Question: In this activity, you'll calculate a probability and use it to predict the result of repeating a simple chance-based trial many times. You are playing
In this activity, you'll calculate a probability and use it to predict the result of repeating a simple chance-based trial many times.
You are playing a game called Odd Odds.In the game, one player rolls two six-sided dice.The player gets points if the product of the two numbers rolled is odd.So, success in the game depends on the chances of getting an odd number for the result.
Question 1
Find the number of outcomes in the sample space,n(S), of the trial of this game.
Question 2
List and count all the outcomes for eventE, in which the product of the two numbers rolled is odd.
Question 3
Find the probability of getting an odd number. Calculate the probability,P(E), of eventE, in which the product of the two numbers rolled is odd.Write the probability as a fraction reduced to lowest terms and as a decimal correct to two places.
Question 4
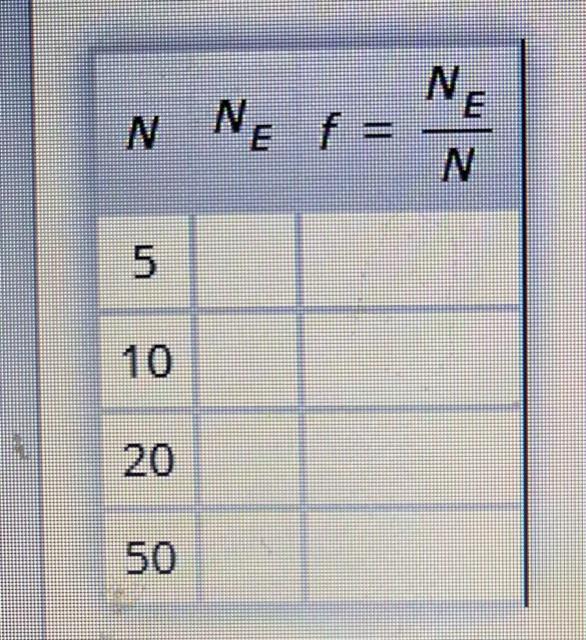
What happens when the player performs the trial (rolling two dice)Ntimes?Perform the trial by using the "Dice Roller" in thissimulator.Perform the simulationNtimes for these values of N:5, 10, 20, and 50.In this simulation, you will roll two dice (or, strictly speaking, click the button that simulates the roll), write down the numbers shown on the faces (a pair of numbers obtained on each roll is a outcome), and calculate the product of the two numbers for each roll.
Nis the number of times you roll the two dice.In the table below, fill in the value ofNE, whereNEis the number of times eventE(the product of the two numbers rolled is odd) occurs.
Then calculate the fraction of times it occurs,f=NEN
, correct to two decimal places.
NE N Nef = N 5 10 20 50
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


