Question: In C# I have an Assignment to create a simple calculator that accepts 2 operands and an operator from the user and should pass these
In C# I have an Assignment to create a simple calculator that accepts 2 operands and an operator from the user and should pass these 3 arguments into a method and then display the result to the user.
The line if (Convert.ToBoolean(Operator = "/")) returns an error
"String was not recognized as a valid Boolean." 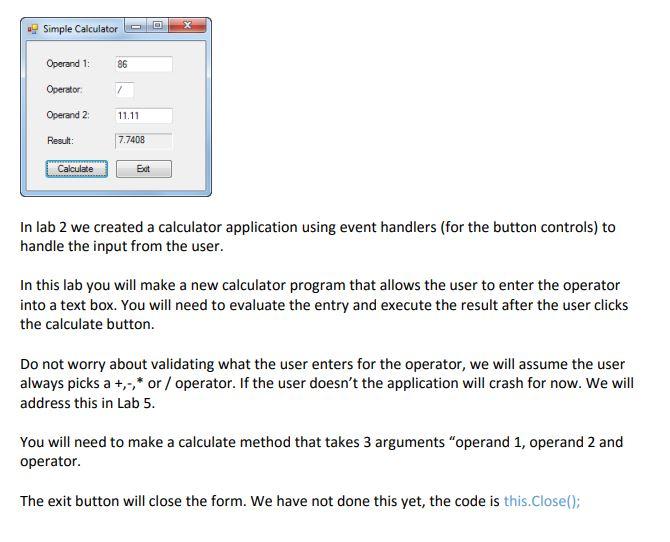
The code I am using is:
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Lab4_Part3_SimpleCalculator_CRupe { public partial class SimpleCalculator : Form { public SimpleCalculator() { InitializeComponent(); }
private void BtnCalculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //Declare a vairable for each entry Decimal Value1 = Convert.ToDecimal(TxtValue1.Text); string Operator = TxtOperator.Text; Decimal Value2 = Convert.ToDecimal(TxtValue2.Text); //Run the CalculateValue method CalculateValue(Value1, Operator, Value2); //Pass the Result from CalculateValue method to a variable and convert to string String DisplayMessage = Convert.ToString(CalculateValue(Value1, Operator, Value2)); //Display result to user TxtResult.Text = DisplayMessage; } private string CalculateValue(Decimal Value1, string Operator, Decimal Value2) { // Declare a variable for result calculation Decimal Result = .0m; //Convert entered number to Decimal and determine tax rate and amount if (Convert.ToBoolean(Operator = "/")) Result = Value1 / Value2; else if (Convert.ToBoolean(Operator = "*")) Result = Value1 * Value2; else if (Convert.ToBoolean(Operator = "+")) Result = Value1 + Value2; else if (Convert.ToBoolean(Operator = "-")) Result = Value1 - Value2; return (Convert.ToString(Result)); } } }
namespace Lab4_Part3_SimpleCalculator_CRupe { partial class SimpleCalculator { /// /// Required designer variable. /// private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
/// /// Clean up any resources being used. /// /// true if managed resources should be disposed; otherwise, false. protected override void Dispose(bool disposing) { if (disposing && (components != null)) { components.Dispose(); } base.Dispose(disposing); }
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
/// /// Required method for Designer support - do not modify /// the contents of this method with the code editor. /// private void InitializeComponent() { this.LblOperand1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.LblOperator = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.LblOperand2 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.LblResult = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.BtnCalculate = new System.Windows.Forms.Button(); this.BtnExit = new System.Windows.Forms.Button(); this.TxtValue1 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.TxtOperator = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.TxtValue2 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.TxtResult = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.SuspendLayout(); // // LblOperand1 // this.LblOperand1.AutoSize = true; this.LblOperand1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(13, 20); this.LblOperand1.Name = "LblOperand1"; this.LblOperand1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(60, 13); this.LblOperand1.TabIndex = 0; this.LblOperand1.Text = "Operand 1:"; // // LblOperator // this.LblOperator.AutoSize = true; this.LblOperator.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(13, 56); this.LblOperator.Name = "LblOperator"; this.LblOperator.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(51, 13); this.LblOperator.TabIndex = 1; this.LblOperator.Text = "Operator:"; // // LblOperand2 // this.LblOperand2.AutoSize = true; this.LblOperand2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(13, 92); this.LblOperand2.Name = "LblOperand2"; this.LblOperand2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(60, 13); this.LblOperand2.TabIndex = 2; this.LblOperand2.Text = "Operand 2:"; // // LblResult // this.LblResult.AutoSize = true; this.LblResult.