Question: I'm stuck on requirement 9 & need help with req. 9-12. The right side of the spreadsheet is supposed to help create the left side.
I'm stuck on requirement 9 & need help with req. 9-12. The right side of the spreadsheet is supposed to help create the left side.
I've posted all the work I've done up till that point. If you see any errors in 5-8 please let me know. TIA.
Quivers Inc. began operations on January 1 of the current year. The company produces eight-ounce bottles of jet wax called Ophelia Shine. The wax is sold wholesale in 12-bottle cases for $100 per case. There is a selling commission of $20 per case . The January direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead costs are as follows:
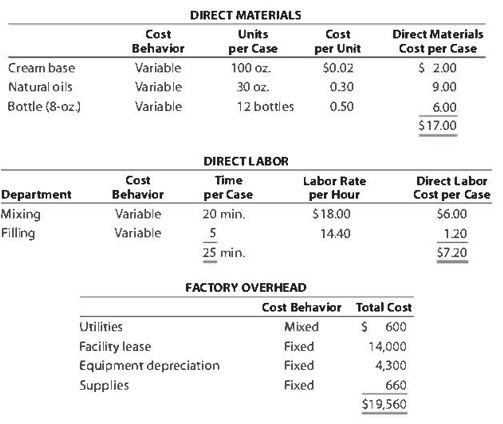
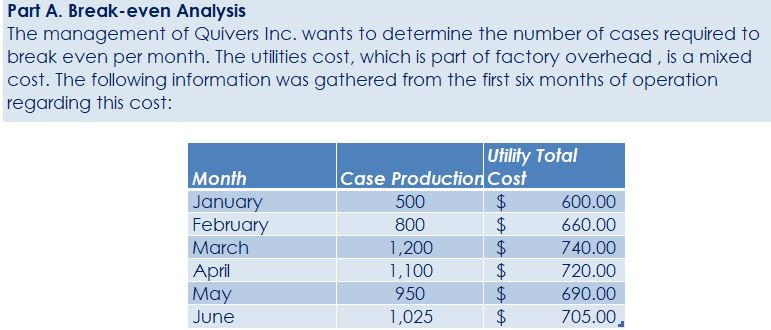
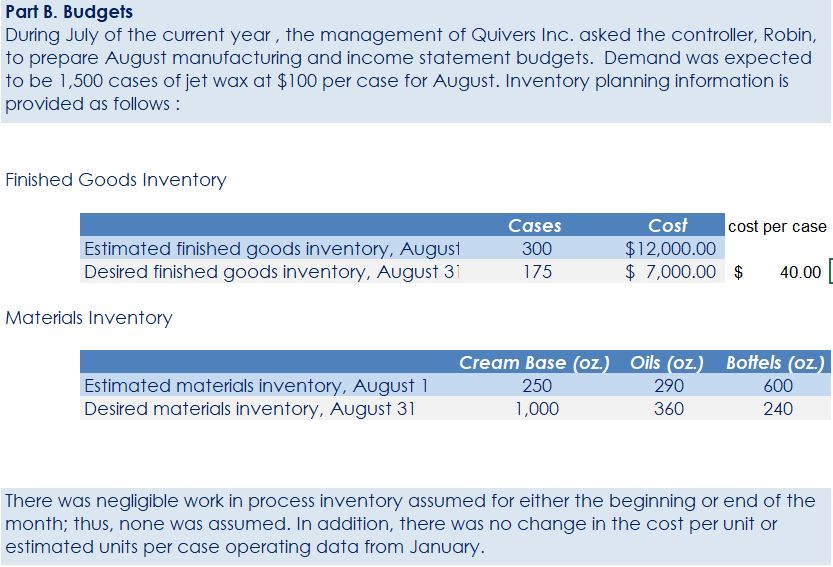
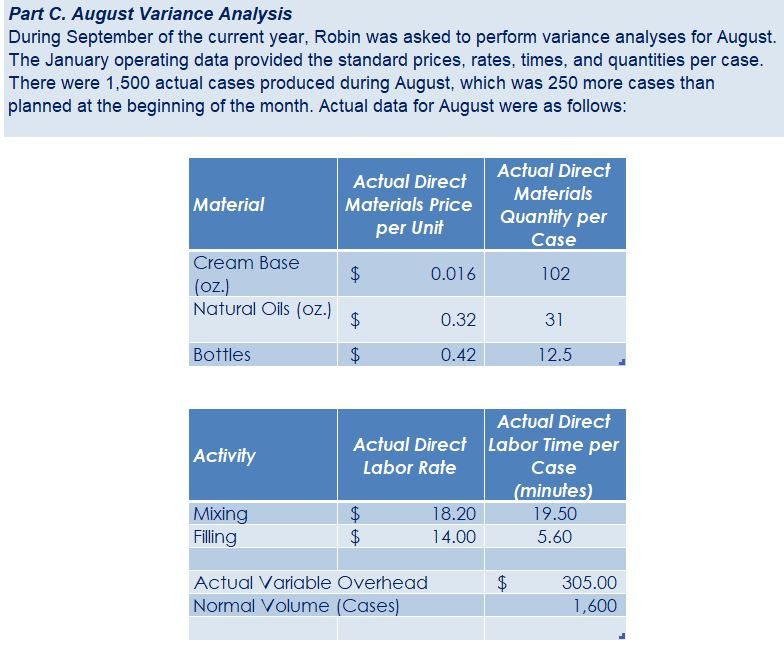

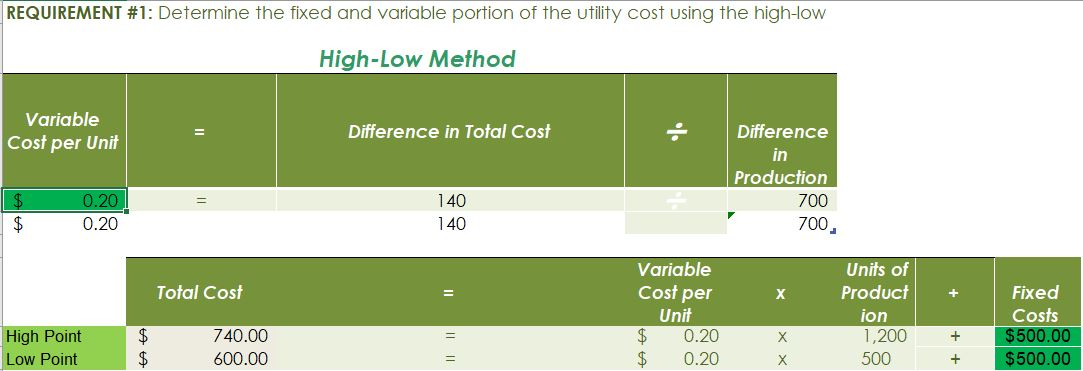
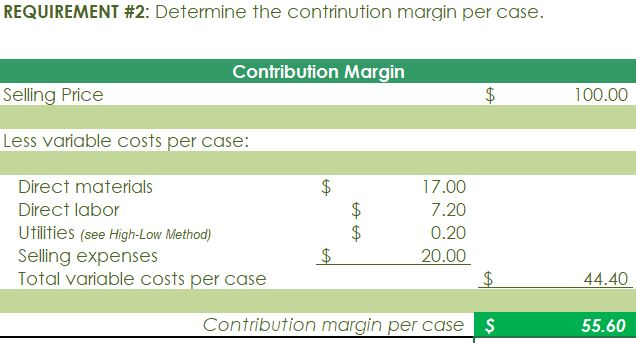
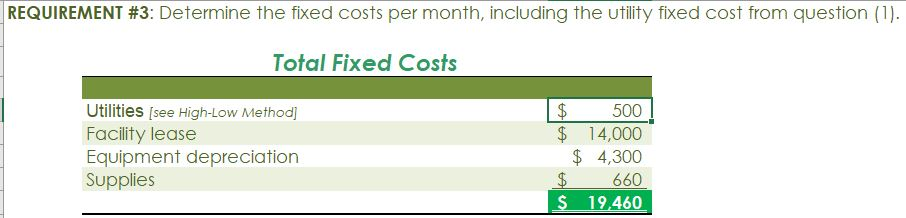

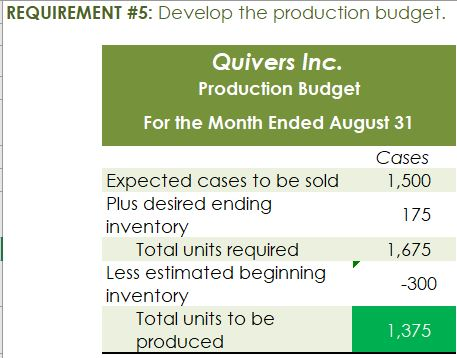
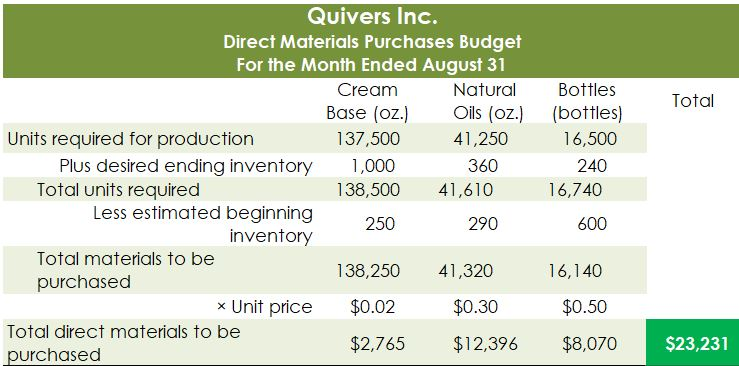
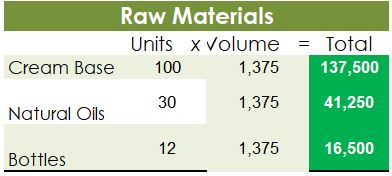
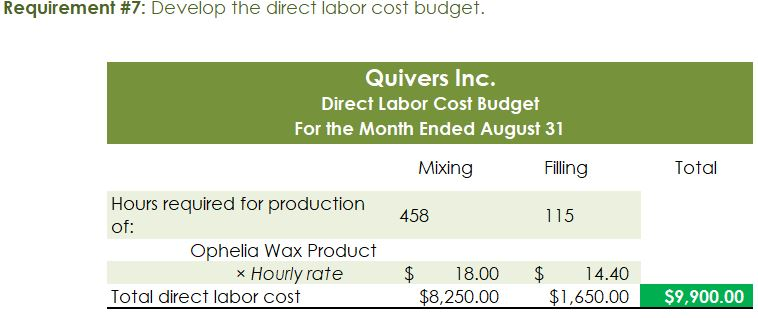
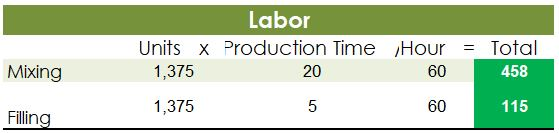
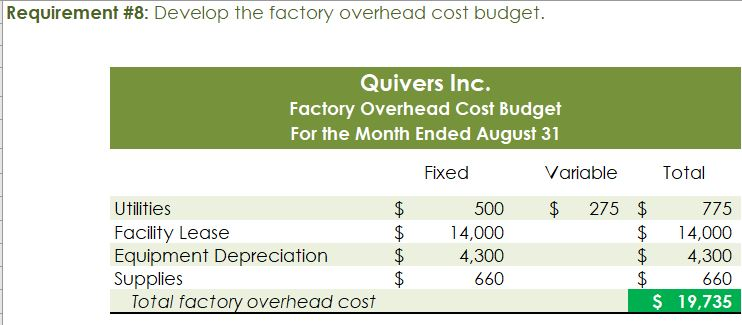
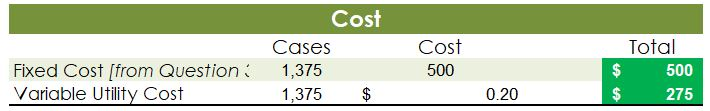

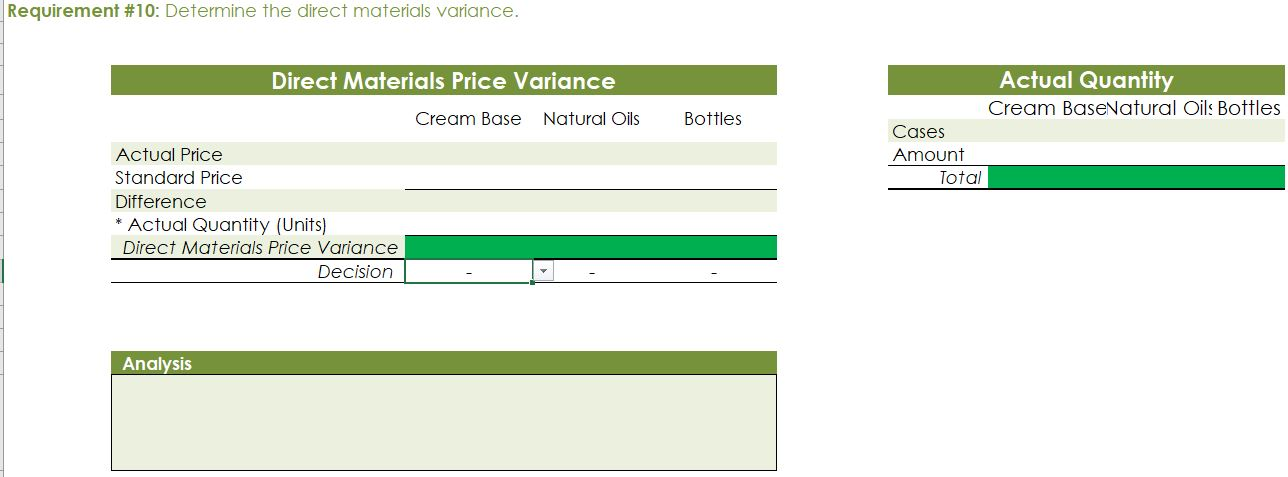
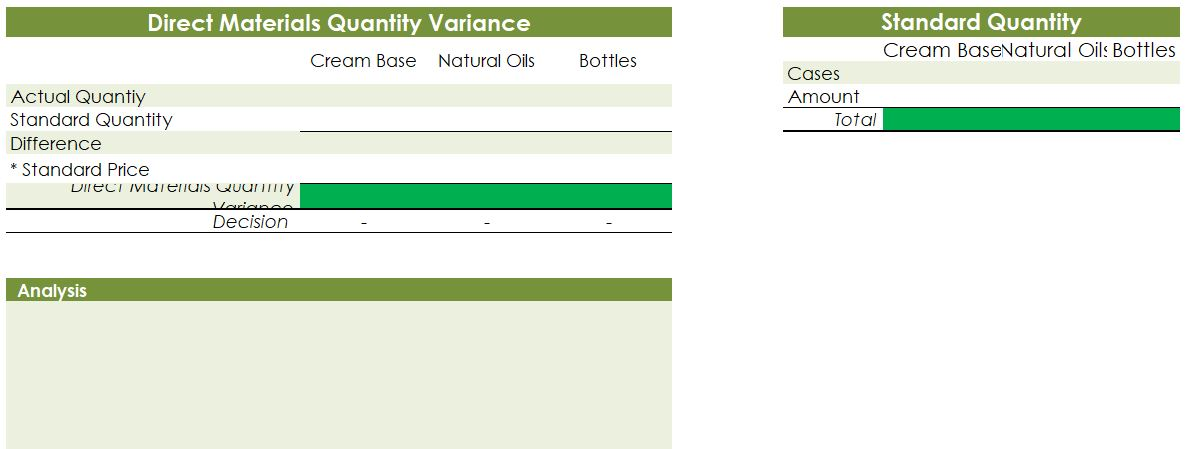
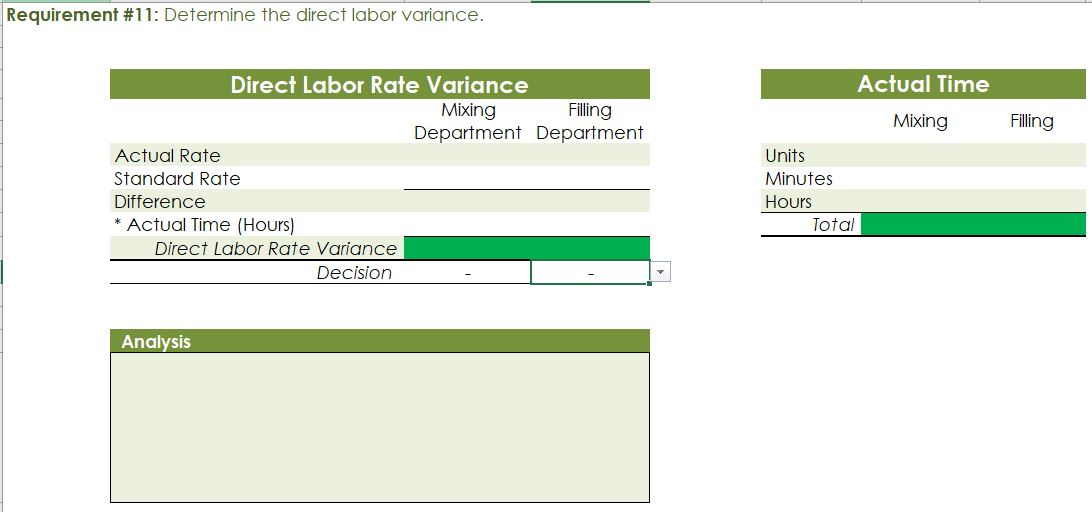
