Question: If someone could help me. I do not understand how to play this game. If you explain to me that the numbers mean and how
If someone could help me. I do not understand how to play this game. If you explain to me that the numbers mean and how you got them, step by step on making the proposals 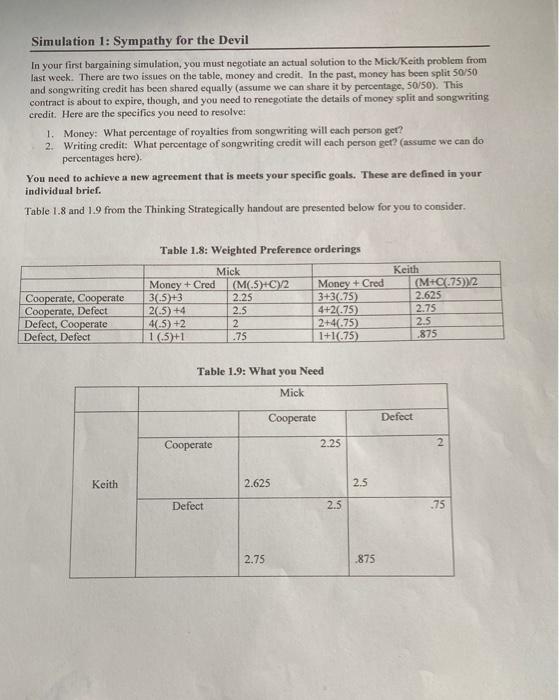

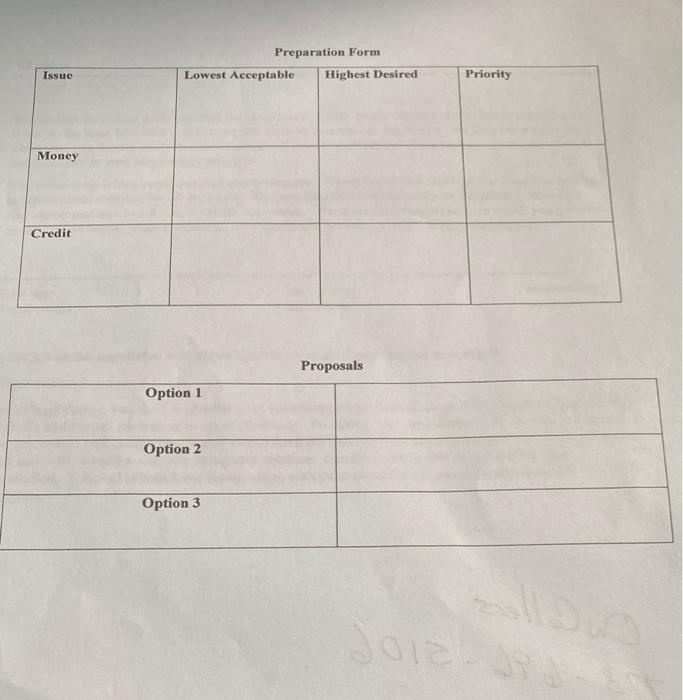
Simulation 1: Sympathy for the Devil In your first bargaining simulation, you must negotiate an actual solution to the Mick/Keith problem from last week. There are two issues on the table, money and credit. In the past, money has been split 50/50 and songwriting credit has been shared equally (assume we can share it by percentage, 50/50). This contract is about to expire, though, and you need to renegotiate the details of money split and songwriting credit. Here are the specifies you need to resolve: 1. Money: What percentage of royalties from songwriting will each person get? 2. Writing credit: What percentage of songwriting credit will each person get? (assume we can do percentages here). You need to achieve a new agreement that is meets your specific goals. These are defined in your individual brief. Table 1.8 and 1.9 from the Thinking Strategically handout are presented below for you to consider, Table 1.8: Weighted Preference orderings Cooperate, Cooperate Cooperate, Defect Defect, Cooperate Defect, Defect Mick Money + Cred (M(.5) C)/2 30.5)+3 2.25 2.5) +4 2.5 4.5) +2 2 1(5)+1 .75 Money + Cred 3+3.75) 4+2.75) 2+4675) 1+1675 Keith (M+C1.75))2 2.625 2.75 2.5 .875 Table 1.9: What you Need Mick Cooperate Defect Cooperate 2.25 2 Keith 2.625 2.5 Defect 2.5 .75 2.75 .875 Mick The current agreement gives you half the money and half the credit. Neither of you has an incentive to break up the team (the double defect payoffs are both less than 1, and much lower than other payoffs). Therefore, you should easily be able to achieve at least a continuation of the current agreement. This is one boundary to your bargaining range (B). You value songwriting credit twice as much as money. Therefore, at one extreme you would be willing to take half the royalties for all the credit. This sets the other boundary of your bargaining range (A). Any agreement between A and B will be acceptable. The other extreme outcome, in which you get all the money but no credit, is not acceptable. Any agreement between B and C is thus unacceptable. -B half money half credit O money Total credit total money no credit Your job as the negotiator is to get as close to your ideal position (A) as possible. Preparation Before negotiating, you need to identify your bargaining range (lowest acceptable to highest (realistically) desired), and to rank each issue in terms of priority. From this, you should be able to develop 2-3 options that you would find acceptable. These should form the basis of your negotiation, positions from which to start and work toward a mutually acceptable solution. Use the forms below to prepare for your megotiation. You will submit these forms, along with your