Question: In statistics, estimation refers to the process by which one makes inferences about a population or model, based on information obtained from a sample. In






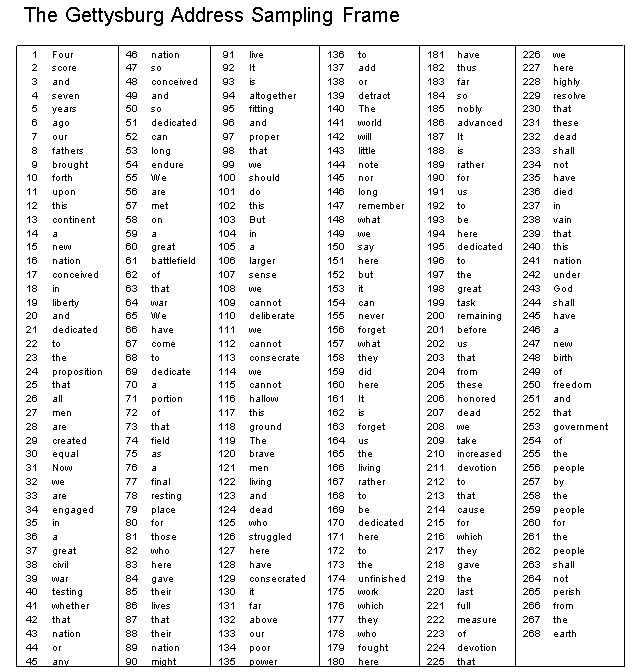
In statistics, estimation refers to the process by which one makes inferences about a population or model, based on information obtained from a sample. In practice, it is often impossible to examine every unit of the population, so data from a subset, or sample, of the population is examined instead. The sample data provides statisticians with the best estimate of the exact "truth" about the population. The "truth" one is searching for in the population is typically a summary measure such as the population mean or population percentage. Summary measures of a population are called parameters. The estimates of these values from sample data are referred to as statistics. When estimating a parameter for an unknown model, there are several qualities that are ideal to have. Two of those qualities are unbiased ness and precision. Both of these qualities describe the estimation or sampling method used. You will examine unbiased ness in this activity and precision in up coming activities. Unbiasedness Unbiased ness is a quality that indicates that the estimation method used produces a distribution of the estimated parameter that is neither systematically too large nor too small. To illustrate this, consider the following two targets which show the locations of five darts thrown overhanded (target on the left) and underhanded (target on the right). Both throwing methods, under- and overhanded, would be unbiased. If you examine the set of throws as a whole on the target on the left, they "average out" to be on center. Now examine the throws on the target on the right. Again, even though none of the darts thrown hit the center exactly, as a whole. the five darts "average out" to have "hit" the center. Now compare this with the targets below in which the darts were thrown under- and overhanded while the thrower had closed her eyes. (Not a good idea when throwing darts!)In both targets, the throwing method would be considered biased. On "average", the throws did not hit the center of the target. It is important to note that in examining the dart throwing methods, you used the distribution of throws to judge whether the throwing method was unbiased. Similarly, in judging whether an estimation or sampling method is unbiased, you will have to examine a distribution of the estimates produced using that method. Does the sampling method used impact whether the estimation is unbiased? To help answer this research question, you are going to compare two different sampling methods using the population of 260 words in the passage on the following page. The passage is, of course, Lincoln's Gettysburg Address, given November 19, 1863 on the battlefield near Gettysburg, PA. Four score and seven years ago, our fathers brought forth upon this continent a new nation: conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal Nowwe are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of that field as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this But, in a larger sense, we cannot dedicate, we cannot consecrate, we cannot hallow this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember, what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here It is for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us, that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion, that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain, that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom, and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.The goal in many studies is to provide information about some characteristic of a population. For example, you may want to say something about the percentage of Americans who would support a piece of legislation. Or, you may want to provide information about the average amount of time University of Minnesota students take to graduate. One potential solution to obtain such information would be to collect the necessary data from every member of the target population. In many studies, however, it may not be feasible given time and money constraints to collect data from each member of the population. In these cases, it is only possible to consider data collected for a smaller subset, or sample from that population. In these cases, the characteristic of the population would be estimated from the sample data and inferences would be drawn about the population. The key is then to carefully select the sample so that the results estimated from the sample are representative of the characteristic in the larger population. The population is the entire collection of who orwhat (e.g. , the observational units) that you would like to draw inferences about. A sample is a subset of observational units from the population. Choose ten words in the text of the Gettysburg Address such that the ten words you select constitute a epresentative sample (1.e., have the same characteristics) of the entire passage. 