Question: IN Python eApprox (n) compute e to n 2 1 significant digits, using Bernoulli's formula k-+00 and a while loop. In this question, we will
IN Python
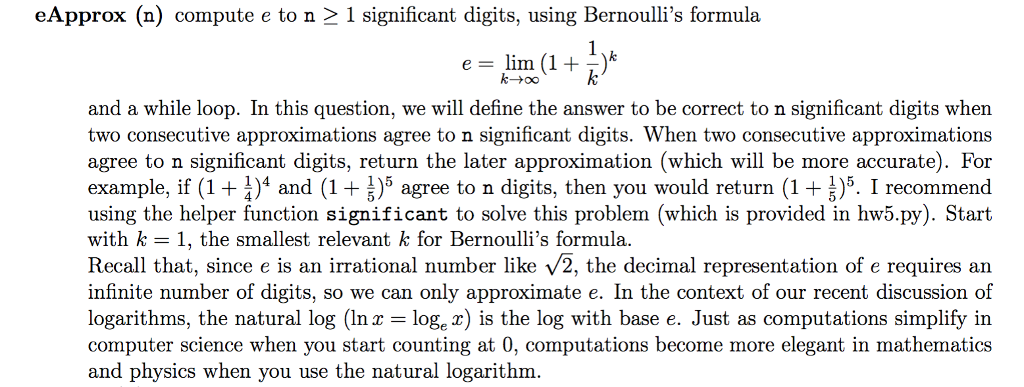
eApprox (n) compute e to n 2 1 significant digits, using Bernoulli's formula k-+00 and a while loop. In this question, we will define the answer to be correct to n significant digits when two consecutive approximations agree to n significant digits. When two consecutive approximations agree to n significant digits, return the later approximation (which will be more accurate). For example, if (1 + 4 and (1 + 5 agree to n digits, then you would return (1+ 5. I d using the helper function significant to solve this problem (which is provided in hw5.py). Start with k- 1, the smallest relevant k for Bernoulli's formula Recall that, since e is an irrational number like /2, the decimal representation of e requires an infinite number of digits, so we can only approximate e. In the context of our recent discussion of logarithms, the natural log (In x -log, r) is the log with base e. Just as computations simplify in computer science when you start counting at 0, computations become more elegant in mathematics and physics when you use the natural logarithm reconmen eApprox (n) compute e to n 2 1 significant digits, using Bernoulli's formula k-+00 and a while loop. In this question, we will define the answer to be correct to n significant digits when two consecutive approximations agree to n significant digits. When two consecutive approximations agree to n significant digits, return the later approximation (which will be more accurate). For example, if (1 + 4 and (1 + 5 agree to n digits, then you would return (1+ 5. I d using the helper function significant to solve this problem (which is provided in hw5.py). Start with k- 1, the smallest relevant k for Bernoulli's formula Recall that, since e is an irrational number like /2, the decimal representation of e requires an infinite number of digits, so we can only approximate e. In the context of our recent discussion of logarithms, the natural log (In x -log, r) is the log with base e. Just as computations simplify in computer science when you start counting at 0, computations become more elegant in mathematics and physics when you use the natural logarithm reconmen
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


