Question: In [16]: # Example 3. As an input, a list of sorted numbers is given. # write a function to check whether a given number
![In [16]: # Example 3. As an input, a list of](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3e17e1bbc5_00566f3e17dac2d6.jpg)
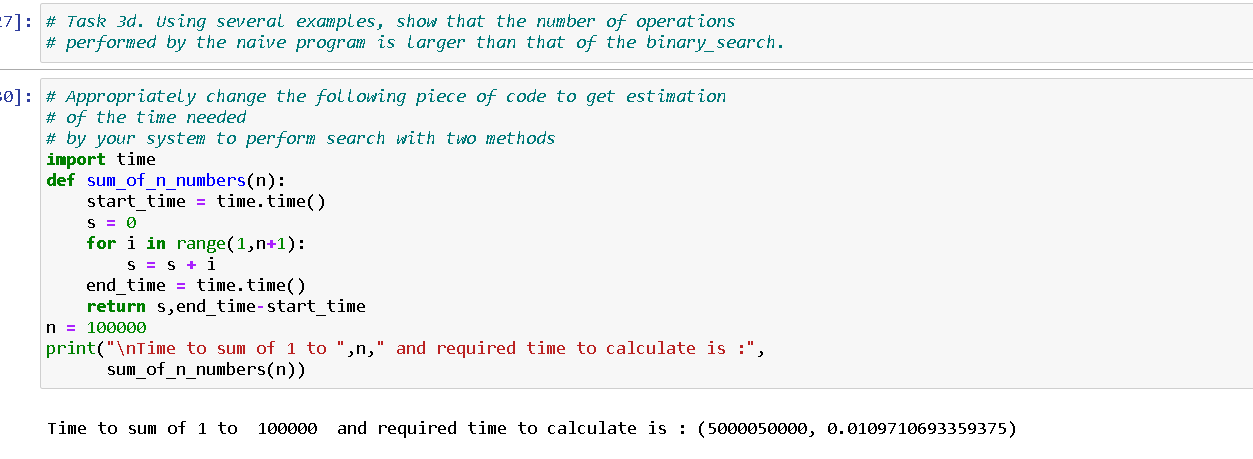
In [16]: # Example 3. As an input, a list of sorted numbers is given. # write a function to check whether a given number x is in the input list. In [20] : def binary_search( numbers, X_number): low index = 0 high_index = len(numbers) - 1 while low_index numbers[middle_index] : low_index = middle_index + 1 else: return True; return false In [23] : # Task 30. Test the above function for some tists and values of x_number. In [24]: # Task 36. show that the complexity of the best (most favourable) case # is 0(1). Precisely when this can happen? In [25] : # Task 36. write a naive program to check the presence of x_number # in the list numbers comparing consecutive elements of the list # with x_number. what is the complexity of the algorithm implemented # this way? 7]: # Task 3d. Using several examples, show that the number of operations # performed by the naive program is larger than that of the binary_search. 0]: # Appropriately change the following piece of code to get estimation # of the time needed # by your system to perform search with two methods import time def sum_of_n_numbers(n): start_time = time. time() S = 0 for i in range(1, n+1): S = S + i end time = time. time) return s,end_time-start_time n = 100000 print(" Time to sum of 1 to ",n," and required time to calculate is :", sum_of_n_numbers(n)) Time to sum of 1 to 100000 and required time to calculate is : (5000050000, 0.0109710693359375)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


