Question: import java.util.*; public class Node { private static String removeLeadingWhitespace(String str) { int i = 0; while (i i++; } // Completing the loop means

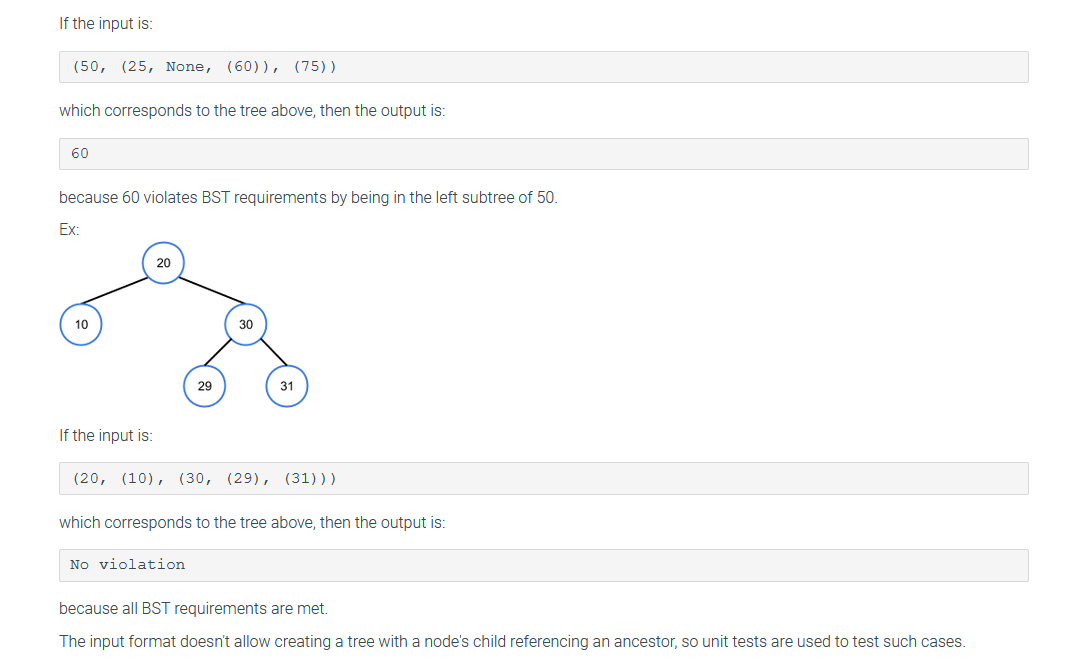
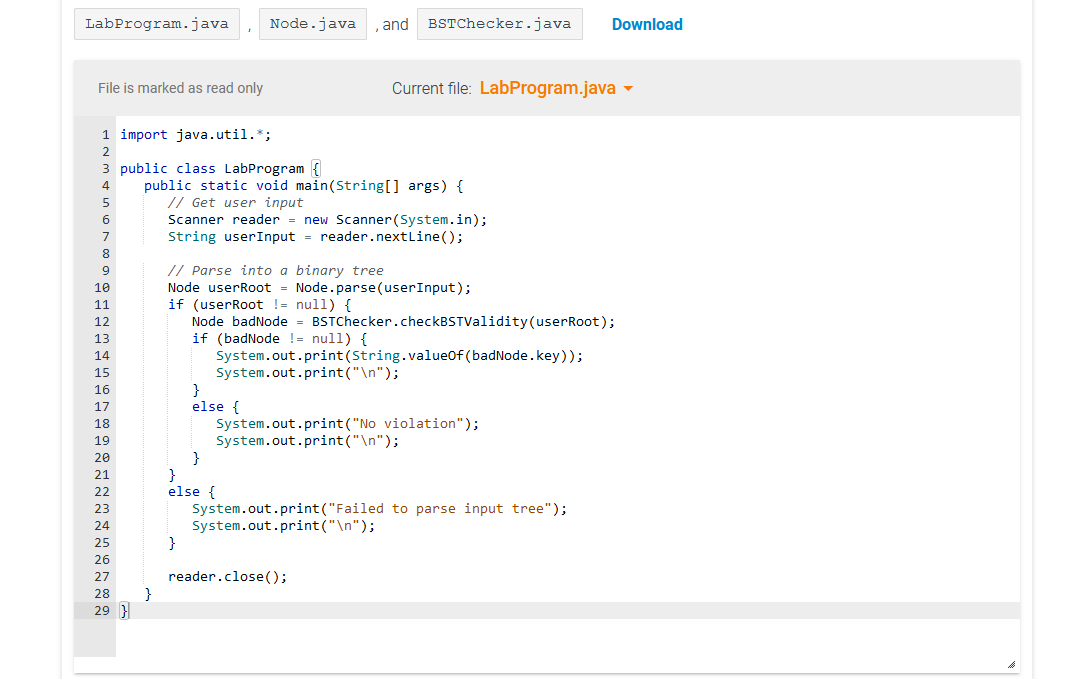

import java.util.*;
public class Node { private static String removeLeadingWhitespace(String str) { int i = 0; while (i
i++; }
// Completing the loop means the entire string is whitespace return new String(); }
public int key; public Node left; public Node right;
public Node(int nodeKey, Node leftChild) { this(nodeKey, leftChild, null); }
public Node(int nodeKey) { this(nodeKey, null, null); }
public Node(int nodeKey, Node leftChild, Node rightChild) { key = nodeKey; left = leftChild; right = rightChild; }
public void close() { }
// Counts the number of nodes in this tree public int count() { int leftCount = 0; if (left != null) { leftCount = left.count(); } int rightCount = 0; if (right != null) { rightCount = right.count(); } return 1 + leftCount + rightCount; }
// Inserts the new node into the tree. public void insert(Node node) { Node currentNode = this; while (currentNode != null) { if (node.key
public void insertAll(final ArrayList
public static Node parse(String treeString) { // A node is enclosed in parentheses with a either just a key: (key), // or a key, left child, and right child triplet: (key, left, right). The // left and right children, if present, can be either a nested node or // "null".