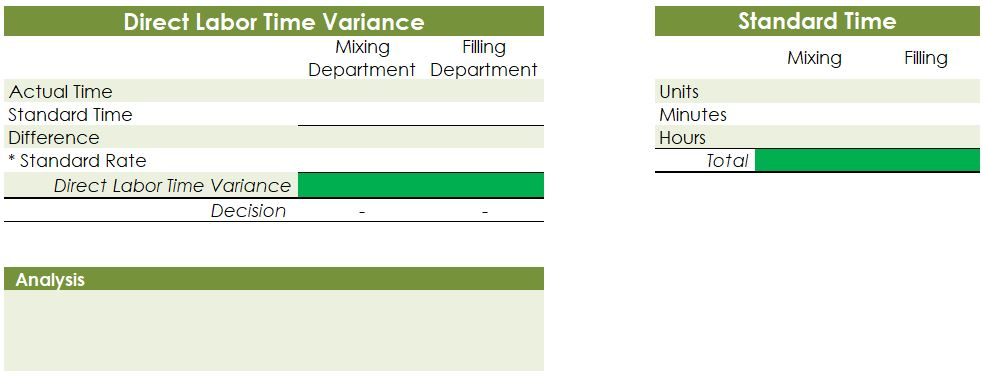
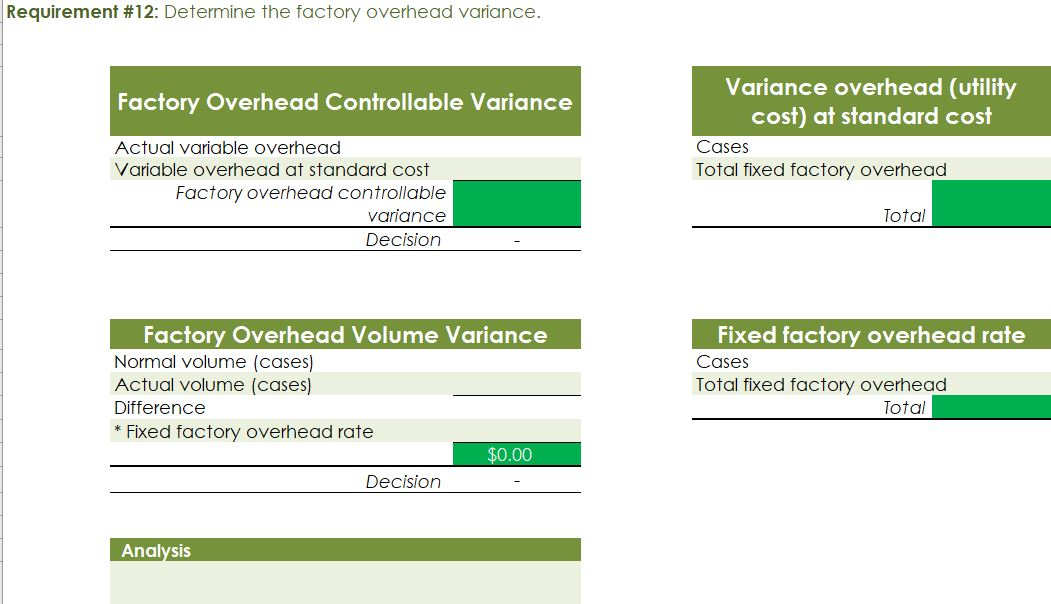
Crearn base Natural oils Bottle (8-oz) DIRECT MATERIALS Cost Units Behavior per Case Variable 100 oz. Variable 30 oz. Variable 12 bottles Cost per Unit $0.02 0.30 0.50 Direct Materials Cost per Case $ 2.00 9.00 6.00 $17.00 Department Mixing Cost Behavior Variable Variable DIRECT LABOR Time per Case 20 min. 5 25 min. Labor Rate per Hour $18.00 14.40 Direct Labor Cost per Case $6.00 1.20 $720 Filling FACTORY OVERHEAD Cost Behavior Total Cost Orilities Mixed $ 600 Facility lease Fixed 14,000 Equipment depreciation Fixed 4,300 Supplies Fixed 660 $19,560 Part A. Break-even Analysis The management of Quivers Inc. wants to determine the number of cases required to break even per month. The utilities cost, which is part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. The following information was gathered from the first six months of operation regarding this cost: Month January February March April May June Utility Total Case Production Cost 500 600.00 800 $ 660.00 1,200 $ 740.00 1,100 $ 720.00 950 690.00 1,025 $ 705.00 A A A A Part B. Budgets During July of the current year, the management of Quivers Inc. asked the controller, Robin, to prepare August manufacturing and income statement budgets. Demand was expected to be 1,500 cases of jet wax at $100 per case for August. Inventory planning