Question: IMPORTANT: For this exercise, you will be defining a function which USES the Queue ADT. A queue implementation is provided to you - you should
IMPORTANT: For this exercise, you will be defining a function which USES the Queue ADT. A queue implementation is provided to you - you should not define your own Queue class. Instead, your code can make use of any of the Queue ADT methods: Queue(), enqueue(), dequeue(), peek(), size() and is_empty().
Write a function called evaluate_subtraction(a_queue) which takes a queue of integers as a parameter and returns an integer. The function should dequeue two elements from the queue, subtracts them and enqueues the result back to the end of the queue. The steps are repeated until there is only one element left in the queue. Then, the function returns the remaining element in the queue.
Note: you can assume that there are at least two integers in the queue.
For example:
| Test | Result |
|---|---|
q = Queue() q.enqueue(2) q.enqueue(10) print(evaluate_subtraction(q)) | 8 |
q = Queue() q.enqueue(2) q.enqueue(4) q.enqueue(3) print(evaluate_subtraction(q)) | -1 |
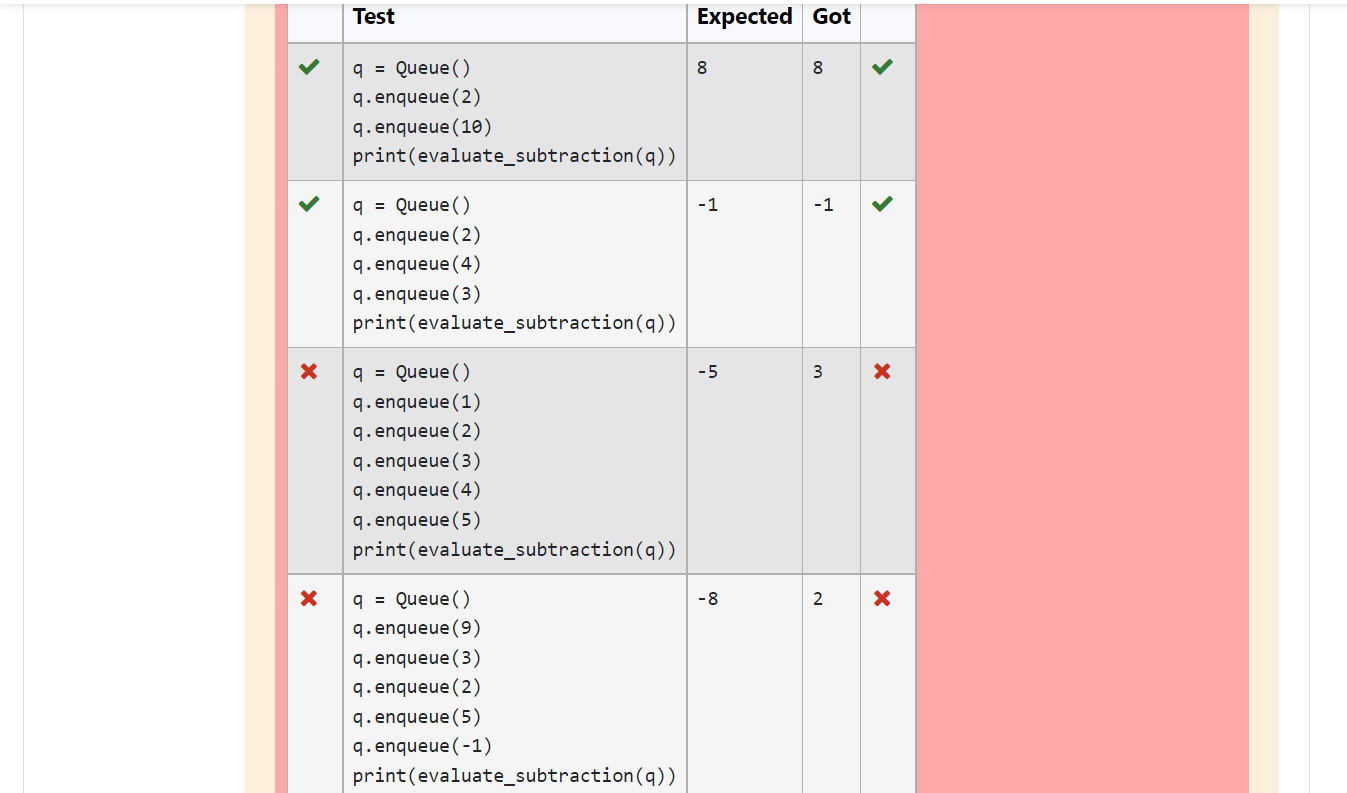
Test Expected Got 8 00 8 q = Queue () q.enqueue (2) q.enqueue (10) print(evaluate_subtraction(q)) -1 -1 > q = Queue () q. enqueue (2) q. enqueue (4) q. enqueue (3) print(evaluate_subtraction(q)) X -5 3 X q = Queue () q. enqueue (1) q. enqueue (2) q. enqueue (3) q.enqueue (4) q. enqueue (5) print(evaluate_subtraction(q)) X -8 2 x q = Queue () q.enqueue (9) q.enqueue (3) q.enqueue (2) q. enqueue (5) q.enqueue (-1) print(evaluate_subtraction(q))
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


