Question: i'm having difficulties finding the critical value and confidence interval Provided below are summary statistics for independent simple random samples from two conduct the required
i'm having difficulties finding the critical value and confidence interval
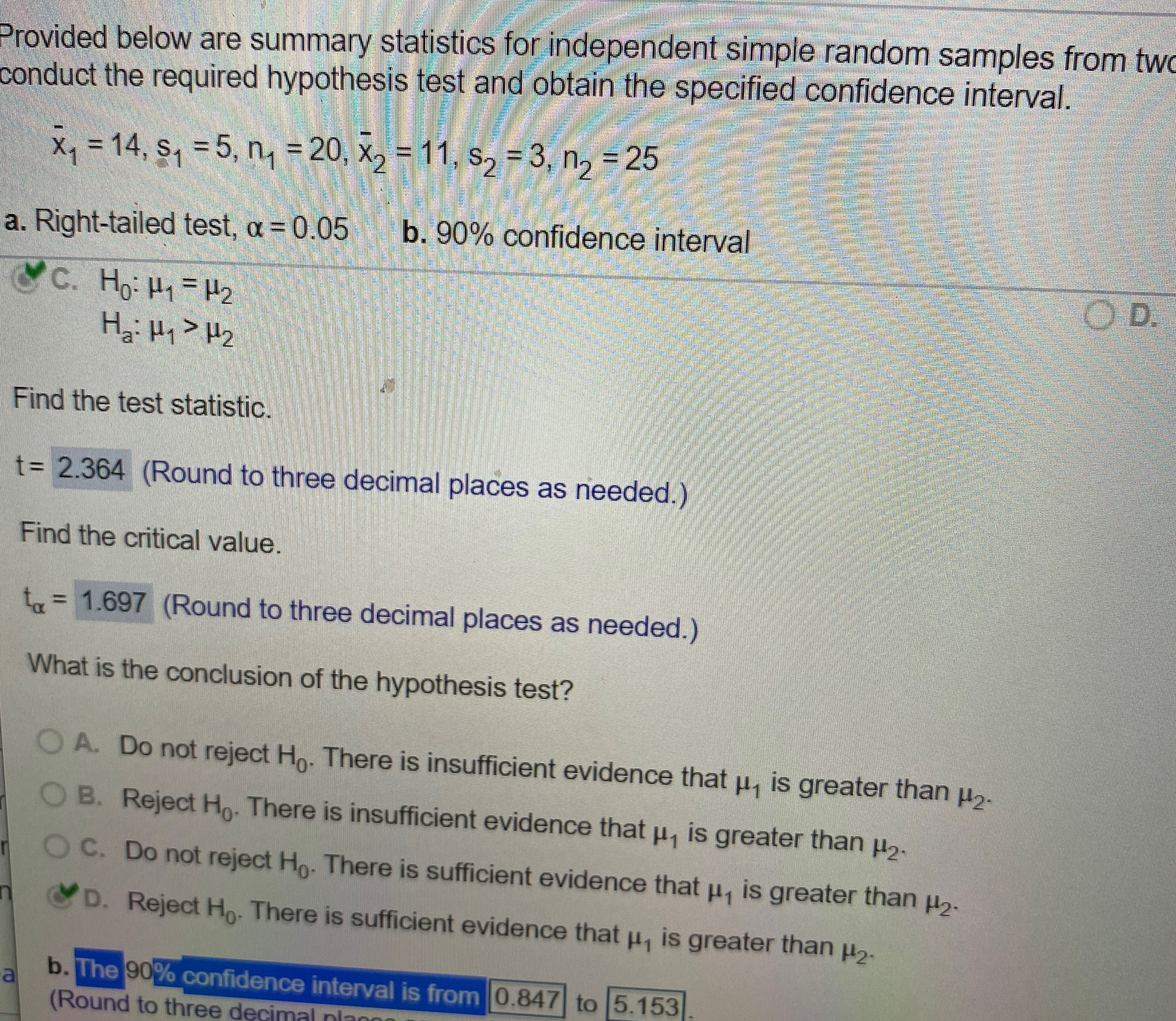

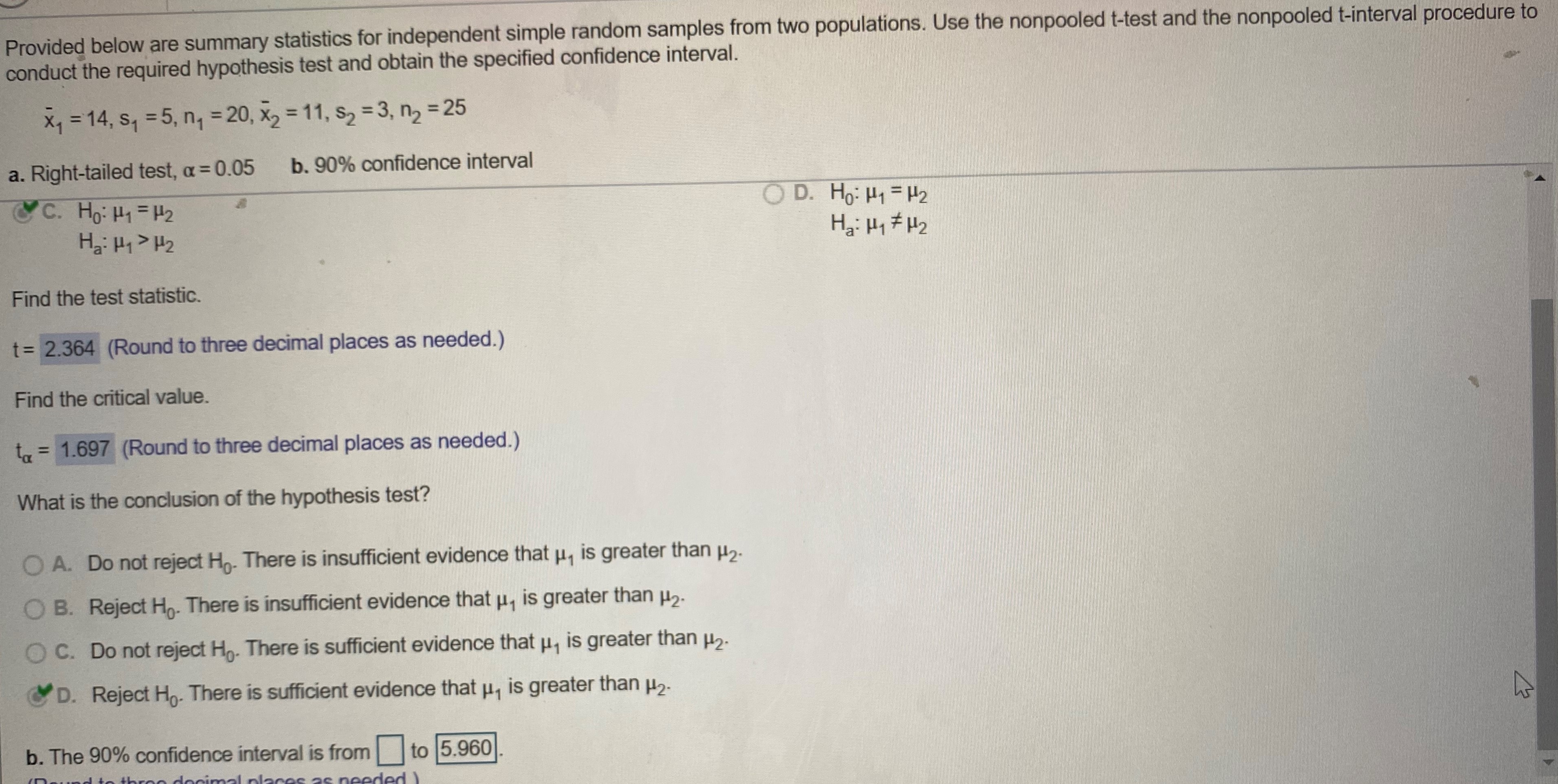

Provided below are summary statistics for independent simple random samples from two conduct the required hypothesis test and obtain the specified confidence interval. xy = 14, s, = 5, n, = 20, X, $2 - 3, n2 = 25 a. Right-tailed test, a =0.05 b. 90% confidence interval C. Ho: Hy = Hz Hai Hy > H2 Find the test statistic. t= 2.364 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Find the critical value. to = 1.697 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion of the hypothesis test? O A. Do not reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence that , is greater than #2- O B. Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence that u, is greater than #2- O C. Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence that , is greater than #2- D. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence that u, is greater than #2- a b. The 90% confidence interval is from 0.847 to 5.153 (Round to three decinPreliminary analyses indicate that you can consider Chronic the assumptions for using nonpooled t-procedures Remitted satisfied. Researchers randomly and independently X1 = 26.9 X2 = 24.9 selected 33 prisoners diagnosed with chronic posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and 23 S, = 3 So = 8 prisoners that were diagnosed with PTSD but had n1 = 33 n = 23 since recovered (remitted). Obtain a 95% confidence interval for the difference, Hy - 2, between the mean ages at arrest for prisoners with chronic PTSD and remitted PTSD The 95% confidence interval is from to (Round to three decimal places as needed.)Provided