Question: In the following problem sets, we will use this expanded set of opcodes for our hypothetical machine: 0001 = Load AC from memory (LOAD) 0010

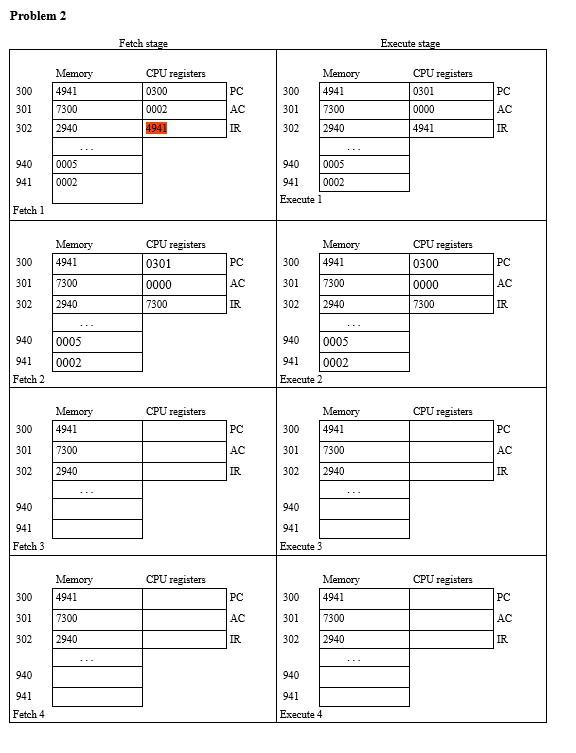
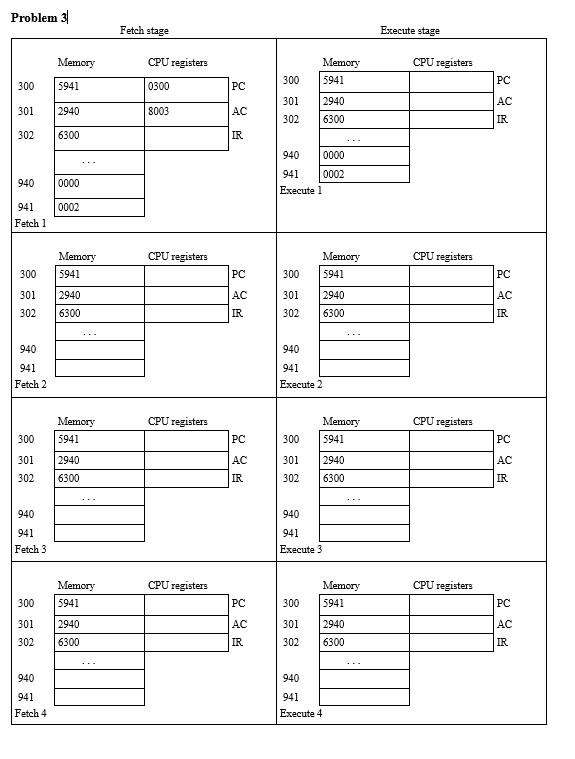
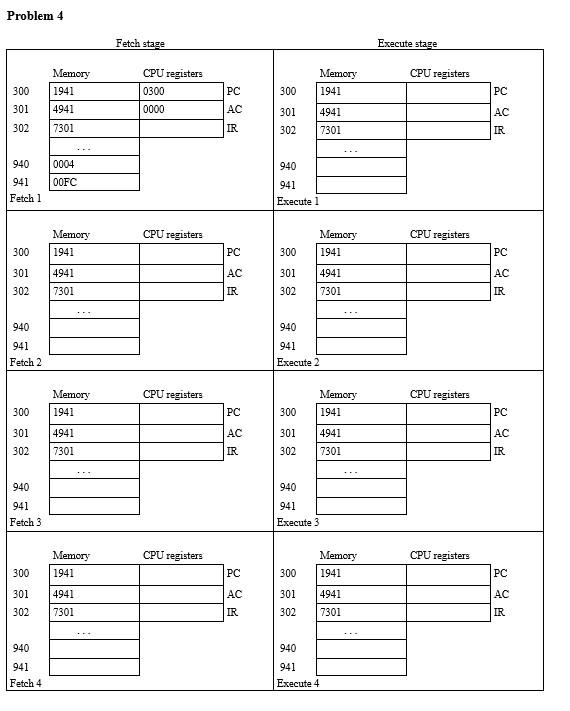
In the following problem sets, we will use this expanded set of opcodes for our hypothetical machine: 0001 = Load AC from memory (LOAD) 0010 = Store AC to memory (STORE) 0100 = Subtract memory from AC (result in AC) (SUB) 0101 = Add to AC from memory (result in AC) (ADD) 0110 = Jump to address, absolute jump (JMP) 0111 = Jump to address if result was 0. conditional jump (JMPZ) 1000 = Jump to address if result was negative, conditional jump (JMPN) Perform program fetch/execute cycles for the following initial memory and program states. Here are some notes/hints and clarifications for how to perform these hypothetical machine simulations by hand: 1. When executing the machine instructions, if the PC ends up referencing a memory address that you were not given values for, then you are done. This means that for some of the questions you may only fill in the first 6 of the 8 cells. But for others, like if there is an infinite loop, if you fill up all 8 cells you don't have to do any more work, you are done at that point. 2. It is possible for one or more of the questions to end up with a negative number as your result in the accumulator. If you read our textbook, and look at the figure, there is a definition for our hypothetical machine of how integers are to be represented. This integer representation uses a simple sign bit for the most significant bit, and the sign bit should be 1 to indicate a negative integer number. If you get a negative number in your AC, make sure you correctly represent it using the defined integer representation format for our hypothetical machine. It should be displayed as a hexadecimal number in the answer you give for the problem set. 3. All values given in the memory and registers for the problem are hexadecimal (base 16), that represent 16 bits of information. You should represent all results as hexadecimal values as well, including signed integers. So for example, you should not result -1 if your result is negative 1, but the signed integer representation of this value according to our hypothetical machine, 0x8001 4. The jump if zero instruction performs a conditional