Question: Implement the BinarySearchTree ADT in a file BinarySearchTree.h exactly as shown below. // BinarySearchTree.h #ifndef BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_H #define BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_H #include #include using namespace std; template class
Implement the BinarySearchTree ADT in a file BinarySearchTree.h exactly as shown below. // BinarySearchTree.h #ifndef BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_H #define BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_H #include#include using namespace std; template class BinarySearchTree { public: BinarySearchTree( ) : root{ nullptr } { } ~BinarySearchTree( ) { makeEmpty(); } const C & findMin( ) const { assert(!isEmpty()); return findMin( root )->element; } const C & findMax( ) const { assert(!isEmpty()); return findMax( root )->element; } bool contains( const C & x ) const { return contains( x, root ); } bool isEmpty( ) const { return root == nullptr; } void printTree( ) const { if( isEmpty( ) ) cout element ) insert( x, t->left ); else if( t->element right ); else ; // Duplicate; do nothing } // Internal method to remove from a subtree. // x is the item to remove. // t is the node that roots the subtree. // Set the new root of the subtree. void remove( const C & x, BinaryNode* & t ) { if( t == nullptr ) return; // Item not found; do nothing if( x element ) remove( x, t->left ); else if( t->element right ); else if( t->left != nullptr && t->right != nullptr ) // Two children { t->element = findMin( t->right )->element; remove( t->element, t->right ); } else { BinaryNode* oldNode = t; t = ( t->left != nullptr ) ? t->left : t->right; delete oldNode; } } // Internal method to find the smallest item in a subtree t. // Return node containing the smallest item. BinaryNode* findMin( BinaryNode* t ) const { if( t == nullptr ) return nullptr; if( t->left == nullptr ) return t; return findMin( t->left ); } // Internal method to find the largest item in a subtree t. // Return node containing the largest item. BinaryNode* findMax( BinaryNode* t ) const { if( t != nullptr ) while( t->right != nullptr ) t = t->right; return t; } // Internal method to test if an item is in a subtree. // x is item to search for. // t is the node that roots the subtree. bool contains( const C & x, BinaryNode* t ) const { if( t == nullptr ) return false; else if( x element ) return contains( x, t->left ); else if( t->element right ); else return true; // Match } void makeEmpty( BinaryNode* & t ) { if( t != nullptr ) { makeEmpty( t->left ); makeEmpty( t->right ); delete t; } t = nullptr; } void printTree( BinaryNode* t) const { if( t != nullptr ) { printTree( t->left); cout element right); } } }; #endif
Program your own file main.cpp in which your main() function will test the new data structure.
- The main function is contained in the file main.cpp.
- Declare an instance of BinarySearchTree (short: BST) suitable to hold integer values.
- Prompt user to enter a random sequence of integer values, insert these values into the data structure (the entered values should NOT be in sorted order).
- Call the printTree() member function in order to print out the values of the BST structure.
- Prompt user to enter a random sequence of integer values, remove these values from your BST. Print out the reduced BST.
Add the following member function in your BinarySearchTree class template.
public: void printInternal() { print_Internal(root,0); } private: void printInternal(BinaryNode* t, int offset) { if (t == nullptr) return; for(int i = 1; i element left, offset + 1); printInternal(t->right, offset + 1); }Go back to your program main.cpp and call printInternal. Compile and run your program, and see what you get.
You should have theses files:
- BinarySearchTree.h: the implementation file of the BinarySearchTree class template.
- main.cpp: the test file containing main() funcion.
- main result: the script file which captures the result.
NOTE: please write down the code for the TWO files :
1- BinarySearchTree.h
2-main.cpp
3- show me your output
Thank you.
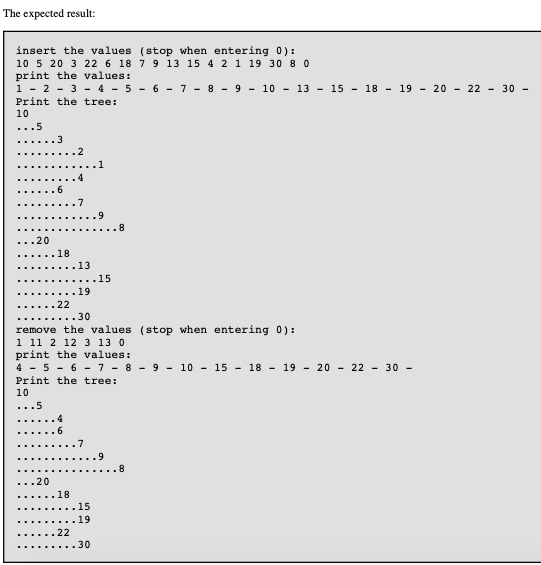
The expected result: insert the values (stop when entering 0): 10 5 20 3 22 6 18 7 9 13 15 4 2 1 19 30 8 0 print the values: 12 34-567-8 -9 10 13151819202230 Print the tree: 10 remove the values (stop when entering 0): 1 11 2 12 3 13 0 print the values: 4 -56- 7-8 -9- 10-151819202230- Print the tree: 10 The expected result: insert the values (stop when entering 0): 10 5 20 3 22 6 18 7 9 13 15 4 2 1 19 30 8 0 print the values: 12 34-567-8 -9 10 13151819202230 Print the tree: 10 remove the values (stop when entering 0): 1 11 2 12 3 13 0 print the values: 4 -56- 7-8 -9- 10-151819202230- Print the tree: 10
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


