Question: In the caplet example 23.6, construct the synthetic caplet using the three- period zero and mma (the caplet has a strike rate of k 0.04
-
In the caplet example 23.6, construct the synthetic caplet using the three- period zero and mma (the caplet has a strike rate of k 0.04 or 4 percent). Show that the cost of construction is 0.003, the same as that with the two- period zero-coupon bond.(Attached pictures is example 23.6)
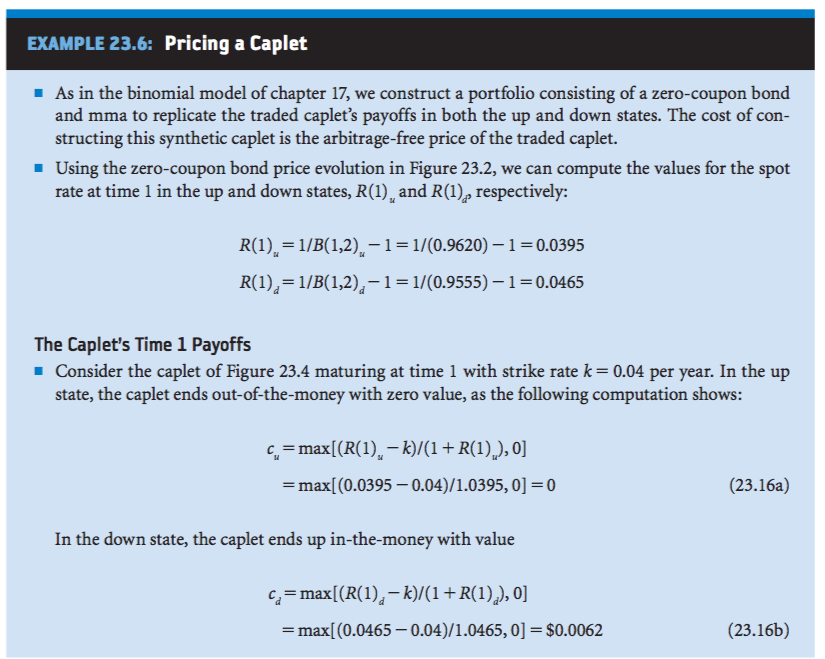
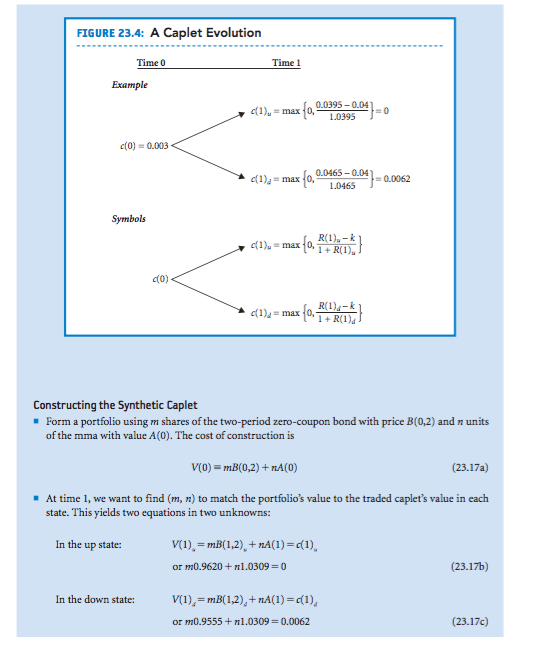
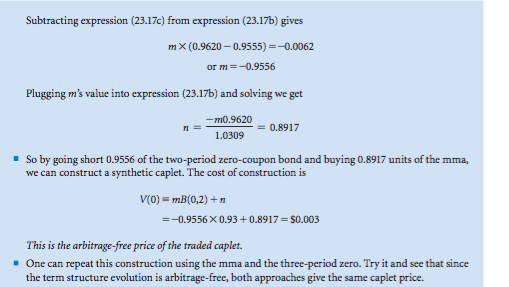
EXAMPLE 23.6: Pricing a Caplet - As in the binomial model of chapter 17, we construct a portfolio consisting of a zero-coupon bond and mma to replicate the traded caplet's payoffs in both the up and down states. The cost of con- structing this synthetic caplet is the arbitrage-free price of the traded caplet. Using the zero-coupon bond price evolution in Figure 23.2, we can compute the values for the spot rate at time 1 in the up and down states, R(1), and R(1 respectively: R(1) 1/B(,2)-1-1/0.9620)-10.0395 R(),-1/B(1,2),11/(0.9555)-1-0.0465 The Caplet's Time 1 Payoffs Consider the caplet of Figure 23.4 maturing at time 1 with strike rate k 0.04 per year. In the up state, the caplet ends out-of-the-money with zero value, as the following computation shows: ,max[(R()-k)+R(I)),O max[(0.0395-0.04)/1.0395,0] 0 (23.16a) In the down state, the caplet ends up in-the-money with value c. = max[(R(1), _ k)/(1 + R(1),), 0] max[(0.0465-0.04)/1.0465, 0] $0.0062 (23.16b) FIGURE 23.4: A Caplet Evolution Time 0 Time 1 Example r(1), = max fo, 0.0395-a04 c(0) 0.003 0.0465-0.04 c(1) mx00465 Symbols 1 +R1) Constructing the Synthetic Caplet Form a portfolio using m shares of the two-period zero-coupon bond with price B(0,2) and n units of the mma with value A(0). The cost of construction is V(0) = m1B(0,2) + n 4(0) (23.17a) At time 1, we want to find (m, n) to match the portfolio's value to the traded caplet's value in each state. This yields two equations in two unknowns: In the up state or m0.9620 + 1.0309 0 (23.17b) In the down state: or '720.9555 + n 1.0309 0.0062 (23.17c) Subtracting expression (23.17c) from expression (23.17b) gives m (0.9620-0.9555) =-0.0062 or m =-0.9556 Plugging m's value into expression (23.17b) and solving we get 0.9620 1.0309 n = 0.8917 So by going short 0.9556 of the two-period zero-coupon bond and buying 0.8917 units of the mma, we