Question: In this case study, your task is to compare hill-climbing search and simulated annealing as local search algorithms to solve the 8-puzzle problem. For example,

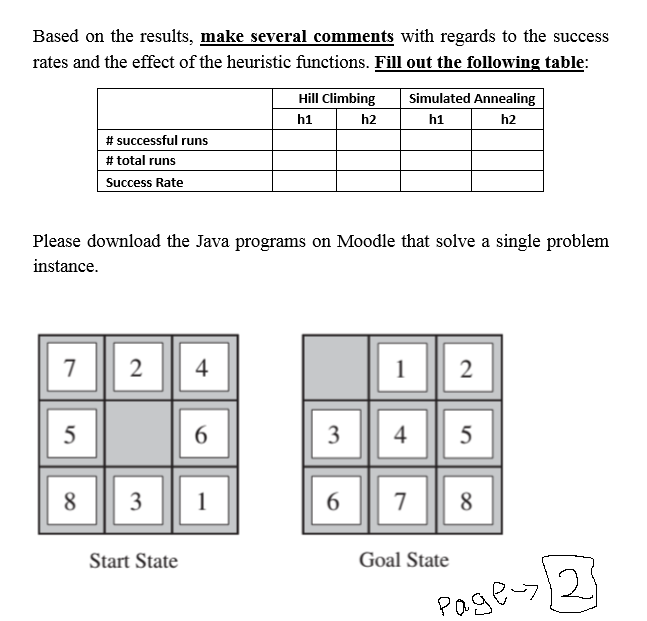
In this case study, your task is to compare hill-climbing search and simulated annealing as local search algorithms to solve the 8-puzzle problem. For example, consider a start state as in the figure below. The goal state is also shown in the figure. We will use the following h of misplaced tiles h2 is the sum of the horizontal and vertical distances of the tiles from their goal positions (this is sometimes called the Manhattan distance) euristics: hl is the number Follow these steps: 1. Using the given start state, run both algorithms using any heuristic 10 times. What do vou observe? Explain (are the returned solution states goal states? Do you get the same solution state every time?). 2. Generate 100000 random initial states 3. Run the hll climbing algorithm on each problem instance using hl. For each run, record if the goal state is reached. 4. Determine the fraction of runs that resulted in a success i.e., the goal state is identified. 5. Repeat Steps 2-4 using h2. 6. Repeat Steps 2-4 using simulated annealing search and h1. 7. Repeat Steps 2-4 using simulated annealing search and h2. Based on the results, make several comments with regards to the success rates and the effect of the heuristic functions. Fill out the following table: Hill Climbing Simulated Annealing h1 h2 h1 h2 # successful runs # total runs Success Rate Please download the Java programs on Moodle that solve a single problem instance. 2 6 Start State Goal State 82 0-7 WCase Study 1 For the Case Study, please refer to: https://github.com/aimacode/aima-java Use eclipse. For setup, refer to: https://github.com/aimacode/aima-java/wiki/AIMA3e-Using-Eclipse-IDE You will edit and run the following file: aima-gui src mainNavalaimalguidemo search\EightPuzzleDemo.java In this case study, your task is to compare hill-climbing search and simulated annealing as local search algorithms to solve the 8-puzzle problem. For example, consider a start state as in the figure below. The goal state is also shown in the figure. We will use the following h of misplaced tiles h2 is the sum of the horizontal and vertical distances of the tiles from their goal positions (this is sometimes called the Manhattan distance) euristics: hl is the number Follow these steps: 1. Using the given start state, run both algorithms using any heuristic 10 times. What do vou observe? Explain (are the returned solution states goal states? Do you get the same solution state every time?). 2. Generate 100000 random initial states 3. Run the hll climbing algorithm on each problem instance using hl. For each run, record if the goal state is reached. 4. Determine the fraction of runs that resulted in a success i.e., the goal state is identified. 5. Repeat Steps 2-4 using h2. 6. Repeat Steps 2-4 using simulated annealing search and h1. 7. Repeat Steps 2-4 using simulated annealing search and h2. Based on the results, make several comments with regards to the success rates and the effect of the heuristic functions. Fill out the following table: Hill Climbing Simulated Annealing h1 h2 h1 h2 # successful runs # total runs Success Rate Please download the Java programs on Moodle that solve a single problem instance. 2 6 Start State Goal State 82 0-7 WCase Study 1 For the Case Study, please refer to: https://github.com/aimacode/aima-java Use eclipse. For setup, refer to: https://github.com/aimacode/aima-java/wiki/AIMA3e-Using-Eclipse-IDE You will edit and run the following file: aima-gui src mainNavalaimalguidemo search\EightPuzzleDemo.java
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