information is provided as follows: Finished Goods Inventory Estimated finished goods inventory, August Desired finished goods inventory, August 31 Cases 300 175 Cost cost per case $12,000.00 $ 7,000.00 $ 40.00 Materials Inventory Estimated materials inventory, August 1 Desired materials inventory, August 31 Cream Base (oz.) Oils (oz.) Bottels (oz.) 250 290 600 1,000 360 240 There was negligible work in process inventory assumed for either the beginning or end of the month; thus, none was assumed. In addition, there was no change in the cost per unit or estimated units per case operating data from January. Part C. August Variance Analysis During September of the current year, Robin was asked to perform variance analyses for August. The January operating data provided the standard prices, rates, times, and quantities per case. There were 1,500 actual cases produced during August, which was 250 more cases than planned at the beginning of the month. Actual data for August were as follows: Material Actual Direct Materials Price per Unit Actual Direct Materials Quantity per Case $ 0.016 102 Cream Base (oz.) Natural Oils (oz.) $ 0.32 31 Bottles $ $ 0.42 12.5 Activity Actual Direct Actual Direct Labor Time per Labor Rate Case (minutes) $ 18.20 19.50 $ 14.00 5.60 Mixing Filling $ Actual Variable Overhead Normal Volume (Cases) 305.00 1,600 The prices of the materials were different from standard