Question: import java.util.Stack; public class ExpressionTree { Node root; // Node sub-class public class Node { private String key; // key private Node left, right; //
import java.util.Stack;
public class ExpressionTree
{
Node root;
// Node sub-class
public class Node
{
private String key; // key
private Node left, right; // links to subtrees
public Node(String key)
{
this.key = key;
}
}
// constructor to build a tree with postFix expression
public ExpressionTree(String postFixExpression)
{
Stack
String[] tokens = postFixExpression.split(" ");
for (String token: tokens)
{
if (isOperator(token))
{
Node right = stack.pop();
Node left = stack.pop();
Node node = new Node(token);
node.left = left;
node.right = right;
stack.push(node);
}
else
{
stack.push(new Node(token));
}
}
root = stack.pop();
}
private boolean isOperator(String token)
{
boolean result = false;
switch(token)
{
case "+":
case "-":
case "*":
case "/":
result = true;
break;
default:
result = false;
}
return result;
}
/**
//NEED HELP HERE
* @return result of the expression
* @throws Exception
*/
public double evaluate() throws Exception
{
//CODE HERE
{
}
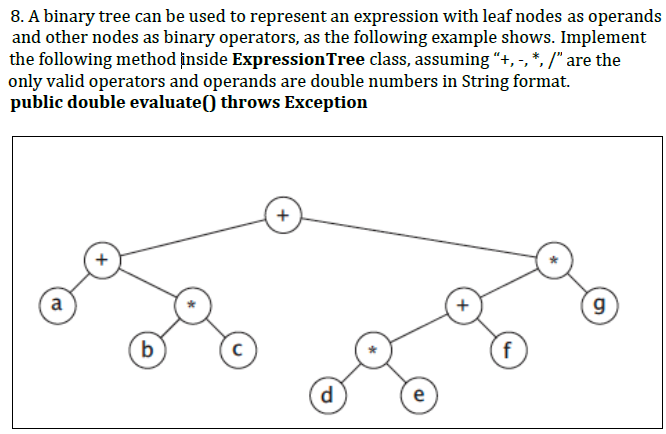
8. A binary tree can be used to represent an expression with leaf nodes as operands and other nodes as binary operators, as the following example shows. Implement the following method inside Expression Tree cl only valid operators and operands are double numbers in String format. public double evaluate) throws Exception ass, assuming "+, -, *, /"are the 9 dl
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