jump depending on if the previous result (the value in the accumulator) was zero or nonzero. Only jump to the indicated address if the result was 0. Likewise the jump if negative instruction depends on the previous accumulator result, and the jump should occur only if the previous accumulator result was a negative number. Problem 2 Fetch stage Execute stage Memory 4941 CPU registers 0300 Memory 4941 300 PC 300 301 CPU registers 0301 0000 PC AC 301 0002 AC 7300 7300 2940 302 4941 IR 302 2940 4941 IR 940 940 941 0005 0002 0005 941 0002 Execute 1 Fetch1 Memory 4941 CPU registers 0301 Memory 4941 CPU registers 0300 300 PC 300 PC 301 7300 AC 301 7300 AC 0000 7300 0000 7300 302 2940 IR 302 2940 IR 940 0005 0002 941 Fetch 2 940 0005 941 0002 Execute 2 CPU registers CPU registers Memory 4941 Memory 4941 300 PC 300 PC 301 7300 AC 301 7300 AC 302 2940 IR 302 2940 IR 940 940 941 941 Fetch 3 Execute 3 CPU registers CPU registers Memory 4941 Memory 4941 300 PC 300 PC 301 7300 AC 301 7300 AC 302 2940 IR 302 2940 IR 940 940 941 941 Fetch 4 Execute 4 Problem 31 Fetch stage Execute stage Memory CPU registers CPU registers Memory 5941 300 5941 300 PC 0300 PC 301 2940 8003 AC 301 302 2940 6300 AC IR 302 6300 IR 940 0000 940 0000 941 0002 Execute 1 0002 941 Fetch 1 CPU registers CPU registers Memory 5941 Memory 5941 300 PC 300 PC 2940 AC 301 302 301 302 2940 6300 AC IR 6300 IR 940 940 941 Fetch 2 941 Execute 2 CPU registers CPU registers Memory 5941 Memory 5941 300 PC 300 PC AC AC 301 302 2940 6300 301 302 2940 6300 IR IR 940 940 941 Fetch 3 941 Execute 3 CPU registers CPU registers Memory 5941 Memory 5941 300 300 PC 301 302 301 PC AC IR 2940 6300 2940 6300 AC IR 302 940 940 941 Fetch 4 941 Execute 4 Problem 4 Fetch stage Execute stage CPU registers Memory 1941 CPU registers 0300 0000 Memory 1941 PC 300 300 301 PC 4941 AC 301 302 4941 7301 AC IR 302 7301 IR 940 940 941 Fetch 1 0004 00FC 941 Execute 1 CPU registers CPU registers Memory 1941 Memory 1941 300 PC 300 PC AC 301 4941 AC 301 302 4941 7301 IR 302 7301 IR 940 940 941 941 Execute 2 Fetch 2 CPU registers CPU registers Memory 1941 Memory 1941 300 PC 300 PC AC AC 301 302 4941 7301 301 302 4941 7301 IR IR 940 940 941 Fetch 3 941 Execute 3 CPU registers CPU registers Memory 1941 Memory 1941 300 PC 300 PC AC 301 4941 AC 301 302 4941 7301 IR 302 7301 IR 940 940 941 941 Fetch 4 Execute 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


