Question: I use a simple model to understand my cat. Each day he gets up, and is in either a good mood, or a bad mood.
I use a simple model to understand my cat. Each day he gets up, and is in either a good mood, or a bad mood. His mood depends on his mood from the previous day; on day 1 he always starts in a good mood. His actions depend on his mood, and are random with some probabilities:
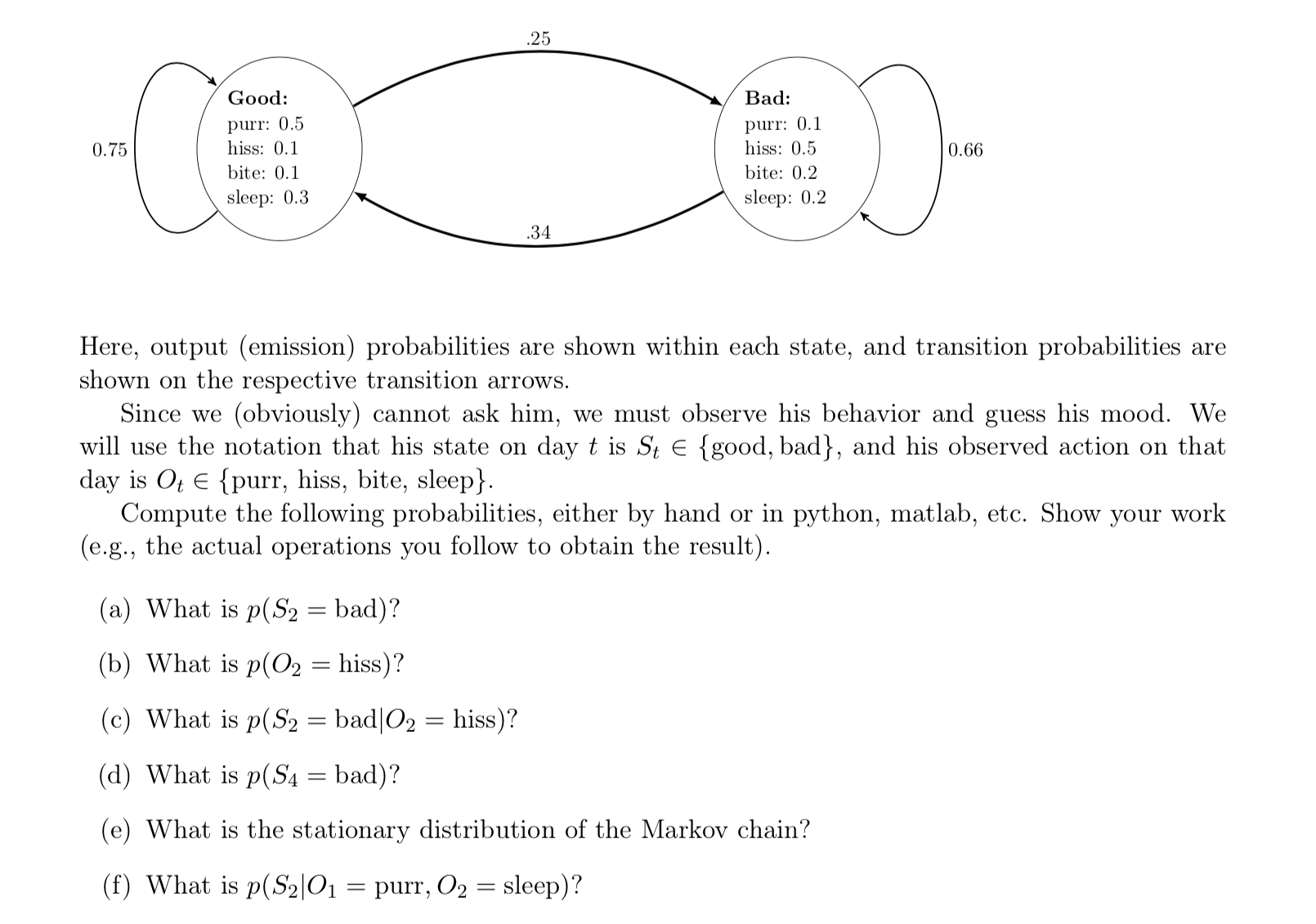
Good: purr: 0.5 . . 0.75 hiss: 0.1 ' : . 0.66 bite: 0.1 ' sleep: 0.3 Here, output (emission) probabilities are shown within each state, and transition probabilities are Shown on the respective transition arrows. Since we (obviously) cannot ask him, we must observe his behavior and guess his mood. We will use the notation that his state on day t is St 6 {good, bad}, and his observed action on that day is 0.4, E {purr, hiss, bite, sleep}. Compute the following probabilities, either by hand or in python, matlab, etc. Show your work (e.g., the actual operations you follow to obtain the result). (a) What is 13(52 bad)? (b) What is p(02= hiss)? (c) What is 13(32 2 bad|02 = hiss). (d) What is p(S4= bad)? (e) What is the stationary distribution of the Markov chain? (f) What is p(5'2)01 = purr, 02 = sleep)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