// Remove leading whitespace first treeString = Node.removeLeadingWhitespace(treeString);
// The string must be non-empty, start with "(", and end with ")" if (0 == treeString.length() || treeString.charAt(0) != '(' || treeString.charAt(treeString.length() - 1) != ')') { return null; }
// Parse between parentheses treeString = treeString.substring(1, treeString.length() - 1);
// Find non-nested commas ArrayList // If no commas, treeString is expected to be just the node's key if (0 == commaIndices.size()) { return new Node(Integer.parseInt(treeString)); } // If number of commas is not 2, then the string's format is invalid if (2 != commaIndices.size()) { return null; } // "Split" on comma int i1 = commaIndices.get(0); int i2 = commaIndices.get(1); String piece1 = treeString.substring(0, i1); String piece2 = treeString.substring(i1 + 1, i2); String piece3 = treeString.substring(i2 + 1); // Make the node with just the key Node nodeToReturn = new Node(Integer.parseInt(piece1)); // Recursively parse children nodeToReturn.left = Node.parse(piece2); nodeToReturn.right = Node.parse(piece3); return nodeToReturn; } } 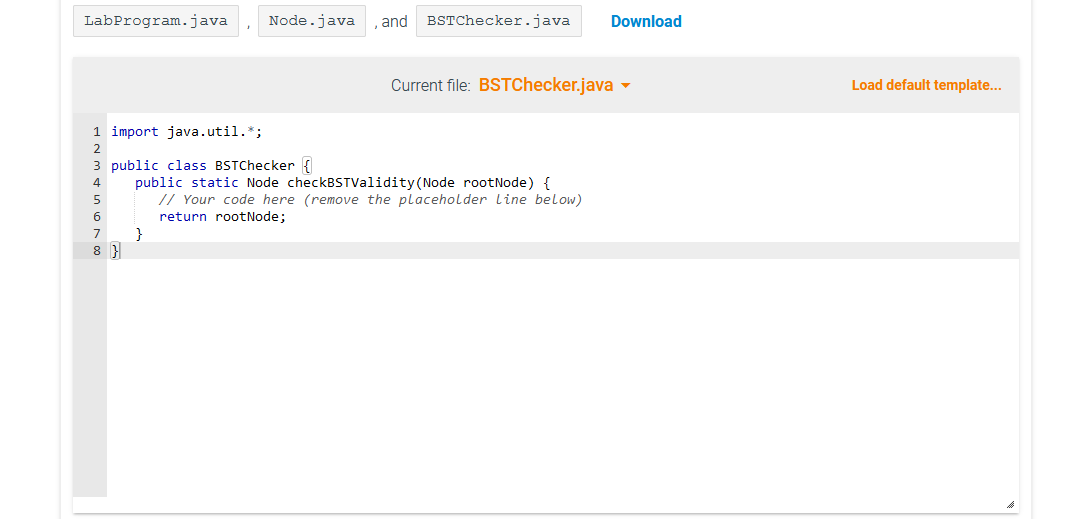
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


