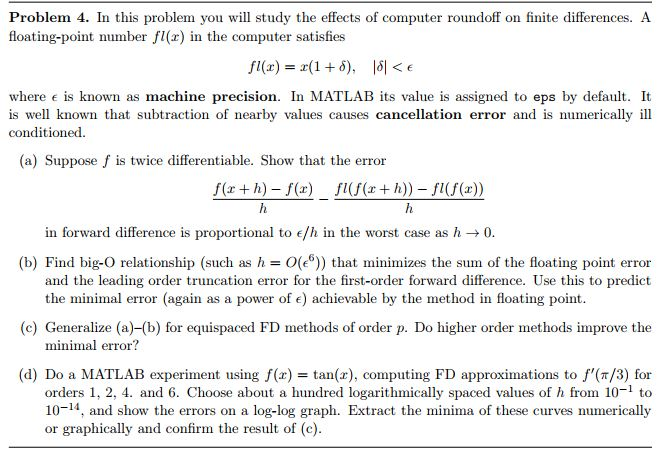
Problem 4. In this problem you will study the effects of computer roundoff on finite differences. A floating-point number fl(x) in the computer satisfies where e is known as machine precision. In MATLAB its value is assigned to eps by default. It is well known that subtraction of nearby values causes cancellation error and is numerically il conditioned (a) Suppose f is twice differentiable. Show that the error f(r + h) - f(x) fl(f(x +h)) - fl(f(z) in forward difference is proportional to c/h in the worst case as h 0. b) Find big-O relationship (such as h = 0(e)) that minimizes the sum of the floating point error and the leading order truncation error for the first-order forward difference. Use this to predict the minimal error (again as a power of e) achievable by the method in floating point. (c) Generalize (a)-(b) for equispaced FD methods of order p. Do higher order methods improve the minimal error? (d) Do a MATLAB experiment using f(x) = tan(x), computing FD approximations to f(+/3) for orders 1, 2, 4. and 6. Choose about a hundred logarithmically spaced values of h from 10-1 to 10-14, and show the errors on a log-log graph. Extract the minima of these curves numerically or graphically and confirm the result of (c). Problem 4. In this problem you will study the effects of computer roundoff on finite differences. A floating-point number fl(x) in the computer satisfies where e is known as machine precision. In MATLAB its value is assigned to eps by default. It is well known that subtraction of nearby values causes cancellation error and is numerically il conditioned (a) Suppose f is twice differentiable. Show that the error f(r + h) - f(x) fl(f(x +h)) - fl(f(z) in forward difference is proportional to c/h in the worst case as h 0. b) Find big-O relationship (such as h = 0(e)) that minimizes the sum of the floating point error and the leading order truncation error for the first-order forward difference. Use this to predict the minimal error (again as a power of e) achievable by the method in floating point. (c) Generalize (a)-(b) for equispaced FD methods of order p. Do higher order methods improve the minimal error? (d) Do a MATLAB experiment using f(x) = tan(x), computing FD approximations to f(+/3) for orders 1, 2, 4. and 6. Choose about a hundred logarithmically spaced values of h from 10-1 to 10-14, and show the errors on a log-log graph. Extract the minima of these curves numerically or graphically and confirm the result of (c)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


