Question: In ArrayBag. java, add the methods described below to the ArrayBag class, and then add code to the main() method to test these methods.



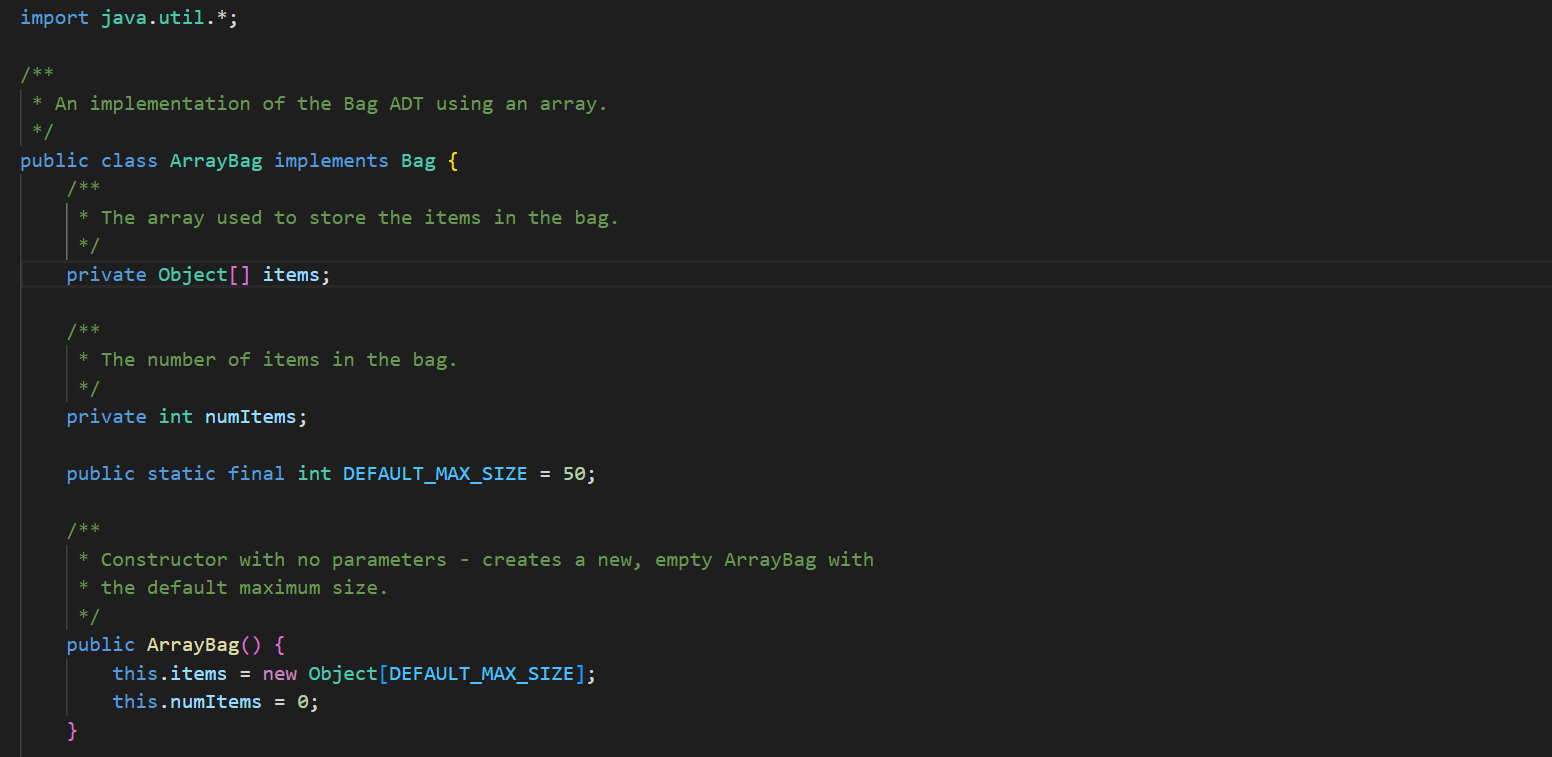
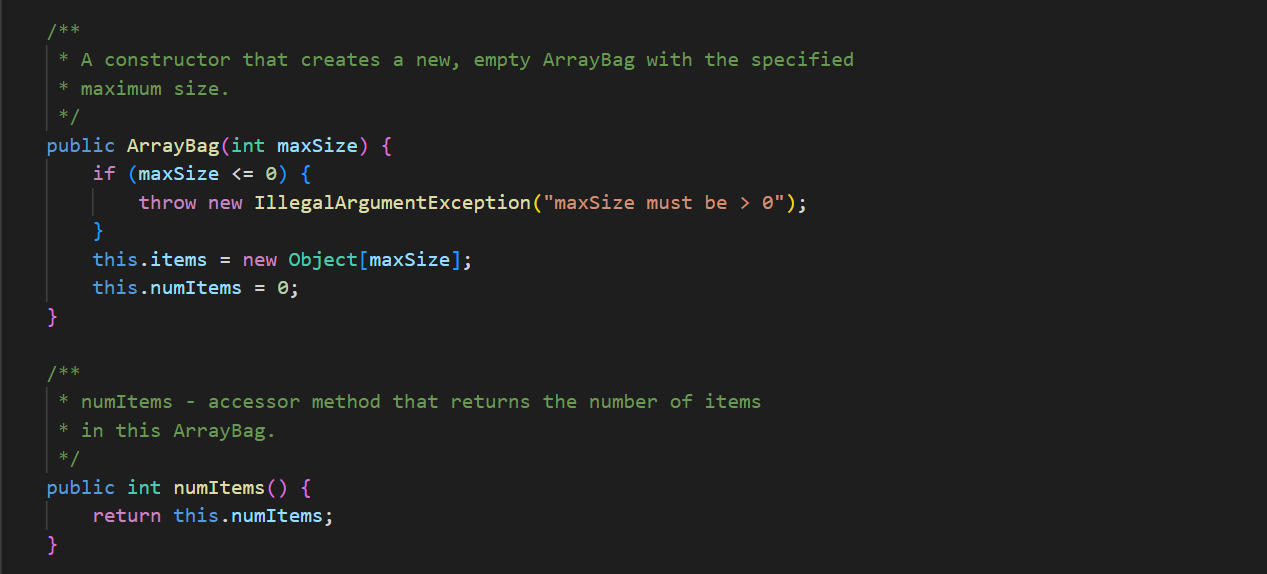
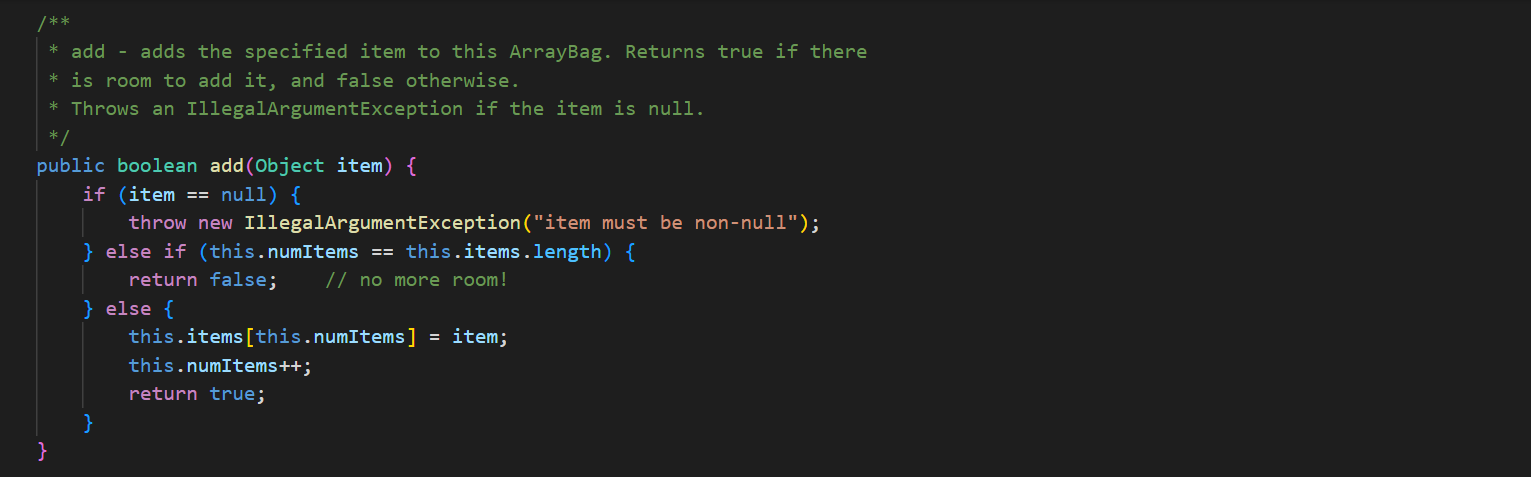
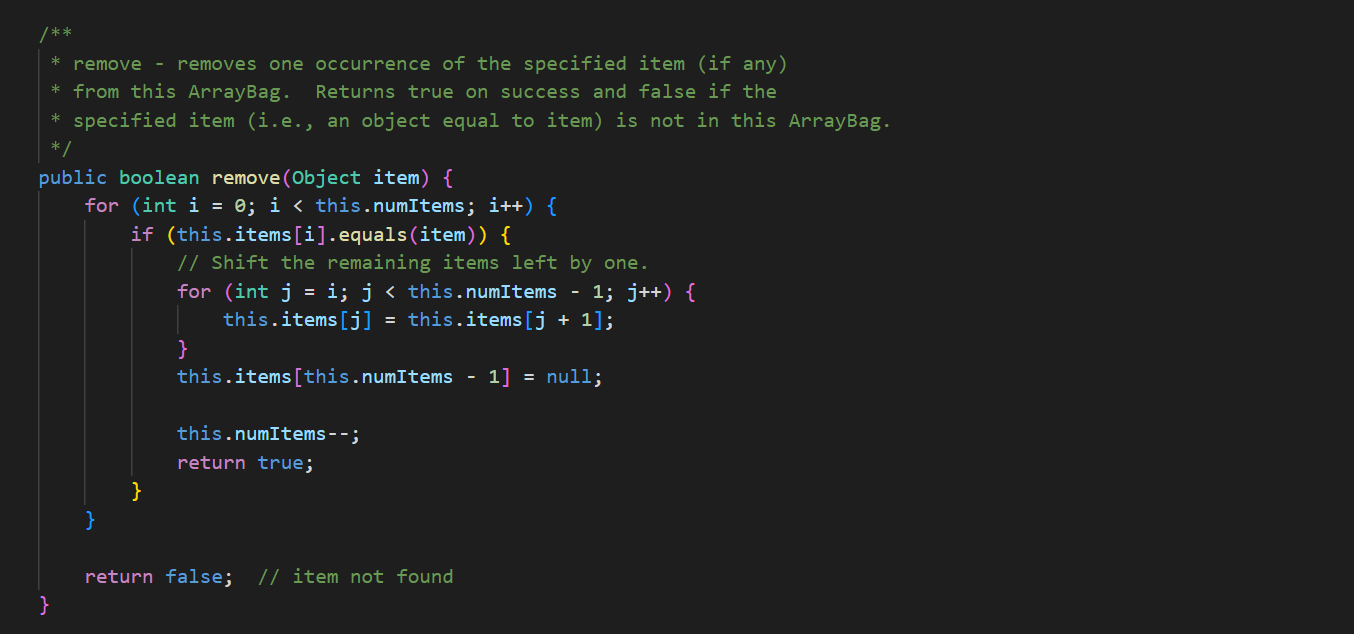
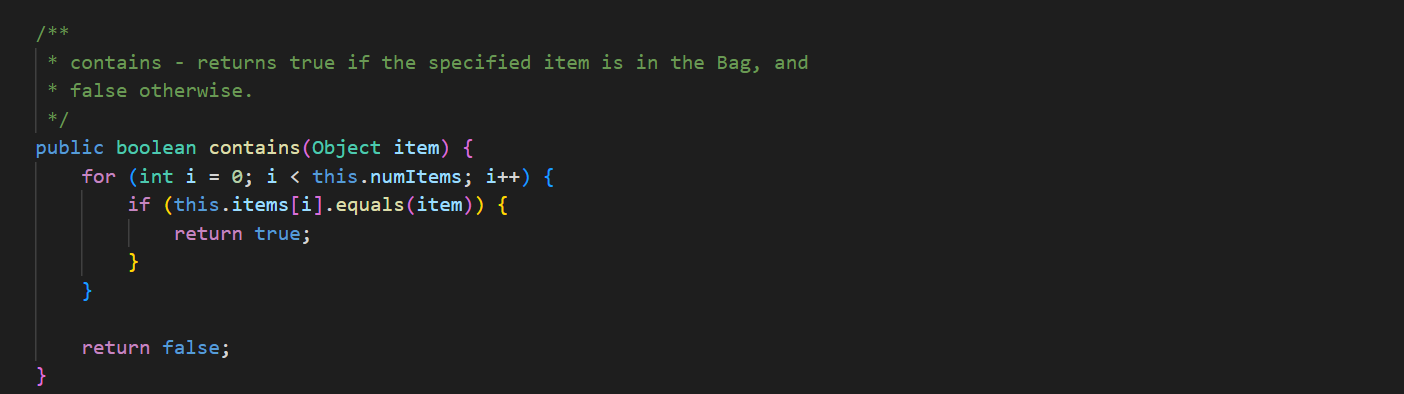
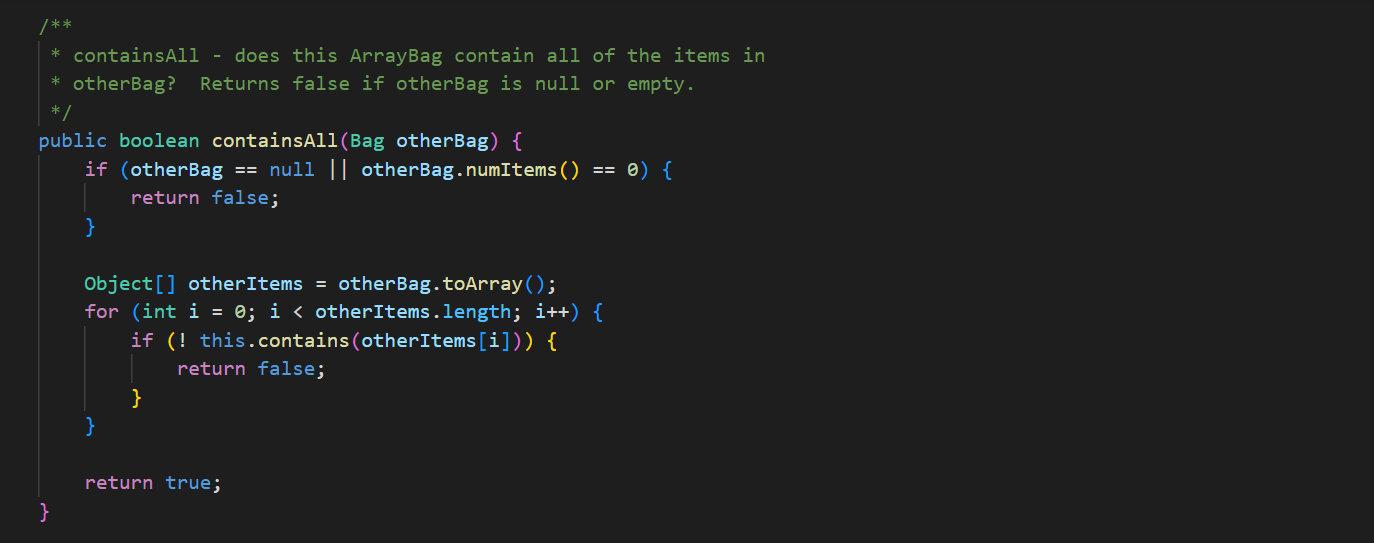
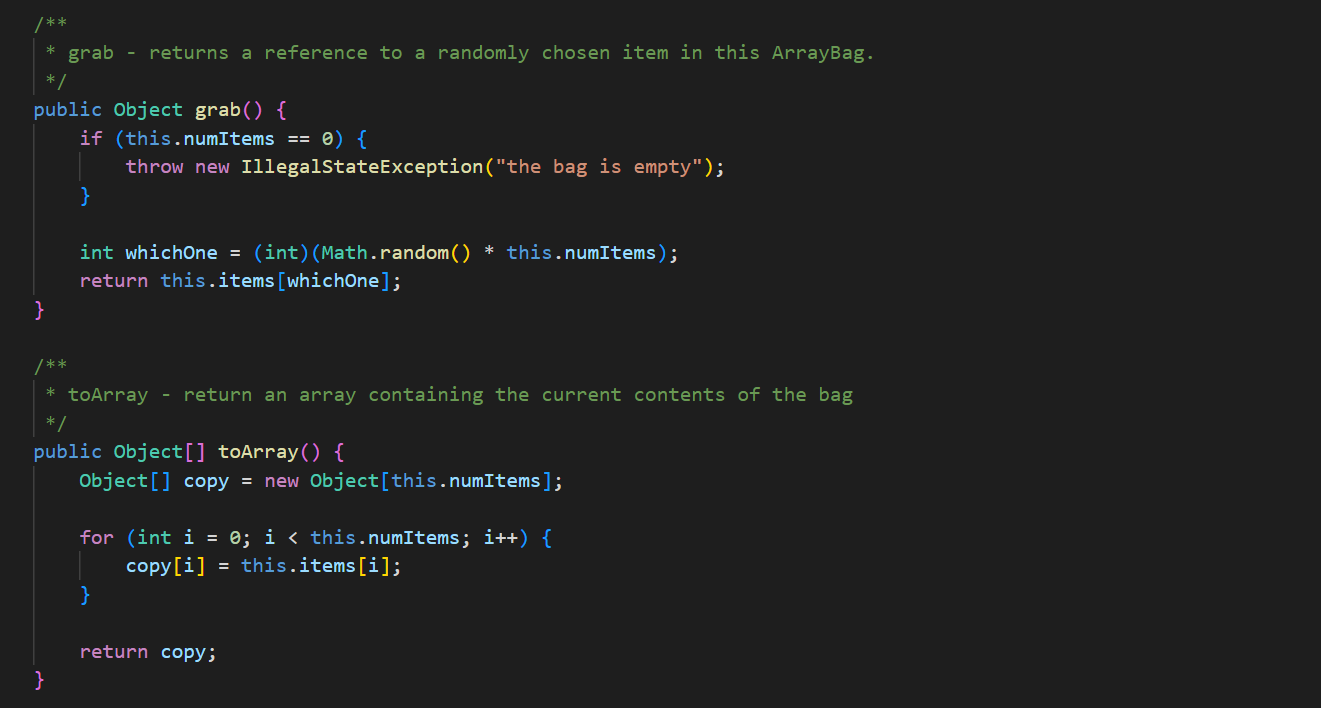
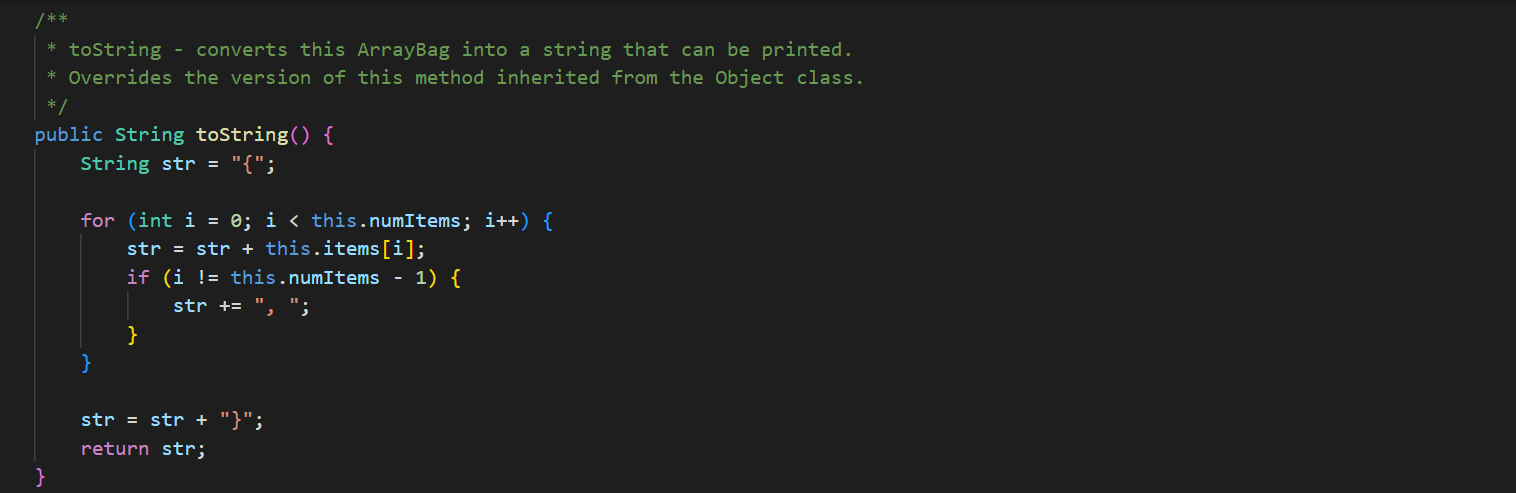
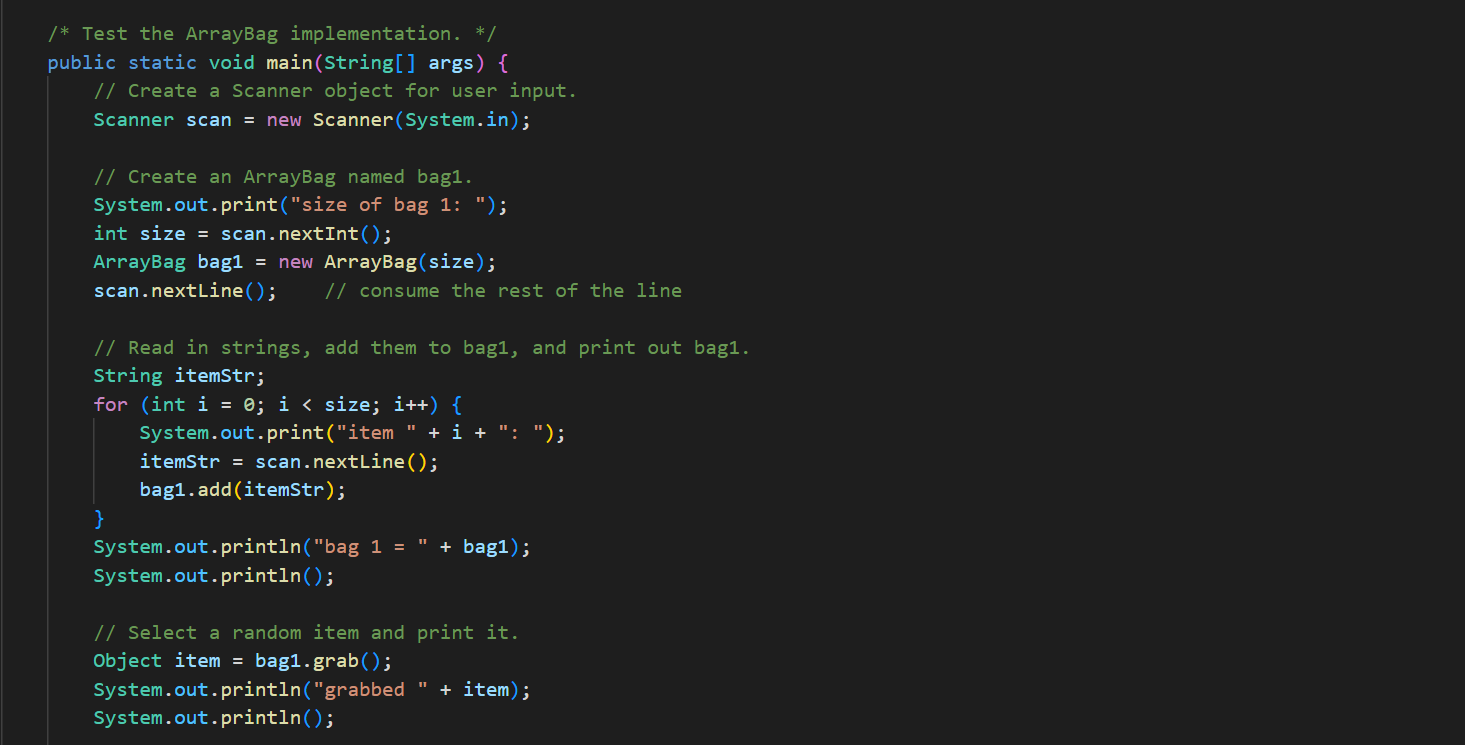
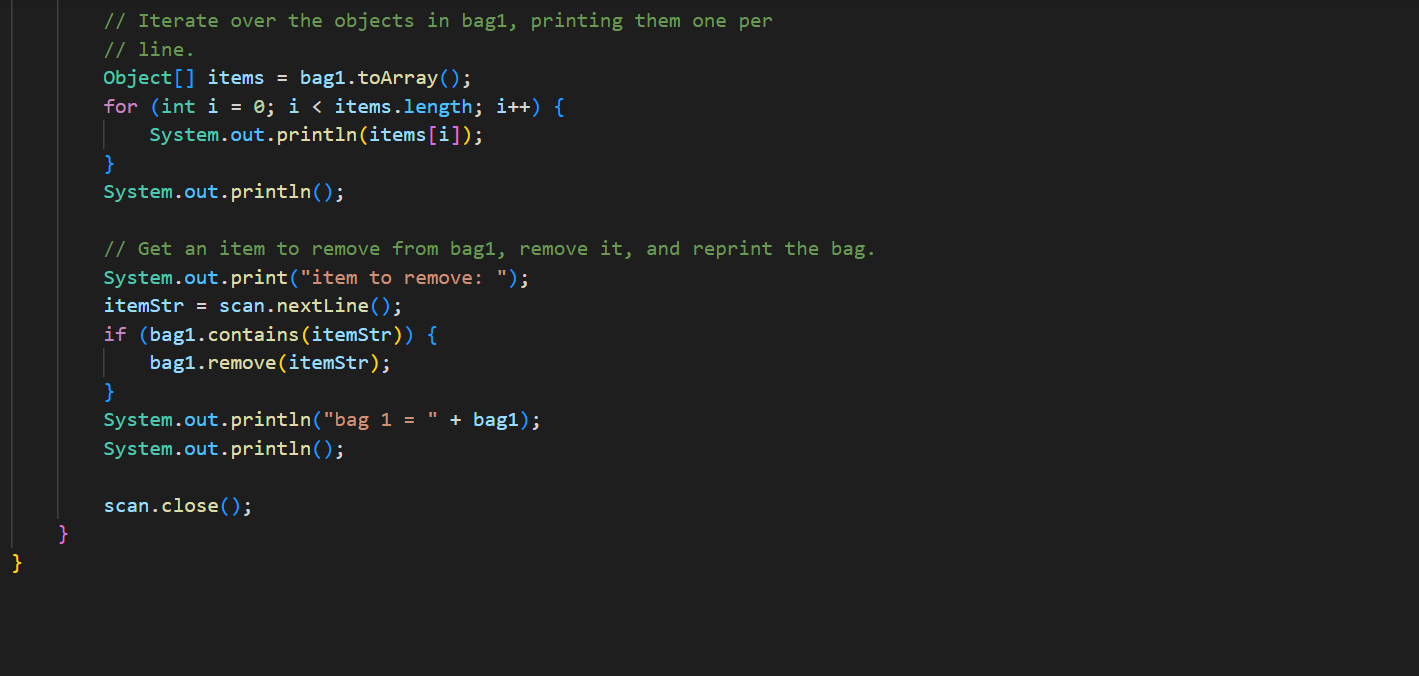
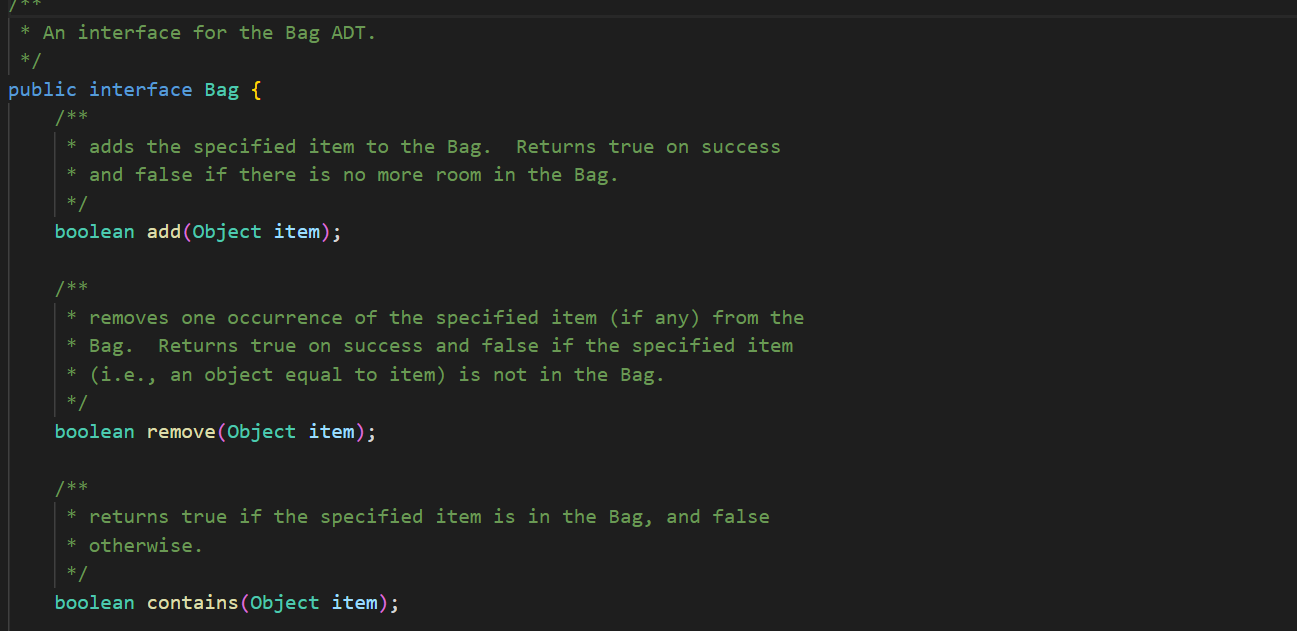
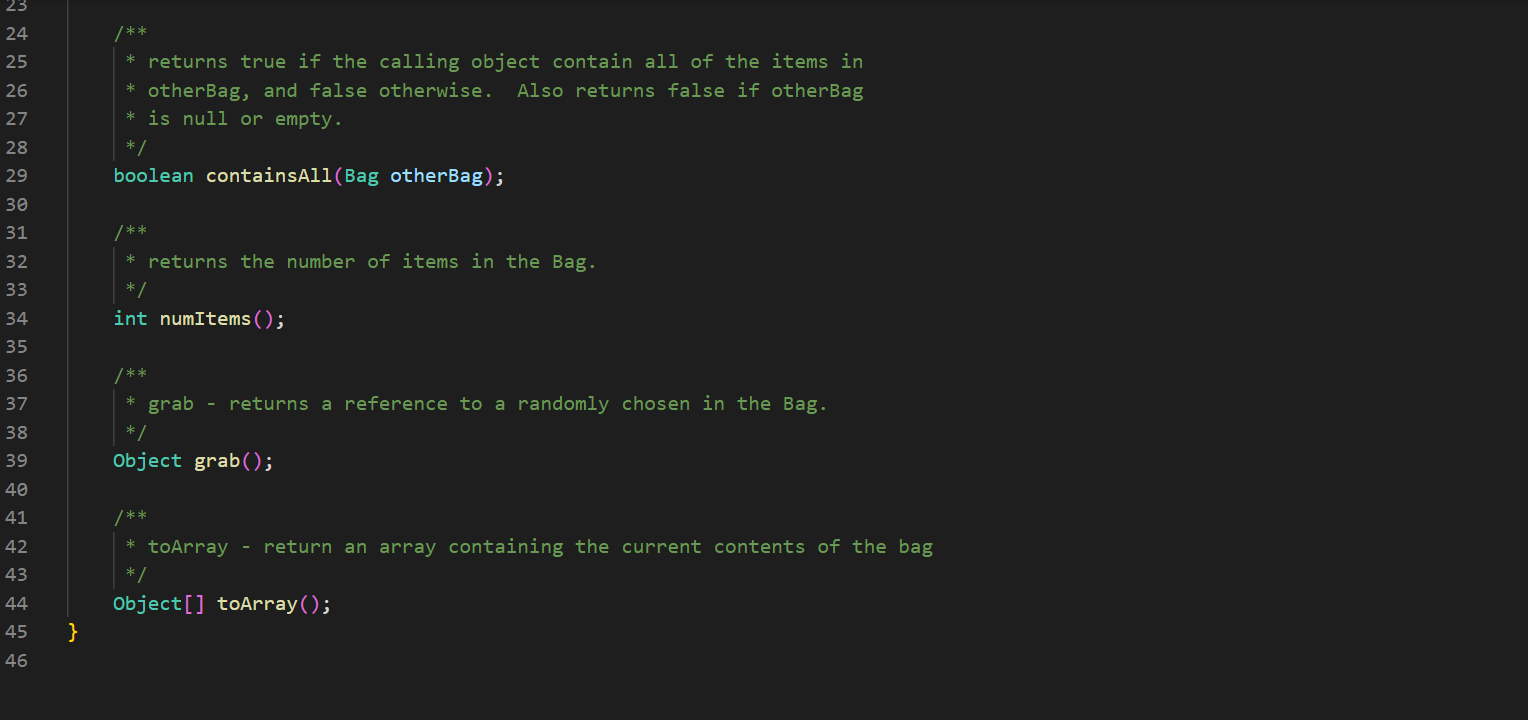
In ArrayBag. java, add the methods described below to the ArrayBag class, and then add code to the main() method to test these methods. In addition, you should update the Bag interface that we have given you in Bag. java to include these new methods. These methods should be publicly accessible. You should not add any new fields to the class. 1. public int capacity() This method should return the maximum number of items that the ArrayBag is able to hold. This value does not depend on the number of items that are currently in the ArrayBag - it is the same as the maximum size specified when the ArrayBag was created. 