Question: In C language. #includelab4-q2.h #include #include #include #include // Hash Table Open Addressing Part #1 #2 #10 // Initialize the hash table to the given
In C language.
#include"lab4-q2.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
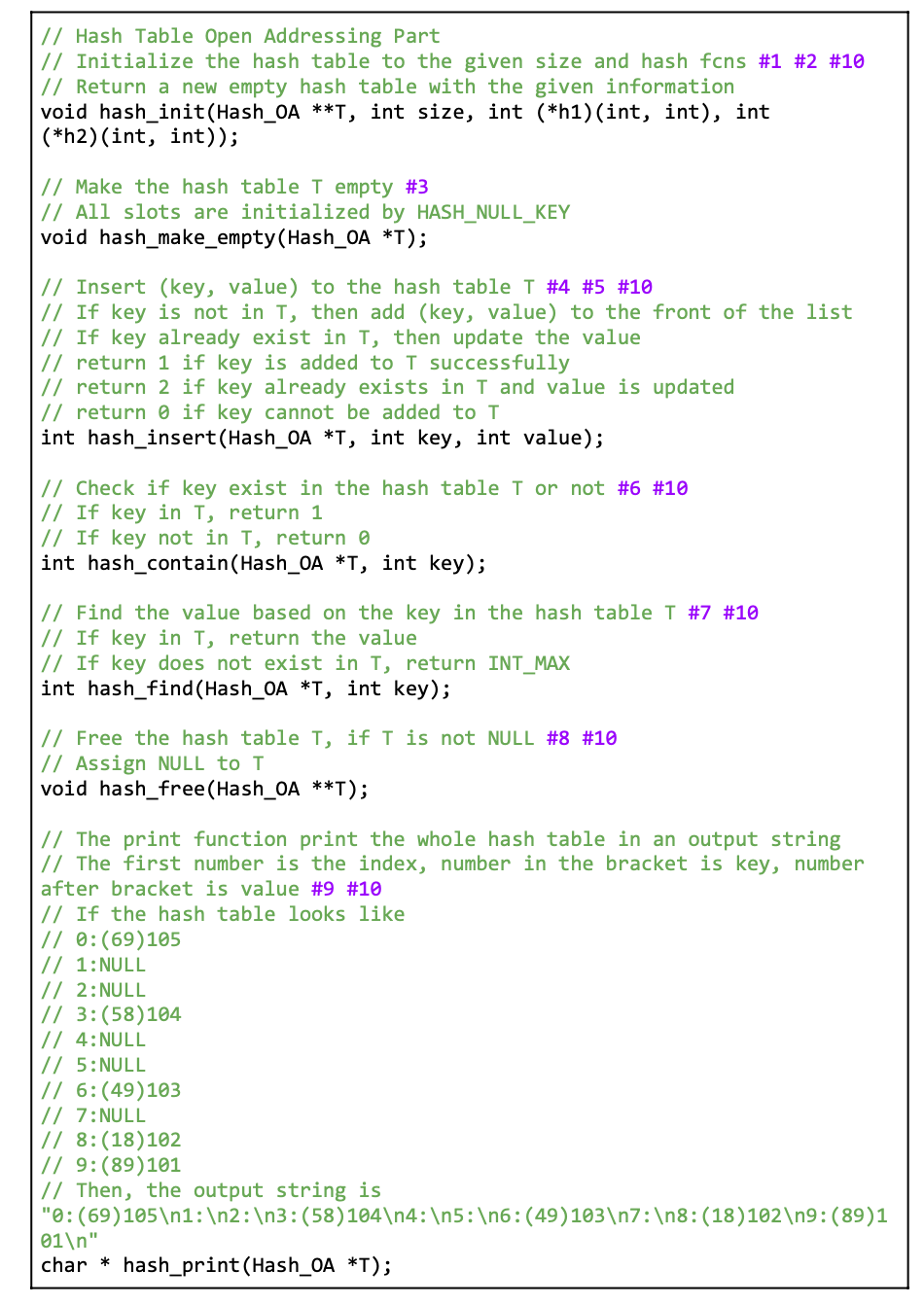
// Hash Table Open Addressing Part #1 #2 #10
// Initialize the hash table to the given size and given hash functions
// Create a new empty hash table with the given information
void hash_init(Hash_OA **T, int size, int (*h1)(int, int), int (*h2)(int, int)){
// Your code here
}
// Make the hash table T empty #3
// All slots are initialized by HASH_NULL_KEY
void hash_make_empty(Hash_OA *T){
// Your code here
}
// Insert (key, value) to the hash table T #4 #5 #10
// If key does not exist in T, then add (key, value) to the front of the list
// If key already exist in T, then update the value
// return 1 if key is added to T successfully
// return 2 if key already exists in T and values is updated accordingly
// return 0 if key cannot be added to T
int hash_insert(Hash_OA *T, int key, int value){
// Your code here
return 0;
}
// Check if key exist in the hash table T or not #6 #10
// If key in T, return 1
// If key not in T, return 0
int hash_contain(Hash_OA *T, int key){
// Your code here
return 0;
}
// Find the value based on the key in the hash table T #7 #10
// If key in T, return the value
// If key does not exist in T, return INT_MAX
int hash_find(Hash_OA *T, int key){
// Your code here
return 0;
}
// Free the hash table T, if T is not NULL #8 #10
// Assign NULL to T
void hash_free(Hash_OA **T){
// Your code here
}
// The print function print the whole hash table in an output string #9 #10
// The first number is the index, number in the bracket is key, number after bracket is value
// If the hash table looks like
// 0:(69)105
// 1:NULL
// 2:NULL
// 3:(58)104
// 4:NULL
// 5:NULL
// 6:(49)103
// 7:NULL
// 8:(18)102
// 9:(89)101
// Then, the output string is "0:(69)105 1: 2: 3:(58)104 4: 5: 6:(49)103 7: 8:(18)102 9:(89)101 "
char * hash_print(Hash_OA *T){
int i, len;
char * output;
// Your code here
return output;
}
Question 2: Hash Table with Open Addressing (30\%) You are going to implement a hash table abstract data type using open addressing with double hashing. The header file "lab4-q2.h" and the description of the functions are as follows. Your program should not contain main(). Name your program as "lab4-q2.c". // lab4-q2.h // Cannot modify this file typedef struct node int key; int value; \} Node; typedef struct hash_os \{ int size; Node * slots; // array of slots // first int: key; second int: size of hash table int (*hash_function )(int, int); // first hash function int (*hash_function2)(int, int); // second hash function // Wash_OA; \#define the slot is unoccupied, the key is HASH_NULL_KEY 2100
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