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(13, 128); this.LblResult.Name = "LblResult"; this.LblResult.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(40, 13); this.LblResult.TabIndex = 3; this.LblResult.Text = "Result:"; // // BtnCalculate // this.BtnCalculate.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(12, 160); this.BtnCalculate.Name = "BtnCalculate"; this.BtnCalculate.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(75, 23); this.BtnCalculate.TabIndex = 4; this.BtnCalculate.Text = "Calculate"; this.BtnCalculate.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true; this.BtnCalculate.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.BtnCalculate_Click); // // BtnExit // this.BtnExit.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(133, 160); this.BtnExit.Name = "BtnExit"; this.BtnExit.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(75, 23); this.BtnExit.TabIndex = 5; this.BtnExit.Text = "Exit"; this.BtnExit.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true; // // TxtValue1 // this.TxtValue1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(108, 17); this.TxtValue1.Name = "TxtValue1"; this.TxtValue1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 20); this.TxtValue1.TabIndex = 6; // // TxtOperator // this.TxtOperator.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(108, 53); this.TxtOperator.Name = "TxtOperator"; this.TxtOperator.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(33, 20); this.TxtOperator.TabIndex = 7; // // TxtValue2 // this.TxtValue2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(108, 89); this.TxtValue2.Name = "TxtValue2"; this.TxtValue2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 20); this.TxtValue2.TabIndex = 8; // // TxtResult // this.TxtResult.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(108, 125); this.TxtResult.Name = "TxtResult"; this.TxtResult.ReadOnly = true; this.TxtResult.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 20); this.TxtResult.TabIndex = 9; // // SimpleCalculator // this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 13F); this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font; this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(220, 195); this.Controls.Add(this.TxtResult); this.Controls.Add(this.TxtValue2); this.Controls.Add(this.TxtOperator); this.Controls.Add(this.TxtValue1); this.Controls.Add(this.BtnExit); this.Controls.Add(this.BtnCalculate); this.Controls.Add(this.LblResult); this.Controls.Add(this.LblOperand2); this.Controls.Add(this.LblOperator); this.Controls.Add(this.LblOperand1); this.Name = "SimpleCalculator"; this.Text = "Simple Calculator"; this.ResumeLayout(false); this.PerformLayout();
}
#endregion
private System.Windows.Forms.Label LblOperand1; private System.Windows.Forms.Label LblOperator; private System.Windows.Forms.Label LblOperand2; private System.Windows.Forms.Label LblResult; private System.Windows.Forms.Button BtnCalculate; private System.Windows.Forms.Button BtnExit; private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox TxtValue1; private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox TxtOperator; private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox TxtValue2; private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox TxtResult; } }
Simple Calculator Operand 1: 86 Operator Operand 2 11.11 Result: 7.7408 Calculate Edt In lab 2 we created a calculator application using event handlers (for the button controls) to handle the input from the user. In this lab you will make a new calculator program that allows the user to enter the operator into a text box. You will need to evaluate the entry and execute the result after the user clicks the calculate button. Do not worry about validating what the user enters for the operator, we will assume the user always picks a +,-* or / operator. If the user doesn't the application will crash for now. We will address this in Lab 5. You will need to make a calculate method that takes 3 arguments "operand 1, operand 2 and operator. The exit button will close the form. We have not done this yet, the code is this.Close()