2. public boolean isFull() This method should return true if the called ArrayBag is full, and false otherwise. 3. public void increaseCapacity (int amount) This method should increase the maximum capacity of the called ArrayBag by the specified amount. For example, if b has a maximum capacity of 10, then b. increaseCapacity (5) should give b a maximum capacity of 15. As part of your implementation, you will need to create a new array with room to support the new maximum capacity, copy any existing items into that array, and replace the original array with the new one by storing its reference in the called object. Special cases: If the parameter is 0, the method should just return without making any changes to the called object. If the parameter is negative, the method should throw an IllegalArgumentException. See our second ArrayBag constructor for an example of throwing an exception. 4. public boolean removeItems (Bag other) This method should attempt to remove from the called ArrayBag all occurrences of the items found in the parameter other. If the called object contains multiple copies of an item from otherBag, all of the copies should be removed. The method should return true if one or more items are removed and false otherwise. Special cases: If the parameter is nu11, the method should throw an IllegalArgumentException. If the parameter is an empty Bag, the method should return false. Note that the parameter is of type Bag. As a result, your method should use method calls to access the internals of that bag. See our implementation of the containsA11() method for an example of this. 5. public Bag unionwith (Bag other) This method should create and return an ArrayBag containing one occurrence of any item that is found in either the called object or the parameter other. For full credit, the resulting bag should not include any duplicates. For example, if b1 represents the bag {2, 2, 3, 5, 7, 7, 7, 8} and b2 represents the bag {2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7}, then b1.unionwith(b2) should return an ArrayBag representing the bag {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}. Give the new ArrayBag a maximum size that is the sum of the two bag's maximum sizes. Special cases: If one of the bags is empty, the method should return an ArrayBag containing one occurrence of each