1. Record the ten words you chose and record the length (number of letters not including punctuation) for each of the ten words in your sample. Word LengthWhen the sampling method produces characteristics of the sample that systematically differ from those characteristics of the population, you say that the sampling method is biased. To try to eliminate potential biases, it is better to take a random sample. This should create a representative sample, no matter what variable is focused on. Humans are not very good "random samplers", so it is important to use other techniques to do the sampling for us.2. Describe how your sample is representative of the 260 words in the population. 3. Determine the average (mean) word length for your ten words. This sample average is an estimate of the average word length in the population. Add your sample estimate to the case table on the instructor's computer. 4. The actual population average word length based on all 268 words is 4.3 letters. For how many groups in your class did the sample estimate exceed the population average? What proportion of the class is this? 5. Based on your answer to the previous question, is a sample estimate just as likely to be above the population average as it is to be below the population average?Simple Random Sampling A simple random sample (SRS) is a specific type of random sample. It gives every observational unit in the population the same chance of being selected. In fact, it gives every sample of size n the same chance of being selected. In this example you want every possible subset of ten words that could be sampled to have the same probability of being selected. The first step in drawing a simple random sample is to obtain a sampling frame or a list of each member of the population. Then, you can use software to randomly select a sample from the sampling frame. We have already prepared a sampling frame of the words in the Gettysburg Address for you. Use Random.org to Draw a SRS 6. Generate 10 random numbers between 1 and 268, either from your calculator or a website such as Random. org (https://www.random. org/integers/). 7. Draw a simple random sample of ten words by matching the ten numbers to the Gettysburg Address sampling frame on the last page. Record the ten randomly sampled words and their lengths: Word LengthB. Compute the mean word length for your ten randomly sampled words. Record the mean below. Add your sample estimate to the case table on the instructor's computer. 9. The actual population average word length based on all 268 words is 4.3 letters. For how many groups in your class did the sample estimate exceed the population average? What proportion of the class is this? 10. Based on your answer to the previous question, is a sample estimate just as likely to be above the population average as it is to be below the population average? 11. If the sampling method is unbiased the estimates of the population average should be centered 'around" the population average word length of 4.3. Does simple random sampling produce an unbiased estimate of the population average? Explain. 12. What can you conclude about the importance of random selection in the sampling process?The Gettysburg Address Sampling Frame 46 nation 31 live 136 to 181 have 226 Four 137 add 182 thus 227 here score 47 92 It 93 183 far 228 highly and 48 conceived 138 49 and 94 altogether 139 detract 184 50 AZZ resolve seven 185 230 that years 50 95 fitting 140 The nobly 141 world 186 advanced 231 these 6 DE 51 dedicated 96 QUE 87 It 232 dead 52 car 97 proper 142 that 143 little 188 233 shall fathers 53 long 144 note 189 rather 234 not brought 54 endure 55 We 100 should 145 nor 190 for 235 have 10 forth 191 US 236 died 11 upon 56 101 do 146 are long to 237 in 12 this 57 met 102 this 147 remember 58 103 But 148 what be 238 vain 13 continent on 59 104 in 149 194 239 that 14 E 150 say 195 dedicated 240 this 15 new great 105 16 31 battlefield 106 larger 151 here 196 to 241 nation nation conceived of 107 sense 152 but 197 the 242 under 17 153 it 198 great 243 God 18 in 63 that 108 244 liberty 54 JEM 109 cannot 154 UEO 199 task shall 19 1 10 deliberate 155 never 200 remaining 245 have 20 and 156 forget 201 before 246 21 dedicated 56 have 111 157 what 202 US 247 new 22 ti come 1 12 cannot 113 158 23 to onsecrate they 203 that 248 birth the 24 39 159 did 204 from 249 proposition dedicate 114 70 205 these 250 freedom 25 that E 115 cannot 160 here honored 251 and 26 71 portion 116 hallow 161 It 206 72 of 117 thiE 162 207 dead 252 that 27 men 253 government 28 are 73 that 118 ground 163 forget 208 254 of 29 created 74 field 119 The 164 US 209 take the 30 equal 75 as 120 brave 165 the 210 increased 255 166 living 211 devotion 256 people 31 Now 76 E 121 men 77 final 122 living 167 rather 212 to 257 by 32 258 the 33 78 resting 123 and 168 to 213 that 79 place 124 dead 169 be 214 cause 259 people 34 engaged 170 260 for 35 dedicated 215 for in 30 for 125 who 36 31 those 126 struggled 171 here 216 which 261 the 262 people 37 127 here 217 who 172 to they great 32 173 the 218 gave 263 shall 38 chril 83 here 128 have 219 the 264 not 39 34 gave 129 174 unfinished IEM consecrated 175 work 220 last 265 perish 40 testing 35 the ir 130 it 221 full 41 176 which from whether 36 lives 131 far the 42 that 37 that 132 above 177 they 222 measure 267 43 38 their 133 OUT 178 who 223 01 268 nation 39 devotion 44 nation 134 poor 179 fought 224 135 power 180 225 that 45 QUE might here
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


