Question: In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, what does the variable R represent? Multiple Choice 0 The annually compounded risk-free rate of return 0 The continuously
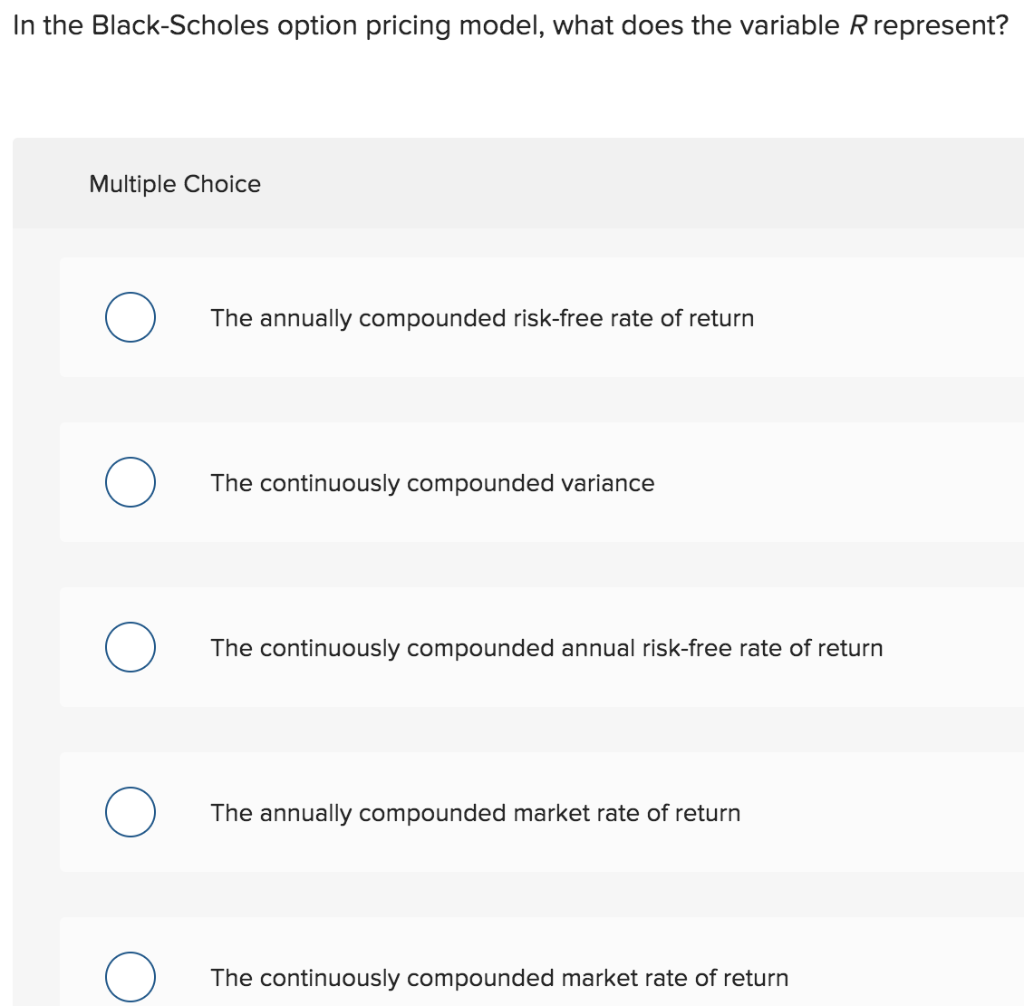
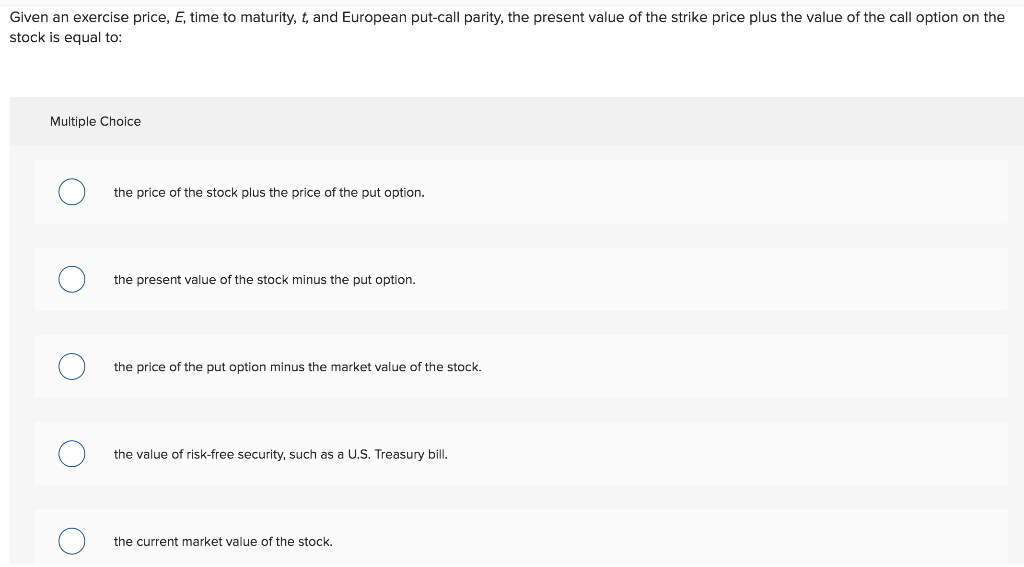
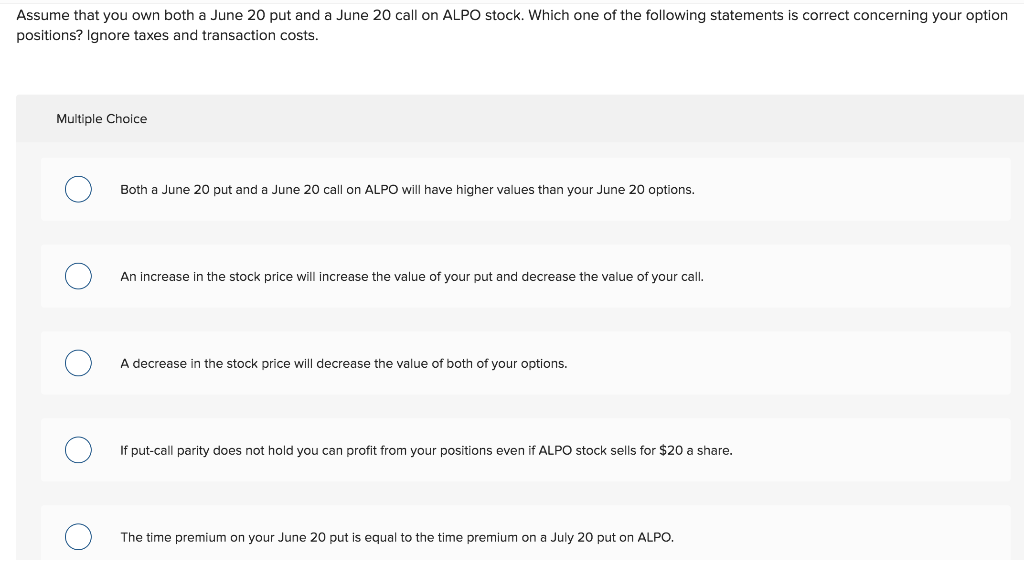
In the Black-Scholes option pricing model, what does the variable R represent? Multiple Choice 0 The annually compounded risk-free rate of return 0 The continuously compounded variance 0 The continuously compounded annual risk-free rate of return 0 The annually compounded market rate of return 0 The continuously compounded market rate of return Given an exercise price, E, time to maturity, t, and European put-call parity, the present value of the strike price plus the value of the call option on the stock is equal to: Multiple Choice the price of the stock plus the price of the put option. 0 the present value of the stock minus the put option. 0 the price of the put option minus the market value of the stock. 0 the value of risk-free security, such as a U.S. Treasury bill. 0 the current market value of the stock. Assume that you own both a June 20 put and a June 20 call on ALPO stock. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning your option positions? Ignore taxes and transaction costs. Multiple Choice 0 O Both a June 20 put and a June 20 call on ALPO will have higher values than your June 20 options. 0 An increase in the stock price will increase the value of your put and decrease the value of your call. 0 A decrease in the stock price will decrease the value of both of your options. 0 C) If put-call parity does not hold you can profit from your positions even if ALPO stock sells for $20 a share. 0 The time premium on your June 20 put is equal to the time premium on a July 20 put on ALPO
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