due to fluctuations in market prices. The standard quantity of materials used per case was an ideal standard. The Mixing Department used a higher grade labor classification during the month, thus causing the actual labor rate to exceed standard. The Filling Department used a lower grade labor classification during the month, thus causing the actual labor rate to be less than standard. REQUIREMENT #1: Determine the fixed and variable portion of the utility cost using the high-low High-Low Method Variable Cost per Unit Difference in Total Cost Difference in Production 700 0.20 140 140 $ 0.20 700. Total Cost Variable Cost per Unit $ 0.20 $ 0.20 Units of Product ion 1,200 500 High Point Low Point Fixed Costs $500.00 $500.00 $ $ 740.00 600.00 X + + REQUIREMENT #2: Determine the contrinution margin per case. Contribution Margin Selling Price $ 100.00 Less variable costs per case: $ Direct materials Direct labor Utilities (see High-Low Method) Selling expenses Total variable costs per case AA 17.00 7.20 0.20 20.00 $ $ 44.40 Contribution margin per case $ 55.60 REQUIREMENT #3: Determine the fixed costs per month, including the utility fixed cost from question (1). Total Fixed Costs Utilities (see High-Low Method] Facility lease Equipment depreciation Supplies $ 500 $ 14,000 $ 4,300 $ 660 $ 19,460 Requirement #4: Determine the break-even number of cases per month. Break-even Analysis Break-even