Question: In python code ty Part V: War Variant #1 : Suit Rank (20 points) Complete the function play with.suits (), which takes two arguments, in
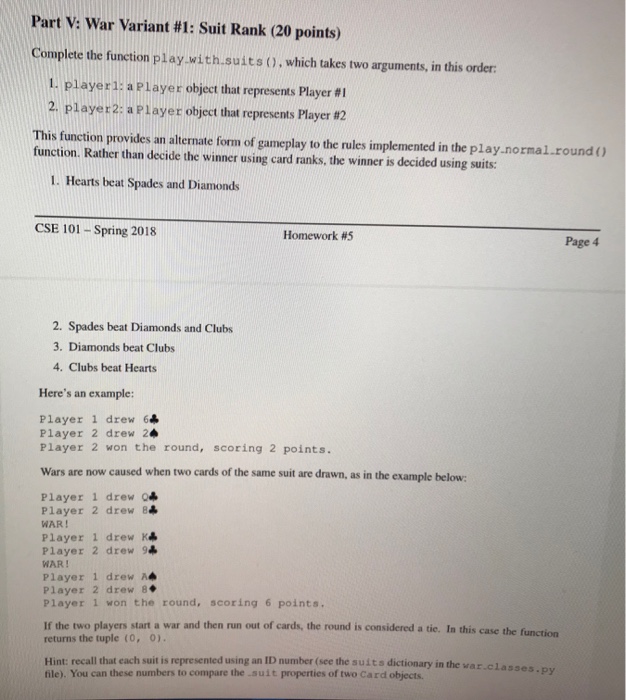
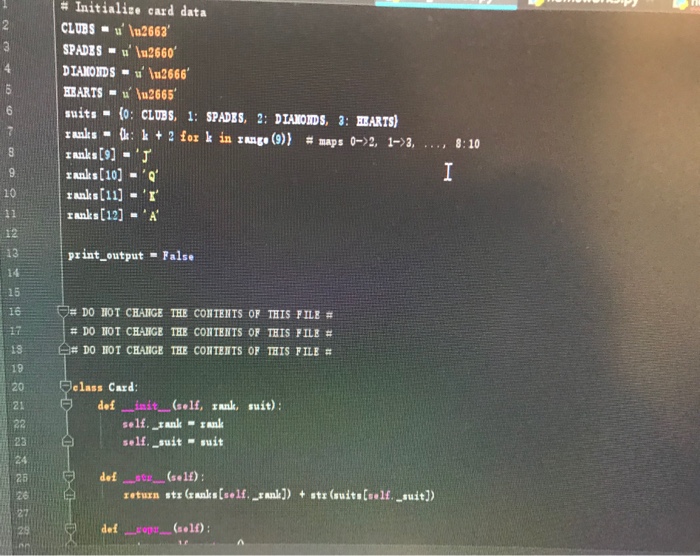
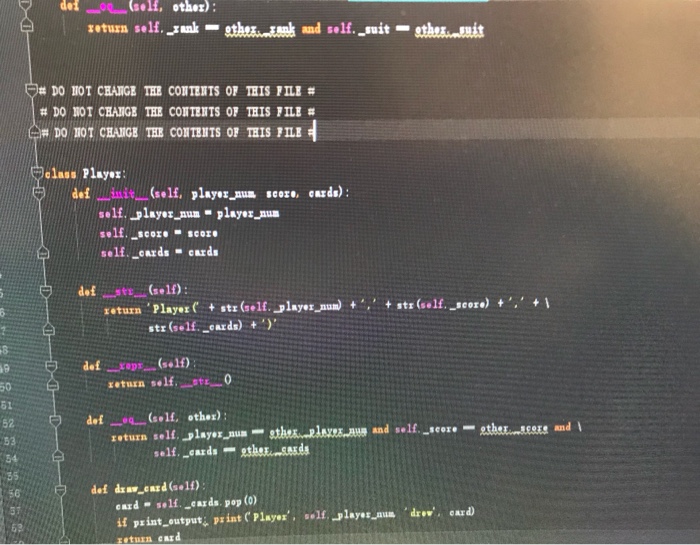
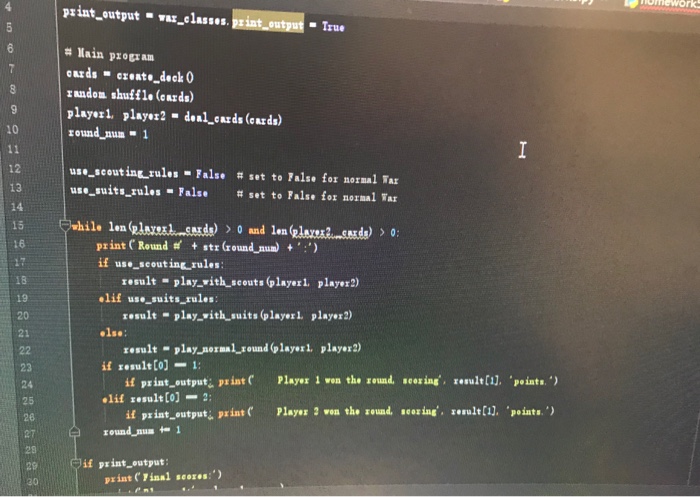
Part V: War Variant #1 : Suit Rank (20 points) Complete the function play with.suits (), which takes two arguments, in this order 1. player 1: a Player object that represents Player #1 2, player 2: a Player object that represents Player #2 This function provides an alternate form of gameplay to the rules implemented in the play.normal.round) function. Rather than decide the winner using card ranks, the winner is decided using suits: in the play.normal.round () 1. Hearts beat Spades and Diamonds CSE 101 -Spring 2018 Hom ework #5 Page 4 2. Spades beat Diamonds and Clubs 3. Diamonds beat Clubs 4. Clubs beat Hearts Here's an example: Player 1 drew 6& Player 2 drew 24 Player 2 won the round, scoring 2 points. Wars are now caused when two cards of the same suit are drawn, as in the example below Player 1 drew Q Player 2 drew 84 WAR! Player 1 drew K4 Player 2 drew 94 WAR! Player 1 drew A4 Player 2 drew 8 Player 1 won the round, scoring 6 points. If the two players start a war and then run out of cards, the round is considered a tie. In this case the function returns the tuple (0, 0) Hint: recall that each suit is represented using an ID number (see the suits dictionary in the war.clas file). You can these numbers to compare the suit properties of two Card objects. war classes.py
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