below are summary statistics for independent simple random samples from two populations. Use the nonpooled t-test and the nonpooled t-interval procedure to conduct the required hypothesis test and obtain the specified confidence interval. Xy = 14, Sy = 5, n, = 20, X2 = 11, $2 = 3, n2 = 25 a. Right-tailed test, a = 0.05 b. 90% confidence interval &C. Ho: H1 = H2 OD. Ho: H1 = H2 Ha: Hy > H2 Ha: Hy # H2 Find the test statistic. t= 2.364 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Find the critical value. to = 1.697 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion of the hypothesis test? O A. Do not reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence that u, is greater than #2- O B. Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence that u, is greater than #2- O C. Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence that u, is greater than #2- D. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence that u, is greater than #2- b. The 90% confidence interval is from|to 5.960Preliminary data analyses indicate that you can consider the assumptions for using nonpooled t-procedures satisfied. Researchers Chronic Remitted randomly and independently selected 30 prisoners diagnosed with chronic posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and 24 prisoners that X1 = 26.5 X2 = 20.8 were diagnosed with PTSD but had since recovered (remitted). The ages, in years, at arrest yielded the summary statistics shown in the table to the right. At the 10% significance level, do the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that a difference exists in the mean $1 = 3 $2 = 6 age at arrest of prisoners with chronic PTSD and remitted PTSD? n1 = 30 n2 = 24 What are the hypotheses for the nonpooled t-test? CA. Ho: H1 = H2 OB. Ho: H1 - H2 Hai Hy # H2 Ha: H1 7 H2 OC. Ho: My = H2 OD. Ho: H1 = H2 Ha: Hy
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