scoring sheet when the negotiation is complete. Preparation Form Lowest Acceptable Highest Desired Issue Priority Money Credit Proposals Option 1 Option 2 Option 3 Simulation 1: Sympathy for the Devil In your first bargaining simulation, you must negotiate an actual solution to the Mick/Keith problem from last week. There are two issues on the table, money and credit. In the past, money has been split 50/50 and songwriting credit has been shared equally (assume we can share it by percentage, 50/50). This contract is about to expire, though, and you need to renegotiate the details of money split and songwriting credit. Here are the specifies you need to resolve: 1. Money: What percentage of royalties from songwriting will each person get? 2. Writing credit: What percentage of songwriting credit will each person get? (assume we can do percentages here). You need to achieve a new agreement that is meets your specific goals. These are defined in your individual brief. Table 1.8 and 1.9 from the Thinking Strategically handout are presented below for you to consider, Table 1.8: Weighted Preference orderings Cooperate, Cooperate Cooperate, Defect Defect, Cooperate Defect, Defect Mick Money + Cred (M(.5) C)/2 30.5)+3 2.25 2.5) +4 2.5 4.5) +2 2 1(5)+1 .75 Money + Cred 3+3.75) 4+2.75) 2+4675) 1+1675 Keith (M+C1.75))2 2.625 2.75 2.5 .875 Table 1.9: What you Need Mick Cooperate Defect Cooperate 2.25 2 Keith 2.625 2.5 Defect 2.5 .75 2.75 .875 Mick The current agreement gives you half the money and half the credit. Neither of you has an incentive to break up the team (the double defect payoffs are both less than 1, and much lower than other payoffs). Therefore, you should easily be able to achieve at least a continuation of the current agreement. This is one boundary to your bargaining range (B). You value songwriting credit twice as much as money. Therefore, at one extreme you would be willing to take half the royalties for all the credit. This sets the other boundary of your bargaining range (A). Any agreement between A and B will be acceptable. The other extreme outcome, in which you get all the money but no credit, is not acceptable. Any agreement between B and C is thus unacceptable. -B half money half credit O money Total credit total money no credit Your job as the negotiator is to get as close to your ideal position (A) as possible. Preparation Before negotiating, you need to identify your bargaining range (lowest acceptable to highest (realistically) desired), and to rank each issue in terms of priority. From this, you should be able to develop 2-3 options that you would find acceptable. These should form the basis of your negotiation, positions from which to start and work toward a mutually acceptable solution. Use the forms below to prepare for your megotiation. You will submit these forms, along with your scoring sheet when the negotiation is complete. Preparation Form Lowest Acceptable Highest Desired Issue Priority Money Credit Proposals Option 1 Option 2 Option 3



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


