Question: In Python, A binary heap is conceptually thought of as a tree with two special properties: 1. A shape property - the binary heap is
In Python,
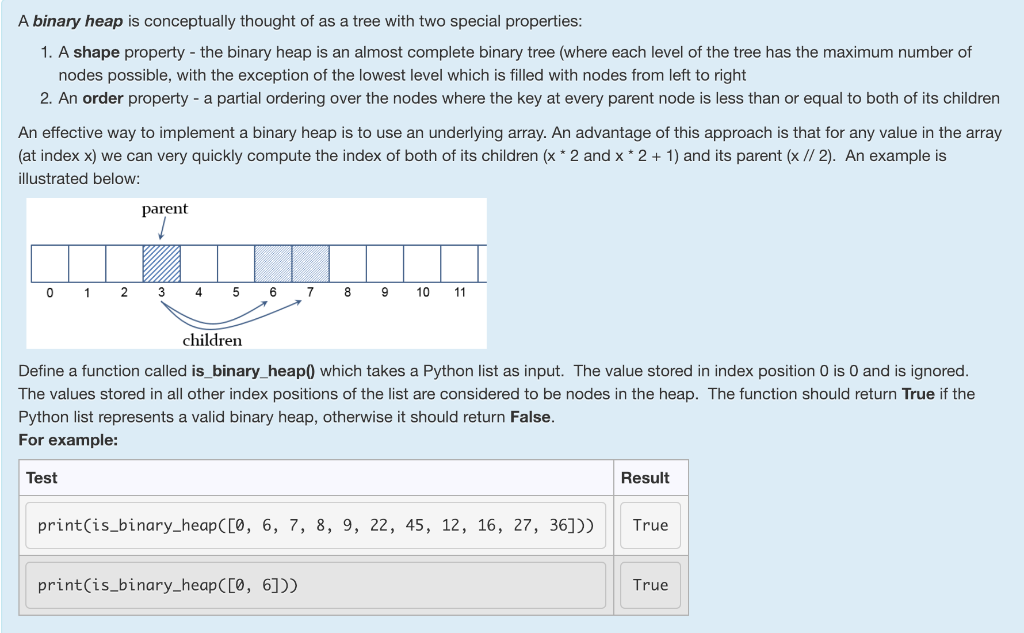
A binary heap is conceptually thought of as a tree with two special properties: 1. A shape property - the binary heap is an almost complete binary tree (where each level of the tree has the maximum number of nodes possible, with the exception of the lowest level which is filled with nodes from left to right 2. An order property - a partial ordering over the nodes where the key at every parent node is less than or equal to both of its children An effective way to implement a binary heap is to use an underlying array. An advantage of this approach is that for any value in the array (at index x) we can very quickly compute the index of both of its children (x * 2 and x 2 +1) and its parent (x // 2). An example is illustrated below: parent 012 3 45 6 7 89 10 11 children Define a function called is_binary_heap0 which takes a Python list as input. The value stored in index position 0 is 0 and is ignored. The values stored in all other index positions of the list are considered to be nodes in the heap. The function should return True if the Python list represents a valid binary heap, otherwise it should return False. For example: Test Result print(is.binary_heap([O, 6, 7, 8, 9, 22, 45, 12, 16, 27, 36])) True print(is_binary_heap ([0, 61)) True
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


