Question: import java.util.*; public class BST > implements Iterable { protected BSTNode root = null; public BST() { } public BST(BSTNode p) { root = p;
import java.util.*;
public class BST> implements Iterable { protected BSTNode root = null;
public BST() { }
public BST(BSTNode p) { root = p;
}
public void clear() { root = null;
}
public boolean isEmpty() { return root == null;
}
protected void visit(BSTNode p) { System.out.print(p.key + " ");
}
public T search(T el) { BSTNode p = root; while (p != null) {
if (el.equals(p.key)) return p.key;
else if (el.compareTo(p.key)
else p = p.right; }
return null; }
public boolean isInTree(T el) { return search(el) != null;
}
public void breadthFirst() {
BSTNode p = root;
LLQueue> queue = new LLQueue>();
if (p != null) { queue.enqueue(p);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
p = queue.dequeue(); visit(p);
if (p.left != null)
queue.enqueue(p.left); if (p.right != null)
queue.enqueue(p.right); }
} }
public void preorder() { preorder(root);
}
protected void preorder(BSTNode p) {
if (p != null) { visit(p);
preorder(p.left);
preorder(p.right); }
}
public void inorder() { inorder(root);
}
protected void inorder(BSTNode p) {
if (p != null) { inorder(p.left); visit(p); inorder(p.right);
} }
public void postorder() { postorder(root);
}
protected void postorder(BSTNode p) {
if (p != null) { postorder(p.left); postorder(p.right); visit(p);
} }
public void insert(T el) {
BSTNode p = root, prev = null;
while (p != null) { // find a place for inserting new node;
prev = p;
if (el.compareTo(p.key)
p = p.left; else p = p.right;
}
if (root == null) // tree is empty; root = new BSTNode(el);
else if (el.compareTo(prev.key) (el);
else prev.right = new BSTNode(el); }
public void deleteByCopying(T el) {
BSTNode node, p = root, prev = null;
while (p != null && !p.key.equals(el)) { // find the node p
prev = p; // with element el; if (el.compareTo(p.key) p) Retums true if the tree is balanced or false otherwise. Hint: A balanced tree is either empty or one in which for each node, the difference between the heights of left and right sub-trees is less than 2 and both left and right sub-trees are balanced.. Example: the tree in Fig (a) is balanced but that of Fig (b) is not (ii) public void printAncestors(T el) protected void printAncestors(T el, BSTNodeT> p) Prints all the ancestors of a given element if it exists in the tree or ptint an error message otherwise Hint: First check that the target element exists in the public method. If it exist, call the recursive method to print all the nodes along the path from the root until the element is reached. Example: The ancestors of 12 in Fig(a) are: 10, 15 (ili) public void printLevelNodes(int targetLevel) protected void printLevelNodes(BSTNodeT> p, int targetLevel, int currentLevel) Prints all the nodes in a given level if the given level is valid (i.e. in the range 1 to height). Prints error message otherwise Hint: First check that the targetLevel is valid in the public method. If valid, call the recusive method with root and initial value of currentLevel as 1. Print the key each time currentLevel is equal to targetLevel. Example: For Fig (a), if targetLevel is 2, output is: 2, 15 Submission Instructions: To submit, create a folder named, YourlD_Assign1B, save your two projects (for question1 and question2) inside this folder, zip the folder into one file and submit. 1. Write each of the following methods inside the BST class. In each case, the protected version MUST be recursive and it is the one that does the real job. The public version only validates the argument(s) (if necessary) and then call the recursive version with valid initial values for the arguments. Add options in TestlntegerBST.java to test your methods. 3 Marks: 1 each 1 0 10 1 5 2 15 1 2 20 Fig (b) Fig (a) (0) public boolean isBalanced protected boolean isBalanced(BSTNode p) Retums true if the tree is balanced or false otherwise. Hint: A balanced tree is either empty or one in which for each node, the difference between the heights of left and right sub-trees is less than 2 and both left and right sub-trees are balanced.. Example: the tree in Fig (a) is balanced but that of Fig (b) is not (ii) public void printAncestors(T el) protected void printAncestors(T el, BSTNodeT> p) Prints all the ancestors of a given element if it exists in the tree or ptint an error message otherwise Hint: First check that the target element exists in the public method. If it exist, call the recursive method to print all the nodes along the path from the root until the element is reached. Example: The ancestors of 12 in Fig(a) are: 10, 15 (ili) public void printLevelNodes(int targetLevel) protected void printLevelNodes(BSTNodeT> p, int targetLevel, int currentLevel) Prints all the nodes in a given level if the given level is valid (i.e. in the range 1 to height). Prints error message otherwise Hint: First check that the targetLevel is valid in the public method. If valid, call the recusive method with root and initial value of currentLevel as 1. Print the key each time currentLevel is equal to targetLevel. Example: For Fig (a), if targetLevel is 2, output is: 2, 15
p = p.left; else p = p.right;
}
node = p;
if (p != null && p.key.equals(el)) {
if (node.right == null) // node has no right child; node = node.left;
else if (node.left == null) // no left child for node; node = node.right;
else {
BSTNode tmp = node.left; // node has both children; BSTNode previous = node; // 1.