can construct a synthetic caplet. The cost of construction is V(0) mB(0,2)+ --0.9556X 0.93+0.8917-$0.003 This is the arbitrage-free price of the traded caplet. the term structure evolution is arbitrage-free, both approaches give the same caplet price. EXAMPLE 23.6: Pricing a Caplet - As in the binomial model of chapter 17, we construct a portfolio consisting of a zero-coupon bond and mma to replicate the traded caplet's payoffs in both the up and down states. The cost of con- structing this synthetic caplet is the arbitrage-free price of the traded caplet. Using the zero-coupon bond price evolution in Figure 23.2, we can compute the values for the spot rate at time 1 in the up and down states, R(1), and R(1 respectively: R(1) 1/B(,2)-1-1/0.9620)-10.0395 R(),-1/B(1,2),11/(0.9555)-1-0.0465 The Caplet's Time 1 Payoffs Consider the caplet of Figure 23.4 maturing at time 1 with strike rate k 0.04 per year. In the up state, the caplet ends out-of-the-money with zero value, as the following computation shows: ,max[(R()-k)+R(I)),O max[(0.0395-0.04)/1.0395,0] 0 (23.16a) In the down state, the caplet ends up in-the-money with value c. = max[(R(1), _ k)/(1 + R(1),), 0] max[(0.0465-0.04)/1.0465, 0] $0.0062 (23.16b) FIGURE 23.4: A Caplet Evolution Time 0 Time 1 Example r(1), = max fo, 0.0395-a04 c(0) 0.003 0.0465-0.04 c(1) mx00465 Symbols 1 +R1) Constructing the Synthetic Caplet Form a portfolio using m shares of the two-period zero-coupon bond with price B(0,2) and n units of the mma with value A(0). The cost of construction is V(0) = m1B(0,2) + n 4(0) (23.17a) At time 1, we want to find (m, n) to match the portfolio's value to the traded caplet's value in each state. This yields two equations in two unknowns: In the up state or m0.9620 + 1.0309 0 (23.17b) In the down state: or '720.9555 + n 1.0309 0.0062 (23.17c) Subtracting expression (23.17c) from expression (23.17b) gives m (0.9620-0.9555) =-0.0062 or m =-0.9556 Plugging m's value into expression (23.17b) and solving we get 0.9620 1.0309 n = 0.8917 So by going short 0.9556 of the two-period zero-coupon bond and buying 0.8917 units of the mma, we can construct a synthetic caplet. The cost of construction is V(0) mB(0,2)+ --0.9556X 0.93+0.8917-$0.003 This is the arbitrage-free price of the traded caplet. the term structure evolution is arbitrage-free, both approaches give the same caplet price
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