Sales (units) II Fixed Costs Unit Contribution Margin $ 55.60 350 $ 19,460.00 REQUIREMENT #5: Develop the production budget. Quivers Inc. Production Budget For the Month Ended August 31 Cases Expected cases to be sold 1,500 Plus desired ending 175 inventory Total units required 1,675 Less estimated beginning -300 inventory Total units to be 1,375 produced Total Quivers Inc. Direct Materials Purchases Budget For the Month Ended August 31 Cream Natural Base (oz.) Oils (oz.) Units required for production 137,500 41,250 Plus desired ending inventory 1,000 360 Total units required 138,500 41,610 Less estimated beginning 250 290 inventory Total materials to be 138,250 41,320 purchased x Unit price $0.02 $0.30 Total direct materials to be $2,765 $12,396 purchased Bottles (bottles) 16,500 240 16,740 600 16,140 $0.50 $8,070 $23,231 Raw Materials Units X Volume = Total Cream Base 100 1,375 137,500 30 Natural Oils 1,375 41,250 12 1,375 16,500 Bottles Requirement #7: Develop the direct labor cost budget. Quivers Inc. Direct Labor Cost Budget For the Month Ended August 31 Mixing Filling Total 458 115 Hours required for production of: Ophelia Wax Product Hourly rate Total direct labor cost $ 18.00 $8,250.00 $ 14.40 $1,650.00 $9,900.00 Labor Units X Production Time Hour 1,375 20 60 Total 458 Mixing 1,375 5 60 115 Filling Requirement #8: Develop the factory overhead cost budget. Quivers Inc. Factory