while (tmp.right != null) { previous = tmp;
tmp = tmp.right;
// 2. find the rightmost
}
node.key = tmp.key;
// if (previous == node)
// 3. overwrite the reference to the element being deleted;
// if node's left child's
// //
position in the
left subtree of node;
previous.left = tmp.left; // right subtree is null; else previous.right = tmp.left; // 4.
}
if (p == root)
root = node;
else if (prev.left == p)
prev.left = node; else prev.right = node;
}
else if (root != null)
System.out.println("el " + el + " is not in the tree"); else System.out.println("the tree is empty");
}
public Iterator iterator() { return new BSTIterator();
}
private class BSTIterator implements Iterator { BSTNode p = root; LLQueue> queue;
public BSTIterator() {
queue = new LLQueue>(); queue.enqueue(p);
}
public boolean hasNext() { return !queue.isEmpty();
}
public T next() {
p = queue.dequeue(); if (p.left != null)
queue.enqueue(p.left); if (p.right != null)
queue.enqueue(p.right); return p.key;
}
public void remove() {
// not implemented
} }
protected boolean isLeaf(BSTNode p){ if(p != null)
if(p.right == null && p.left == null) return true;
return false; }
public int getHeight(){ return getHeight(root);
}
protected int getHeight(BSTNode p){ if( p == null)
return 0;
int hightLift = getHeight(p.left);
int hightRight = getHeight(p.right);
if( hightLift 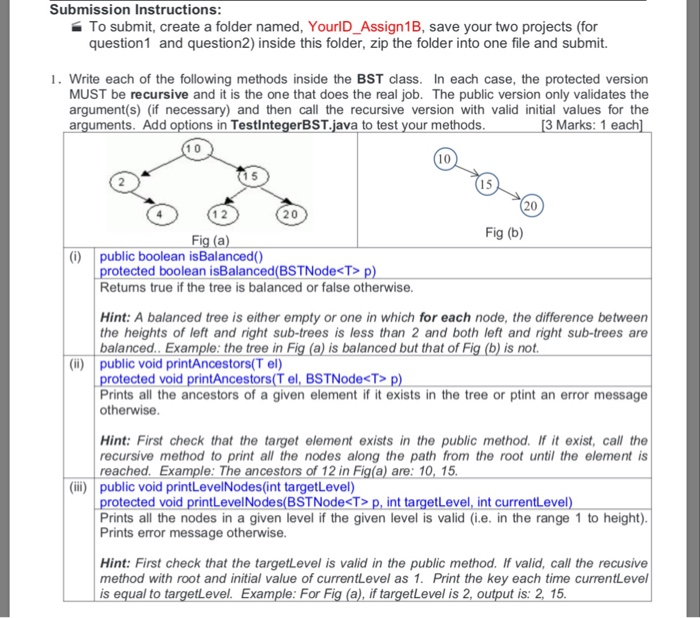
Submission Instructions: To submit, create a folder named, YourlD_Assign1B, save your two projects (for question1 and question2) inside this folder, zip the folder into one file and submit. 1. Write each of the following methods inside the BST class. In each case, the protected version MUST be recursive and it is the one that does the real job. The public version only validates the argument(s) (if necessary) and then call the recursive version with valid initial values for the arguments. Add options in TestlntegerBST.java to test your methods. 3 Marks: 1 each 1 0 10 1 5 2 15 1 2 20 Fig (b) Fig (a) (0) public boolean isBalanced protected boolean isBalanced(BSTNode else
return hightLift+1;
}
public int getCount(){ return getCount(root);
}
protected int getCount(BSTNode p){ if(p == null)
return 0;
return getCount(p.left)+getCount(p.right)+1;
}
public int leavesCount(){ return leavesCount(root);
}
protected int leavesCount(BSTNode p){ if(p == null)
return 0;
else if(isLeaf(p))
return 1; else
return leavesCount(p.left)+leavesCount(p.right); }
public void printTree(){ printTree(root);
}
protected void printTree(BSTNode p){ if ( p != null){
System.out.print("{"); printTree(p.left); System.out.print(p.key); printTree(p.right); System.out.print("}");
} }
//Generic BSTNode class;
private class BSTNode> {
protected T key;
protected BSTNode left, right; public BSTNode() {
left = right = null; }
public BSTNode(T el) { this(el,null,null);
}
public BSTNode(T el, BSTNode lt, BSTNode rt) {
key = el; left = lt; right = rt; }
} }
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.*;
public class TestIntegerBST {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testStudentBST();
} //end of main
public static int sum(BST tree) { int sum = 0;
for (int n : tree) {
sum += n; }
return sum; }
public static void testStudentBST(){ BST tree = new BST();
int option, target;
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
System.out.println(" ***************************"); System.out.println("* Testing Binary Search Tree *"); System.out.println("*************************** "); System.out.println("1. Insert an element"); System.out.println("2. Search for an element"); System.out.println("3. Delete an element"); System.out.println("4. Print in Breadth-First-Order"); System.out.println("5. Print in Pre-Order"); System.out.println("6. Print in In-Order"); System.out.println("7. Print in Post-Order"); System.out.println("9. Print the hight of the tree"); System.out.println("10. Print the number of nods"); System.out.println("11. Print the number of leaves"); System.out.println("12. Print the elements "); System.out.println("13. Exit");
