Question: In JAVA Implement iterative and recursively add explanation as well. The second algorithm (Algorithm 2) is to apply the procedure Partition used in Quicksort. The
In JAVA
Implement iterative and recursively add explanation as well.
The second algorithm (Algorithm 2) is to apply the procedure Partition used in Quicksort. The procedure partitions an array so that all elements smaller than some pivot item come before it in the array and all elements larger than that pivot item come after it. The slot at which the pivot item is located is called the pivotposition. We can solve the Selection Problem by partitioning until the pivot item is at the kth slot. We do this by recursively partitioning the left subarray if k is less than pivotposition, and by recursively partitioning the right subarray if k is greater than pivotposition. When k = pivotposition, we're done.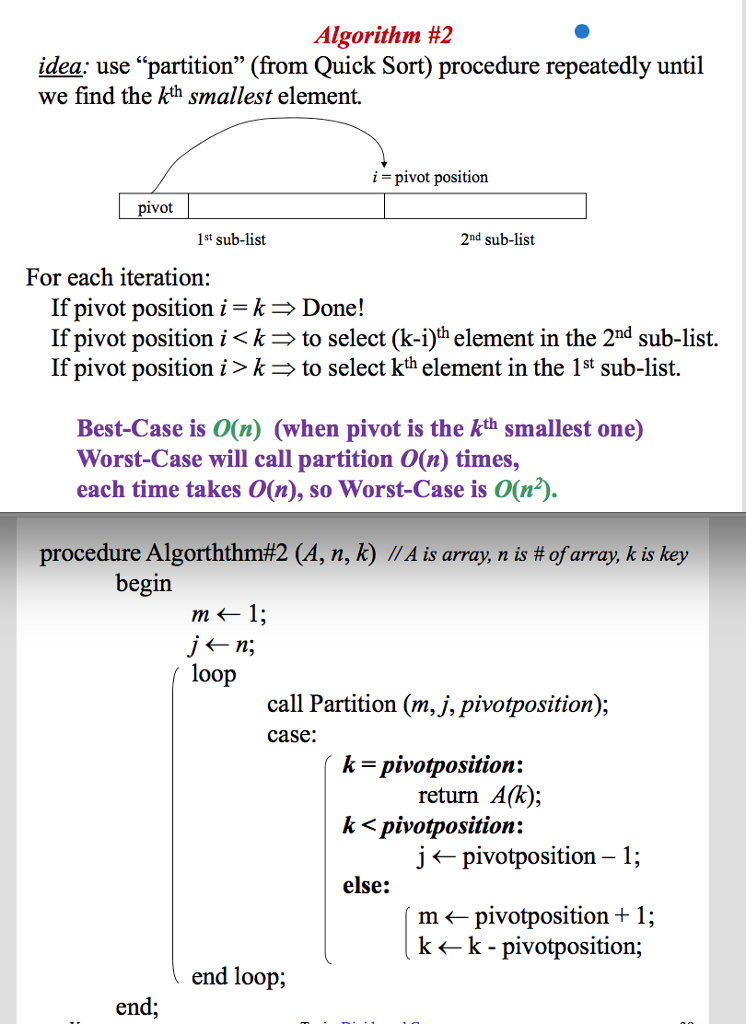
Algorithm #2 idea: use "partition (from Ouick Sort) procedure repeatedly until we find the kth smallest element. pivot position pivot 1st sub-list 2nd sub-list For each iteration: If pivot position i k Done! If pivot position i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


