Question: I sent previously this exercise and the exercise PR 7 2 A that needs the information from this exercise Beginning merchandise IAverntoly Purchases (net) Merchandise
I sent previously this exercise and the exercise PR 7 2 A that needs the information from this exercise
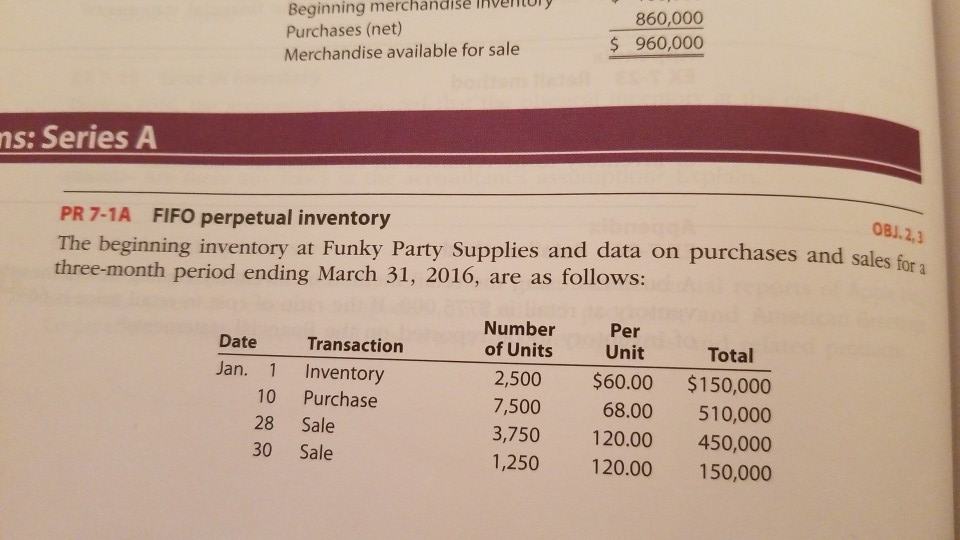
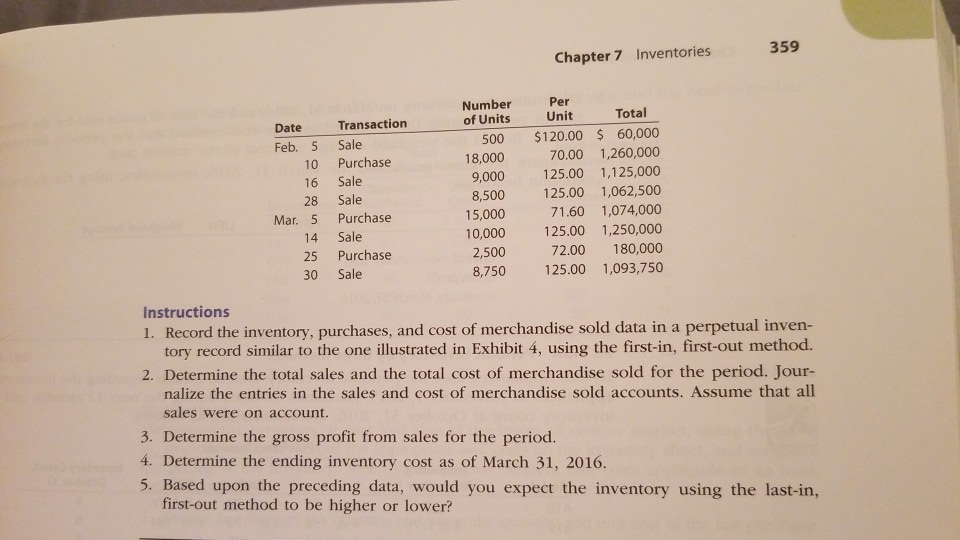
Beginning merchandise IAverntoly Purchases (net) Merchandise available for sale 860,000 s 960,000 s: Series A 08J.2,3 n purchases and sales fora PR 7-1A FIFO perpetual inventory e beiaing emny at runy arty supplies and data on purchases and sloa three-month period ending March 31, 2016, are as follows: Number of Units Per Date Transaction Jan. 1 Inventory 10 Purchase 28 Sale 30 Sale Unit 2,500 $60.00 $150,000 7,500 68.00 510,000 3,750 120.00 450,000 1,250 120.00 150,000 Chapter 7 Inventories 359 Per Number of Units Unit Total 18,000 Date Transaction 500 $120.00 60,000 70.00 1,260,000 9,000 125.00 1,125,000 8,500 125.00 1,062,500 71.60 1,074,000 10,000 125.00 1,250,000 72.00 180,000 8,750 125.00 1,093,750 Feb. 5 Sale 10 Purchase 16 Sale 28 Sale Mar. 5 Purchase 15,000 14 Sale 25 Purchase 30 Sale 2,500 Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of merchandise sold data in a perpetual inven- tory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 4, using the first-in, first-out method. 2. Determine the total sales and the total cost of merchandise sold for the period. Jour- nalize the entries in the sales and cost of merchandise sold accounts. Assume that all sales were on account. 3. Determine the gross profit from sales for the period. 4. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31, 2016. 5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the inventory using the last-in, first-out method to be higher or lower
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


