Question: in ocaml language Write a function buckets : ('a -> 'a -> bool) -> 'a list -> 'a list list that partitions a list into
in ocaml language
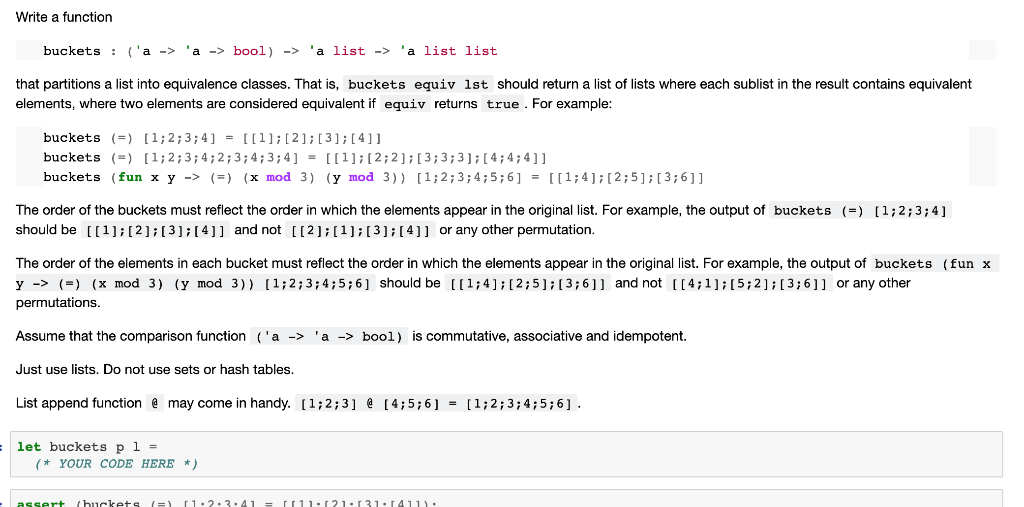
Write a function buckets : ('a -> 'a -> bool) -> 'a list -> 'a list list that partitions a list into equivalence classes. That is, buckets equiv lst should return a list of lists where each sublist in the result contains equivalent elements, where two elements are considered equivalent if equiv returns true . For example: buckets (=) [1;2;3;4] = [[1];[2]; [3];[4]] buckets (=) [1;2;3;4;2;3;4;3;4] = [[1];[2;2];[3;3;3];[4;4;4]] buckets (fun x y -> (=) (x mod 3) (y mod 3)) [1;2;3;4;5;6] = [[174];[2;5];[3;6]] The order of the buckets must reflect the order in which the elements appear in the original list. For example, the output of buckets (=) [1;2;3;4] should be [[1];[2];[3];[4]] and not [[2];[1];[3];[4]] or any other permutation. The order of the elements in each bucket must reflect the order in which the elements appear in the original list. For example, the output of buckets (fun x y -> (=) (x mod 3) (y mod 3)) [1;2;3;4;5;6] should be [[1;4];[2;5),(3;6]] and not [[4;1];[5;2];[3;6]] or any other permutations. Assume that the comparison function ('a -> 'a -> bool) is commutative, associative and idempotent. Just use lists. Do not use sets or hash tables. List append function @ may come in handy. [1;2;3] @[4;5;6] = [1;2;3;4;5;6] . let buckets p 1 = (* YOUR CODE HERE *) assert (bucket (=) 11.2.3.41 11.121.31.1411. Write a function buckets : ('a -> 'a -> bool) -> 'a list -> 'a list list that partitions a list into equivalence classes. That is, buckets equiv lst should return a list of lists where each sublist in the result contains equivalent elements, where two elements are considered equivalent if equiv returns true . For example: buckets (=) [1;2;3;4] = [[1];[2]; [3];[4]] buckets (=) [1;2;3;4;2;3;4;3;4] = [[1];[2;2];[3;3;3];[4;4;4]] buckets (fun x y -> (=) (x mod 3) (y mod 3)) [1;2;3;4;5;6] = [[174];[2;5];[3;6]] The order of the buckets must reflect the order in which the elements appear in the original list. For example, the output of buckets (=) [1;2;3;4] should be [[1];[2];[3];[4]] and not [[2];[1];[3];[4]] or any other permutation. The order of the elements in each bucket must reflect the order in which the elements appear in the original list. For example, the output of buckets (fun x y -> (=) (x mod 3) (y mod 3)) [1;2;3;4;5;6] should be [[1;4];[2;5),(3;6]] and not [[4;1];[5;2];[3;6]] or any other permutations. Assume that the comparison function ('a -> 'a -> bool) is commutative, associative and idempotent. Just use lists. Do not use sets or hash tables. List append function @ may come in handy. [1;2;3] @[4;5;6] = [1;2;3;4;5;6] . let buckets p 1 = (* YOUR CODE HERE *) assert (bucket (=) 11.2.3.41 11.121.31.1411
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