item in the non-empty bag. If both of the bags are empty, the method should return an empty ArrayBag. If the parameter is nu11, the method should throw an IllegalArgumentException. Here again, the parameter is of type Bag. As a result, your method should use method calls to access the internals of that bag. See our implementation of the containsA11() method for an example of this. The return type is also Bag, but polymorphism allows you to just return the ArrayBag that you create, because ArrayBag implements Bag. import java.util.*; /** * An implementation of the Bag ADT using an array. */ public class ArrayBag implements Bag { /** * The array used to store the items in the bag. */ private Object[] items; /** * The number of items in the bag. */ private int numItems; public static final int DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE = 50; /** * Constructor with no parameters - creates a new, empty ArrayBag with * the default maximum size. */ public ArrayBag() { this.items = new Object [DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE]; this.numItems = 0; } /** * A constructor that creates a new, empty ArrayBag with the specified * maximum size. */ public ArrayBag(int maxSize) { if (maxSize /** * add - adds the specified item to this ArrayBag. Returns true if there * is room to add it, and false otherwise. * Throws an IllegalArgumentException if the item is null. */ public boolean add(Object item) { if (item == null) { } throw new IllegalArgumentException("item must be non-null"); } else if (this.numItems == this.items.length) { // no more room! return false; } else { } this.items [this.numItems] this.numItems++; return true; = item; /** remove - removes one occurrence of the specified item (if any) * from this ArrayBag. Returns true on success and false if the specified item (i.e., an object equal to item) is not in this ArrayBag. * */ public boolean remove (Object item) { for (int i = 0; i < this.numItems; i++) { (this.items[i].equals(item)) { if } } // Shift the remaining items left by one. for (int j = i; j < this.numItems 1; j++) { this.items [j] = this.items [j+ 1]; } this.items [this.numItems 1] = null; this.numItems --; return true; return false; // item not found * contains - returns true if the specified item is in the Bag, and * false otherwise. */ public boolean contains (Object item) { for (int i = 0; i < this.numItems; i++) { if (this.items[i].equals(item)) { } } return true; return false; /** * containsAll - does this ArrayBag contain all of the items in * otherBag? Returns false if otherBag is null or empty. */ public boolean containsAll(Bag otherBag) { if (otherBag == null || otherBag.numItems() == 0) { return false; } } Object[] otherItems = other Bag.toArray(); for (int i = 0; i < otherItems.length; i++) { if (! this.contains (otherItems[i])) { return false; } } return true; * grab - returns a reference to a randomly chosen item in this ArrayBag. */ public Object grab() { } ** } if (this.numItems == 0) { throw new IllegalStateException ("the bag is empty"); } int whichOne = (int) (Math.random() * this.numItems); return this.items [whichOne]; toArray - return an array containing the current contents of the bag */ public Object[] toArray() { Object[] copy = new Object[this.numItems]; for (int i = 0; i < this.numItems; i++) { copy[i] = this.items[i]; } return copy; /** *toString - converts this ArrayBag into a string that can be printed. * Overrides the version of this method inherited from the Object class. */ public String toString() { String str = "{"; } for (int i = 0; i < this.numItems; i++) { str = str + this.items[i]; if (i != this.numItems - 1) { str += } } str = str + "}"; return str; /* Test the ArrayBag implementation. */ public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a Scanner object for user input. Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); // Create an ArrayBag named bag1. System.out.print("size of bag 1: "); int size = scan.nextInt (); ArrayBag bag1 = new ArrayBag(size); scan.nextLine(); // consume the rest of the line // Read in strings, add them to bag1, and print out bagl. String itemStr; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { } System.out.print("item " + i + ": "); itemStr = scan.nextLine(); bag1.add(itemStr); System.out.println("bag 1 = " + bag1); System.out.println(); // Select a random item and print it. Object item = bag1.grab(); System.out.println("grabbed " + item); System.out.println(); // Iterate over the objects in bag, printing them one per // line. Object[] items = bag1.toArray(); for (int i = 0; i < items.length; i++) { System.out.println(items[i]); } System.out.println(); // Get an item to remove from bag1, remove it, and reprint the bag. System.out.print("item to remove: "); itemStr = scan.nextLine(); if (bag1.contains (itemStr)) { } bag1.remove(itemStr); System.out.println("bag 1 = + bag1); System.out.println(); scan.close(); * An interface for the Bag ADT. */ public interface Bag { /** * adds the specified item to the Bag. Returns true on success * and false if there is no more room in the Bag. boolean add(Object item); /** removes one occurrence of the specified item (if any) from the * Bag. Returns true on success and false if the specified item * (i.e., an object equal to item) is not in the Bag. */ boolean remove(Object item); * /** * returns true if the specified item is in the Bag, and false * otherwise. */ boolean contains (Object item); 23 4 4 8 8 8 8 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 } ** returns true if the calling object contain all of the items in * otherBag, and false otherwise. Also returns false if otherBag * is null or empty. * */ boolean containsAll(Bag otherBag); /** * returns the number of items in the Bag. */ int numItems (); /** * grab - returns a reference to a randomly chosen in the Bag. */ Object grab(); /** * toArray - return an array containing the current contents of the bag */ Object[] toArray();
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