Overhead Cost Budget For the Month Ended August 31 Fixed Variable Total Utilities 500 $ 275 $ 775 Facility Lease 14,000 14,000 Equipment Depreciation $ 4,300 $ 4,300 Supplies 660 $ 660 Total factory overhead cost $ 19,735 AAAA Cost Cases 1,375 1,375 $ Cost 500 S Fixed Cost [from Questioni Variable Utility Cost Total 500 275 0.20 Requirement #9: Create the budgeted income statement. Units X Price = Total Sales Selling Expenses Cream Base (oz.) Oils (oz.) Bottels (oz.) Total Quivers Inc. Budgeted Income Statement For the Month Ended August 31 Sales Finished goods inventory, August 1 Direct materials: Direct materials inventory, August 1 Direct materials purchases (from Question 6] Cost of direct materials available for use Less direct materials inventory, August 31 Cost of direct materials placed in production Direct labor [from Question 7] Factory overhead [from Question 8] Cost of goods manufactured Cost of finished goods available for sale Less finished goods inventory, August 31 Cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling expenses Income from operations Direct materials inventory, August 1 Direct materials inventory, August 31 Rate Cream Base (oz.) Oils (oz.) Bottels (oz. Requirement #10: Determine the direct materials variance. Direct Materials Price Variance Cream Base Natural Oils Bottles Actual Quantity Cream BaseNatural Oils Bottles Cases Amount Total Actual