Question: - In a periodic crystal, the electron density can be decomposed into Fourier series. n(r)=N(Ghkl)exp(iG) The non-zero N(Ghk1) 's in G-space or (k-space) forms the
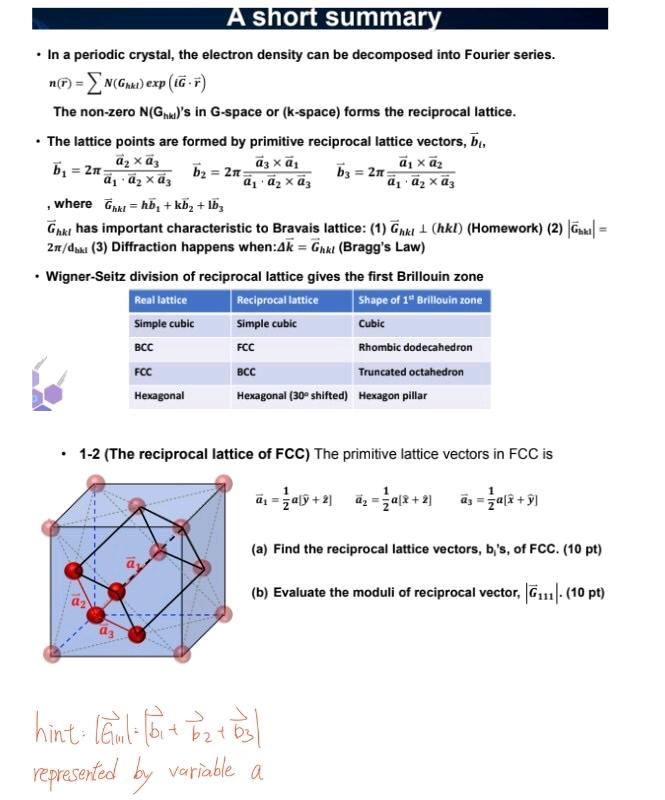
- In a periodic crystal, the electron density can be decomposed into Fourier series. n(r)=N(Ghkl)exp(iG) The non-zero N(Ghk1) 's in G-space or (k-space) forms the reciprocal lattice. - The lattice points are formed by primitive reciprocal lattice vectors, bi, b1=2a1a2a3a2a3b2=2a1a2a3a3a1b3=2a1a2a3a1a2,whereGhkI=hb1+kb2+1b3 Ghkl has important characteristic to Bravais lattice: (1) Ghkl(hkl) (Homework) (2) Gbkl= 2/dhal (3) Diffraction happens when: k=Ghkl (Bragg's Law) - Wigner-Seitz division of reciprocal lattice gives the first Brillouin zone - 1-2 (The reciprocal lattice of FCC) The primitive lattice vectors in FCC is a1=21a[y^+2]a2=21a[x^+2]a3=21a[x^+y^] (a) Find the reciprocal lattice vectors, b,'s, of FCC. (10 pt) (b) Evaluate the moduli of reciprocal vector, G111(10pt) nint:G11=b1+b2>+b3b3 represented by variable a
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


