Question: In c++ please Rationals.h file rationals.cpp file The sampleProgram.cpp We're gonna make a rational number library! Take a look at rationals.h-that file contains the declarations
In c++ please
Rationals.h file
rationals.cpp file
The sampleProgram.cpp
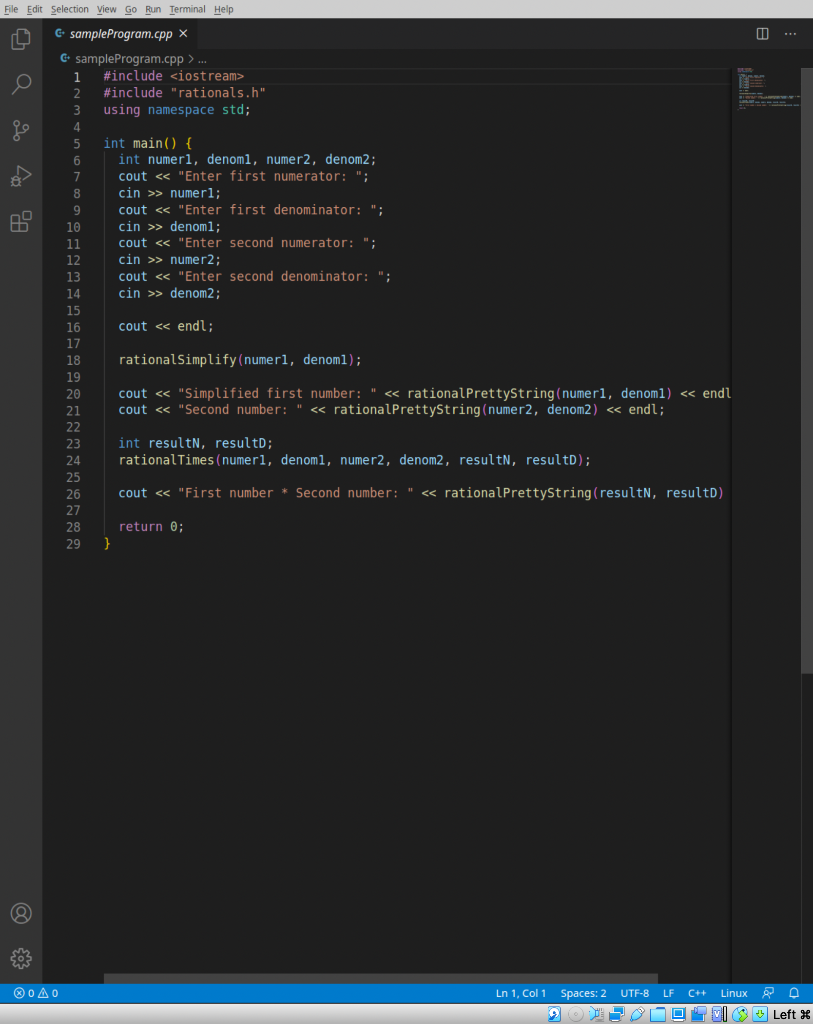
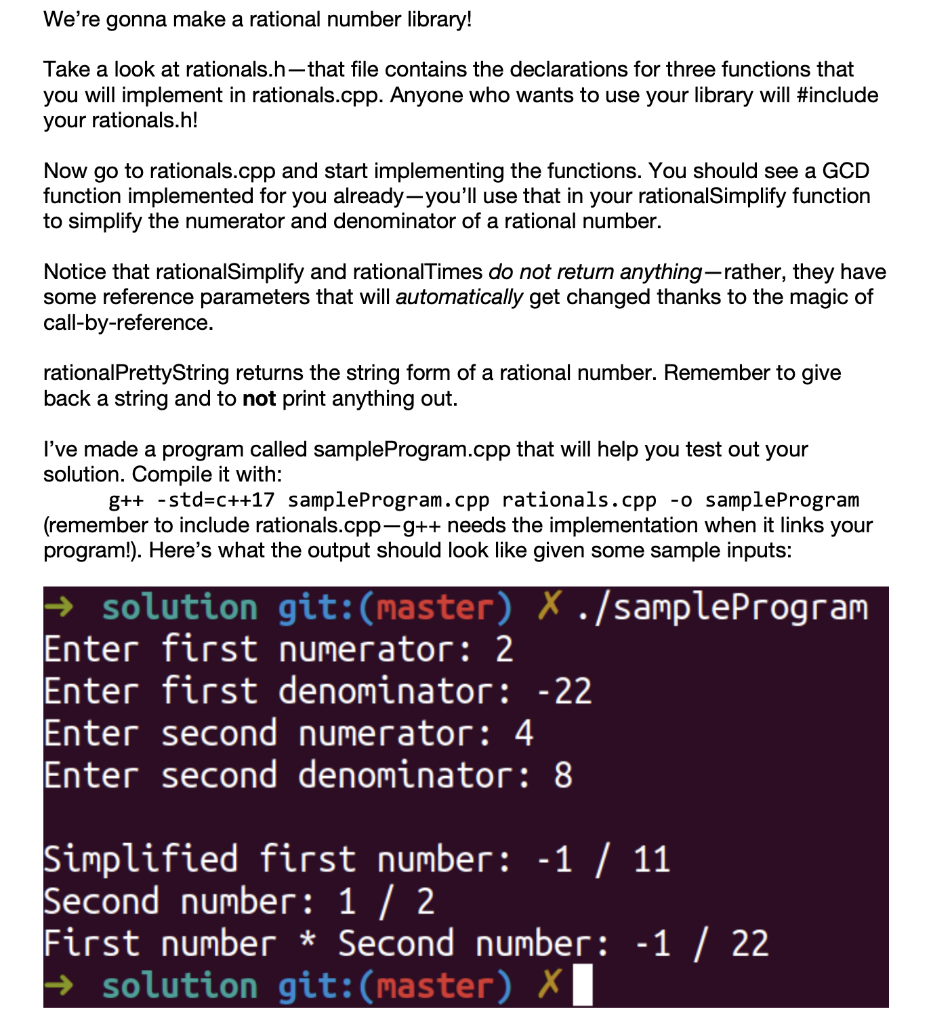
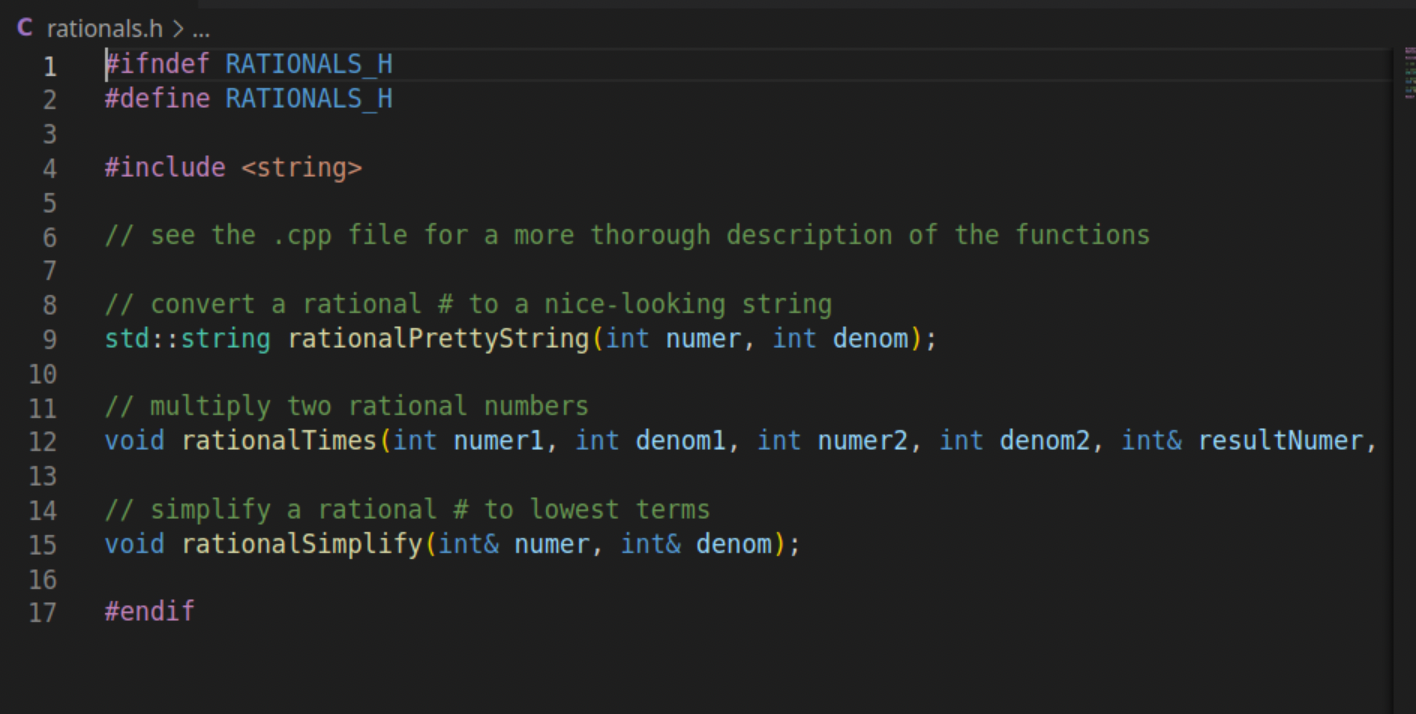
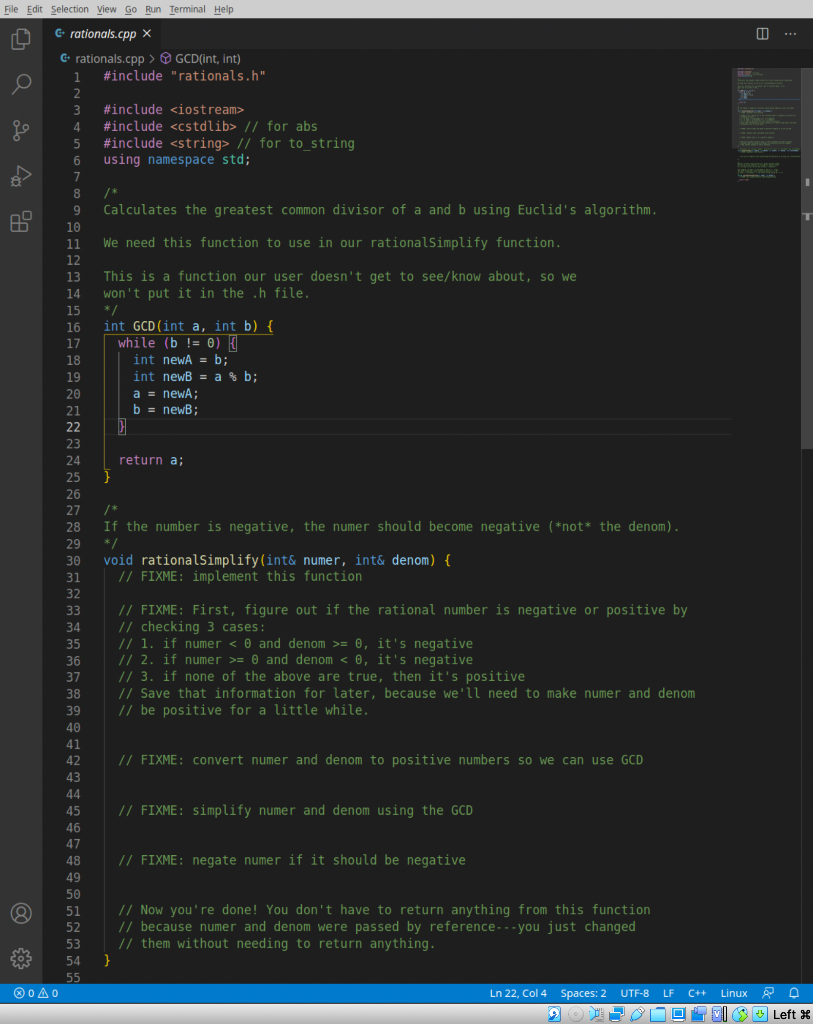
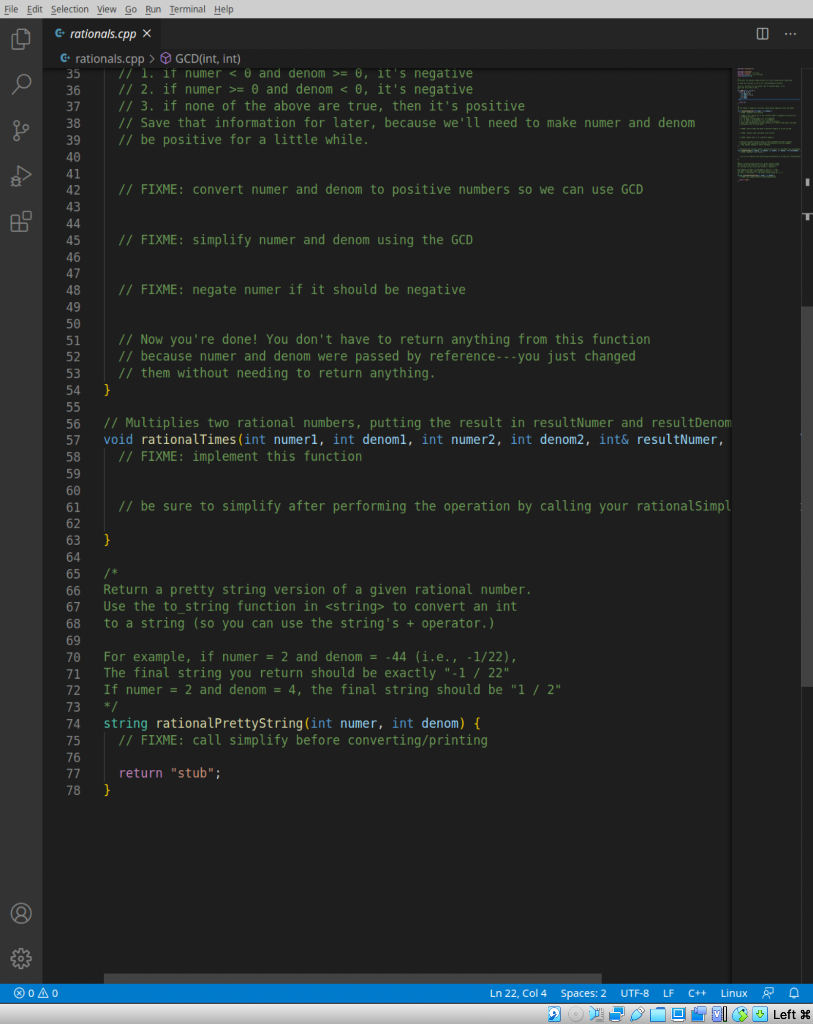
We're gonna make a rational number library! Take a look at rationals.h-that file contains the declarations for three functions that you will implement in rationals.cpp. Anyone who wants to use your library will #include your rationals.h! Now go to rationals.cpp and start implementing the functions. You should see a GCD function implemented for you already-you'll use that in