Question: In this example, you will note that: 1. All internal nodes store operators, 2. Leaf nodes store literals or variables, 3. Each node representing an

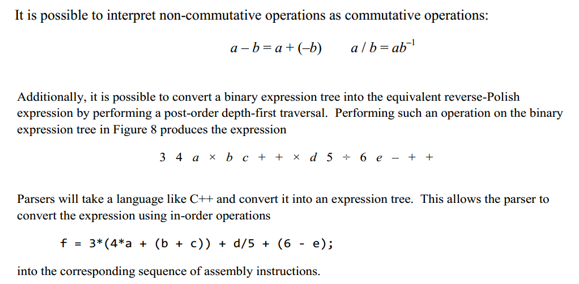
In this example, you will note that: 1. All internal nodes store operators, 2. Leaf nodes store literals or variables, 3. Each node representing an operator has two children 4. The relevance of ordering depends on whether or not the operator is commutative: a. Addition and multiplication are commutative while b. Subtraction and division are not. It is possible to interpret non-commutative operations as commutative operations: a-b= a + (-b) alb= ab! Additionally, it is possible to convert a binary expression tree into the equivalent reverse-Polish expression by performing a post-order depth-first traversal. Performing such an operation on the binary expression tree in Figure 8 produces the expression 34 a b c + + x d 5 + 6 + + Parsers will take a language like C++ and convert it into an expression tree. This allows the parser to convert the expression using in-order operations f = 3*(4*a + (b + c)) + d/5 + (6 - e); into the corresponding sequence of assembly instructions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


