Question: In scenario 2, the table depicts combinations A, B, C, D and E of coffee and lasagne to which Danelle is indifferent. With reference to
In scenario 2, the table depicts combinations A, B, C, D and E of coffee and lasagne to which Danelle is indifferent. With reference to the indifference theory with coffee on the vertical axis and lasagne on the horizontal axis, answer the following questions:
4.1. The indifference curve for the consumer has a negative slope. Explain what the
negative slope implies if Danelle moves from point A to point B.
4.2. Based on the information regarding the price of the two products consumed by Danelle
and her daily income, answer the following questions on Danelle's budget line
illustrated below.
4.2.1. Verify that the points of intersection with the axes depicted in the diagram above
are correct. Show all calculations to substantiate your answer.
4.2.2. According to Danelle, the slope of the budget line has a value of 0.45. Do you
agree with Danelle? Justify your answer.
4.3. The consumer is in equilibrium where the highest indifference curve just touches the
budget line. With reference to consumer equilibrium and the indifference theory, study
the graph below and then answer the questions that follow.
4.3.1. With reference to the inward swivel of the budget line in the diagram above, did
the price of lasagne increase from R30 to R45 or decrease from R30 to R15?
Show all calculations to substantiate your answer.
4.3.2. Explain the impact of the price change on Danelle's consumer equilibrium.
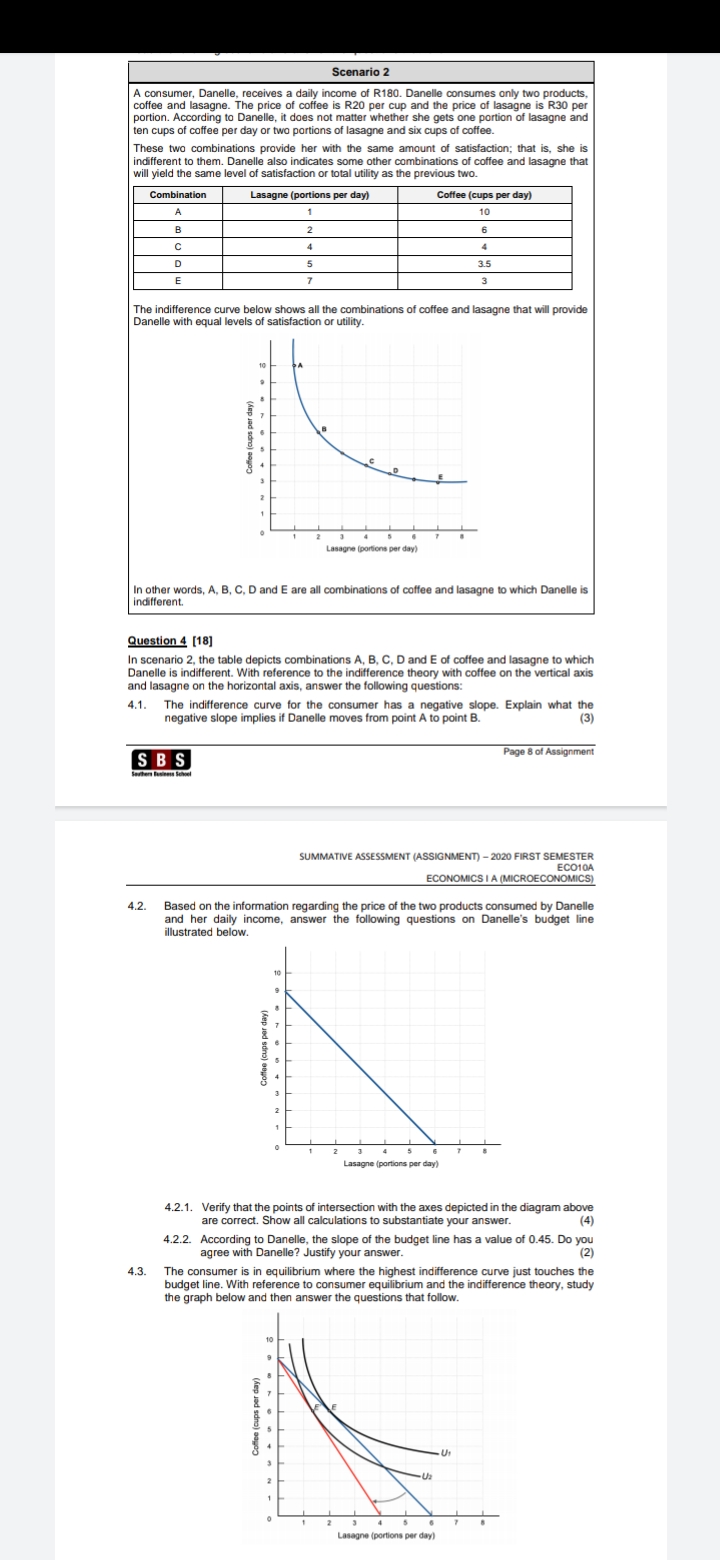
Scenario 2 A consumer, Danelle, receives a daily income of R180. Danelle consumes only two products, coffee and lasagne. The price of coffee is R20 per cup and the price of lasagne is R30 per portion. According to Danelle, it does not matter whether she gets one portion of lasagne and ten cups of coffee per day or two portions of lasagne and six cups of coffee. These two combinations provide her with the same amount of satisfaction; that is, she is indifferent to them. Danelle also indicates some other combinations of coffee and lasagne that will yield the same level of satisfaction or total utility as the previous two. Combination Lasagne (portions per day) Coffee (cups per day) A 10 B 6 C 4 D 5 3.5 E 7 3 The indifference curve below shows all the combinations of coffee and lasagne that will provide Danelle with equal levels of satisfaction or utility. Coffee (cups per day) In other words, A, B, C, D and E are all combinations of coffee and lasagne to which Danelle is indifferent. Question 4 [18] In scenario 2, the table depicts combinations A, B, C, D and E of coffee and lasagne to which Danelle is indifferent. With reference to the indifference theory with coffee on the vertical axis and lasagne on the horizontal axis, answer the following questions: 4.1. The indifference curve for the consumer has a negative slope. Explain what the negative slope implies if Danelle moves from point A to point B. (3) SBS Page 8 of Assignment SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT (ASSIGNMENT) - 2020 FIRST SEMESTER ECO10A ECONOMICS I A (MICROECONOMICS) 4.2. Based on the information regarding the price of the two products consumed by Danelle and her daily income, answer the following questions on Danelle's budget line illustrated below. Coffee (cups per day) Lasagne (portions per day) 4.2.1. Verify that the points of intersection with the axes depicted in the diagram above are correct. Show all calculations to substantiate your answer. (4) 4.2.2. According to Danelle, the slope of the budget line has a value of 0.45. Do you agree with Danelle? Justify your answer. (2) 4.3. The consumer is in equilibrium where the highest indifference curve just touches the budget line. With reference to consumer equilibrium and the indifference theory, study the graph below and then answer the questions that follow. . 8 Coffee (cups per day) Lasagne (portions per day)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