Price Standard Price Difference * Actual Quantity (Units) Direct Materials Price Variance Decision Analysis Direct Materials Quantity Variance Cream Base Natural Oils Bottles Standard Quantity Cream BaseNatural Oils Bottles Cases Amount Total Actual Quantiy Standard Quantity Difference * Standard Price Dieci rutenuis Vuurilly VlaminA Decision Analysis Requirement #11: Determine the direct labor variance. Actual Time Mixing Filling Direct Labor Rate Variance Mixing Filling Department Department Actual Rate Standard Rate Difference * Actual Time (Hours) Direct Labor Rate Variance Decision Units Minutes Hours Total Analysis Standard Time Filling Mixing Filling Direct Labor Time Variance Mixing Department Department Actual Time Standard Time Difference * Standard Rate Direct Labor Time Variance Decision Units Minutes Hours Total Analysis Requirement #12: Determine the factory overhead variance. Factory Overhead Controllable Variance Variance overhead (utility cost) at standard cost Cases Total fixed factory overhead Actual variable overhead Variable overhead at standard cost Factory overhead controllable variance Decision Total Factory Overhead Volume Variance Normal volume (cases) Actual volume (cases) Difference * Fixed factory overhead rate $0.00 Decision Fixed factory overhead rate Cases Total fixed factory overhead Total Analysis
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


