Question: id Quiz: Quiz - Defining X la Week 9 - Biology Con > Inment-Responses/submit?dep=30444701&tags=autosave#question4271807_9 eqs med path. I Pre-Medical Pathwa. L Neurobiology Cour.. Accommodation FO.
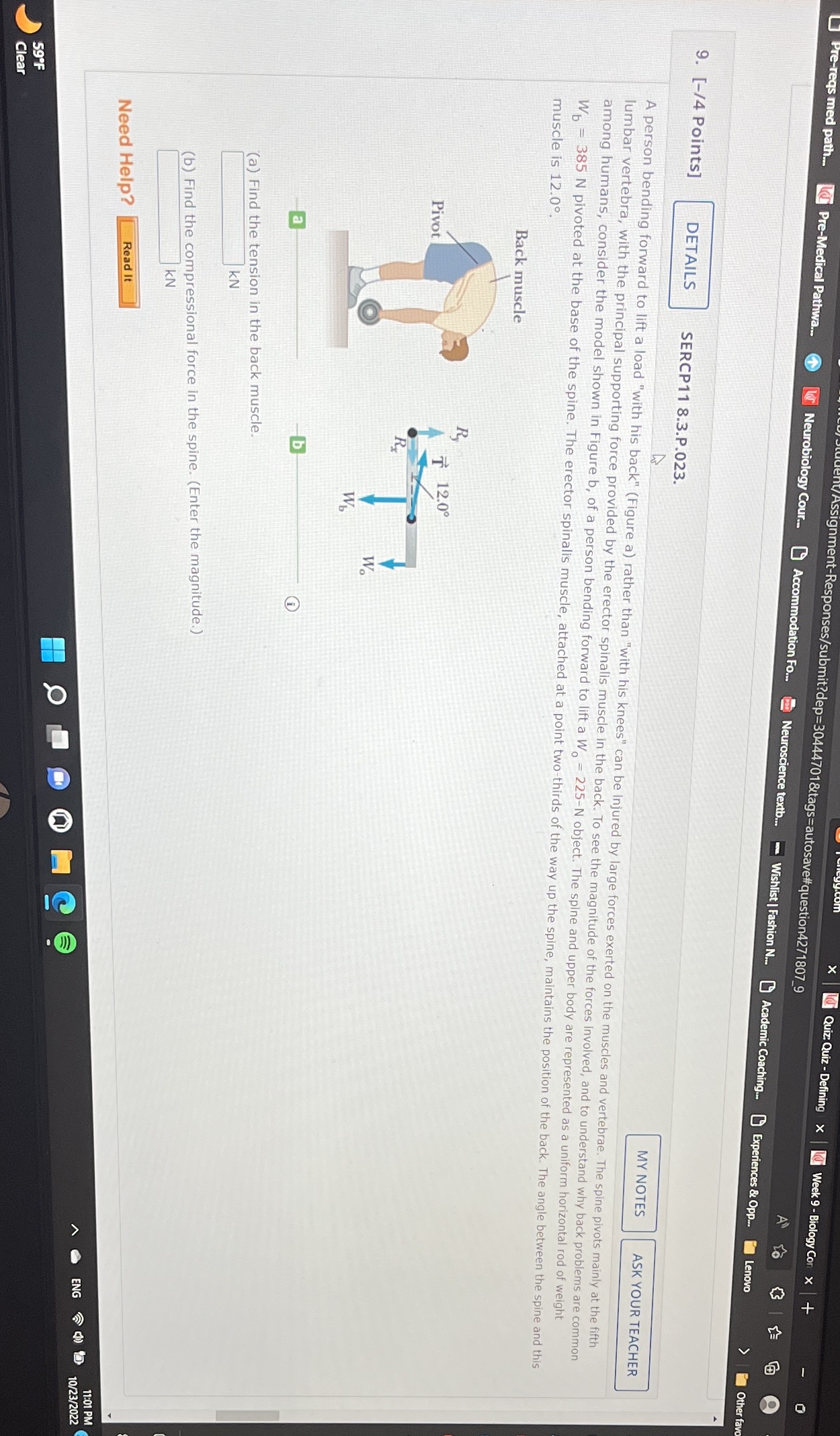
id Quiz: Quiz - Defining X la Week 9 - Biology Con > Inment-Responses/submit?dep=30444701&tags=autosave#question4271807_9 eqs med path. I Pre-Medical Pathwa. L Neurobiology Cour.. Accommodation FO. Neuroscience textb.. - Wishlist | Fashion N. Academic Coaching.. Experiences & Opp. Lenovo Other fav 9. [-/4 Points] DETAILS SERCP11 8.3.P.023. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER A person bending forward to lift a load "with his back" (Figure a) rather than "with his knees" can be Injured by large forces exerted on the muscles and vertebrae. The spine pivots mainly at the fifth lumbar vertebra, with the principal supporting force provided by the erector spinalis muscle in the back. To see the magnitude of the forces involved, and to understand why back problems are common among humans, consider the model shown in Figure b, of a person bending forward to lift a W = 225-N object. The spine and upper body are represented as a uniform horizontal rod of weight W. = 385 N pivoted at the base of the spine. The erector spinalis muscle, attached at a point two-thirds of the way up the spine, maintains the position of the back. The angle between the spine and this muscle is 12.0. Back muscle Pivot T 12.0 (a) Find the tension in the back muscle. KN (b) Find the compressional force in the spine. (Enter the magnitude.) KN Need Help? Read It 11:01 PM ENG @ () 9 10/23/2022 59 F Clear
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