your rationalSimplify function to simplify the numerator and denominator of a rational number. Notice that rationalSimplify and rationalTimes do not return anything-rather, they have some reference parameters that will automatically get changed thanks to the magic of call-by-reference. rational PrettyString returns the string form of a rational number. Remember to give back a string and to not print anything out. I've made a program called sample Program.cpp that will help you test out your solution. Compile it with: g++ -std=c++17 sampleProgram.cpp rationals.cpp -o sampleProgram (remember to include rationals.cpp-g++ needs the implementation when it links your program!). Here's what the output should look like given some sample inputs: solution git:(master) X ./sampleProgram Enter first numerator: 2 Enter first denominator: -22 Enter second numerator: 4 Enter second denominator: 8 Simplified first number: -1 / 11 Second number: 1 / 2 First number * Second number: -1 / 22 solution git: (master) X We're gonna make a rational number library! Take a look at rationals.h-that file contains the declarations for three functions that you will implement in rationals.cpp. Anyone who wants to use your library will #include your rationals.h! Now go to rationals.cpp and start implementing the functions. You should see a GCD function implemented for you already-you'll use that in your rationalSimplify function to simplify the numerator and denominator of a rational number. Notice that rationalSimplify and rationalTimes do not return anything-rather, they have some reference parameters that will automatically get changed thanks to the magic of call-by-reference. rational PrettyString returns the string form of a rational number. Remember to give back a string and to not print anything out. I've made a program called sample Program.cpp that will help you test out your solution. Compile it with: g++ -std=c++17 sampleProgram.cpp rationals.cpp -o sampleProgram (remember to include rationals.cpp-g++ needs the implementation when it links your program!). Here's what the output should look like given some sample inputs: solution git:(master) X ./sampleProgram Enter first numerator: 2 Enter first denominator: -22 Enter second numerator: 4 Enter second denominator: 8 Simplified first number: -1 / 11 Second number: 1 / 2 First number * Second number: -1 / 22 solution git: (master) X HO C rationals.h > ... 1 #ifndef RATIONALS_H 2 #define RATIONALS H 3 4 #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