System.out.print(" Select an Option [1...9] : "); option = reader.nextInt();
switch (option) { case 1:
tree.insert(scaneStudent()); break;
case 2:
System.out.print("Enter the Student id to search for: "); target = reader.nextInt();
Student result = tree.search(new Student(target));
if (result != null) {
System.out.println("Student " + result + " was found in the tree"); } else {
System.out.println("Sorry, the Student was not found"); }
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("Enter the Student id delete: "); tree.deleteByCopying(scaneStudent());
break;
case 4: tree.breadthFirst(); break;
case 5: tree.preorder(); break;
case 6: tree.inorder(); break;
case 7: tree.postorder(); break;
case 9:
System.out.println("The hight of the tree is " + tree.getHeight()); break;
case 10:
System.out.println("the number of nodes in the tree is " + tree.getCount()); break;
case 11:
System.out.println("The number of leaves is " + tree.leavesCount()); break;
case 12: tree.printTree(); break;
} //end of switch
} while (option != 13);
}
public static Student scaneStudent() {
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
Student s = new Student();
System.out.println("Please enter the ID of the student:"); s.id = kb.nextInt();
System.out.println("Please enter the name:"); s.name = kb.next();
System.out.println("Please enter the GPA:"); s.gpa = kb.nextDouble();
return s; }
public static void testIntegerBST(){ BST tree = new BST(); int option, target;
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
System.out.println(" ***************************"); System.out.println("* Testing Binary Search Tree *"); System.out.println("*************************** ");
System.out.println("1. Insert an element"); System.out.println("2. Search for an element"); System.out.println("3. Delete an element"); System.out.println("4. Print in Breadth-First-Order"); System.out.println("5. Print in Pre-Order"); System.out.println("6. Print in In-Order"); System.out.println("7. Print in Post-Order"); System.out.println("8. Print sum of the elements"); System.out.println("9. Print the hight of the tree"); System.out.println("10. Print the number of nods"); System.out.println("11. Print the number of leaves"); System.out.println("12. Print the elements "); System.out.println("13. Exit");
System.out.print(" Select an Option [1...9] : "); option = reader.nextInt();
switch (option) { case 1:
System.out.print("Enter the element to insert: "); tree.insert(reader.nextInt());
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("Enter the element to search for: "); target = reader.nextInt();
Integer result = tree.search(target);
if (result != null) {
System.out.println("Element, " + result + " was found in the tree"); } else {
System.out.println("Sorry, the element was not found"); }
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("Enter the element delete: "); tree.deleteByCopying(reader.nextInt()); break;
case 4: tree.breadthFirst(); break;
case 5: tree.preorder(); break;
case 6: tree.inorder(); break;
case 7: tree.postorder(); break;
case 8:
System.out.print("Sum of the elements in the tree is: " + sum(tree)); break;
case 9:
System.out.println("The hight of the tree is " + tree.getHeight()); break;
case 10:
System.out.println("the number of nodes in the tree is " + tree.getCount()); break;
case 11:
System.out.println("The number of leaves is " + tree.leavesCount()); break;
case 12: tree.printTree(); break;
} //end of switch
} while (option != 13); }
}

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


