Question: In code C, please! The task is to create second-degree polynomial calculator for the function, its integral and its derivative. A second-degree polynomial is described
In code C, please!
The task is to create second-degree polynomial calculator for the function, its integral and
its derivative. A second-degree polynomial is described by the equation
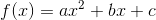 .
.
Evaluation of the derivative gives the instantaneous slope or rate of change as (where
f' (x) is the derivative of f (x) ):
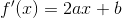
The integral of the function f (x) (let us call it F(x) ) indicates the area underneath the
curve. Between points 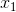 and
and 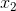 , the area A is
, the area A is
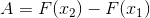 ,
,
where, for a second-degree polynomial,
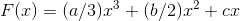 .
.
Your program will be used to create a table of data of the independent variable x versus
f (x) , f' (x) and A. The user will enter the polynomial coefficients {a,b,c} as well as the
starting value of x (denote it 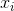 ), the final value of x (denote it
), the final value of x (denote it 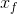 ), and the increment
), and the increment
value between successive x values (denote it 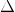 x ).
x ).
Follow these detailed instructions:
1. First, read this document in its entirety. After reading this handout, you may
optionally create a design sheet for the problem. Your design sheet should help you
determine what header files, functions and variables you will need as well as
identifying expected test results. You do NOT turn in your design sheet.
2. When you write your code, include the usual (detailed) comment block including
program name, author, date, inputs, outputs and description.
3. Create a function of type void to explain the program to the user with the
description printed to the terminal. Do not forget to call the function from main().
4. Input the data while executing from your main() function. Query the user to enter
the data. You must enter the parameters from the user in the following order: a, b, c
and then 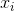 ,
, 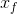 and
and 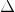 x . Use double for all variables and calculations.
x . Use double for all variables and calculations.
5. Your program is to loop over all possible x values in your main() function. The
first x value is to be 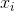 , the second
, the second 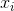 +
+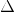 x, etc. with the last value being
x, etc. with the last value being 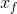 (or
(or
somewhat less than 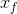 if
if 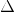 x does not divide evenly into the range).
x does not divide evenly into the range).
6. The calculation of the area A depends on the initial value of x, 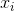 . That is, for each x,
. That is, for each x,
we calculate the area as 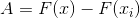 . In order to calculate A, you must know
. In order to calculate A, you must know
both x and 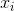 . For the first value of x, it should be that A is zero.
. For the first value of x, it should be that A is zero.
7. From main() and for each x, you are to call a function that accepts a, b, c, x and 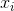 .
.
Calculate and return (via pointer operations) f (x) , f' (x) and A. That is, you must
create a single function that accepts eight inputs five are call-by-value (a, b, c, x and
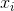 ), and three are call-by-reference (pointers related to f (x) , f' (x) and A). There
), and three are call-by-reference (pointers related to f (x) , f' (x) and A). There
must not be any scan/print statements in your function.
8. Your function uses the values of a, b and c along with the value of x to compute 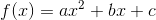
. Similarly, the derivative is computed as 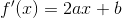 . Then,
. Then,
using 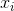 in addition to the other parameters, compute
in addition to the other parameters, compute 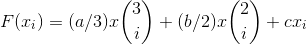 and
and 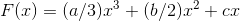 . The area is found as
. The area is found as 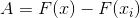 .
.
Return the result of your calculations back to the main() function (it will be necessary to reference your
outputs via pointers).
9. All output for your table of x versus f (x) , f' (x) and A must be displayed via
statements in your main() function. Write your table to the terminal (i.e., the default
output for printf()). Choose a suitable format for your output numbers.
10. An example of what the output table should look like is given below. Assume that the
user enters 2.0 -2.0 -1.0 for a, b, c, respectively, and 0.0 5.0 0.25 for 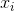 ,
,
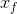 and
and 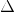 x , respectively. Your output should be the following:
x , respectively. Your output should be the following:
f(x) = 2x^2 + -2x + -1
x f(x) f'(x) A
-------------------------------
0.000 -1.000 -2.000 0.000
0.250 -1.375 -1.000 -0.302
0.500 -1.500 0.000 -0.667
0.750 -1.375 1.000 -1.031
1.000 -1.000 2.000 -1.333
1.250 -0.375 3.000 -1.510
1.500 0.500 4.000 -1.500
1.750 1.625 5.000 -1.240
2.000 3.000 6.000 -0.667
2.250 4.625 7.000 0.281
2.500 6.500 8.000 1.667
2.750 8.625 9.000 3.552
3.000 11.000 10.000 6.000
3.250 13.625 11.000 9.073
3.500 16.500 12.000 12.833
3.750 19.625 13.000 17.344
4.000 23.000 14.000 22.667
4.250 26.625 15.000 28.865
4.500 30.500 16.000 36.000
4.750 34.625 17.000 44.135
5.000 39.000 18.000 53.333
11. Use the test set as given above.
f(1) = ax + bx+c f'(2) = 2ax + b A = F(.22) - F(21) F(x) = (a/3). + (6/2) + cx A = F(I) - FX;) F(3:1) = (a/3)() + (6/2)-(3) + c3 A = F(I) - FX;)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


