Question: In this exercise you are asked to write a program which generates the following process tre (Scheme 1) Scheme 1: A given process tree The
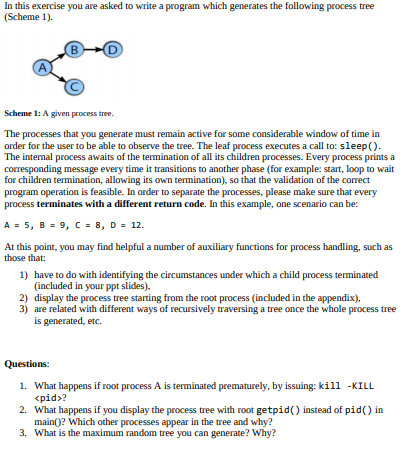
In this exercise you are asked to write a program which generates the following process tre (Scheme 1) Scheme 1: A given process tree The processes that you generate must remain active for some considerable window of time in order for the user to be able to observe the tree. The leaf process executes a call to: sleep) The internal process awaits of the termination of all its children processes. Every process printsa corresponding message every time it transitions to another phase (for example: start, loop to wait for children termination, allowing its own termination), so that the validation of the correct program operation is feasible. In order to separate the processes, please make sure that every process terminates with a different return code. In this example, one scenario can be: At this point, you may find helpful a number of auxiliary functions for process handling, such as those that: 1) 2) have to do with identifying the circumstances under which a child process terminated (included in your ppt slides). display the process tree starting from the root process (included in the appendix), are related with different ways of recursively traversing a tree once the whole process tree is generated, etc. 3) Questions: 1. What happens if root process A is terminated prematurely, by issuing: kill -KILL pid>? 2. What happens if you display the process tree with root getpid() instead of pid) in main? Which other processes appear in the tree and why . What is the maximum random tree you can generate? Why? In this exercise you are asked to write a program which generates the following process tre (Scheme 1) Scheme 1: A given process tree The processes that you generate must remain active for some considerable window of time in order for the user to be able to observe the tree. The leaf process executes a call to: sleep) The internal process awaits of the termination of all its children processes. Every process printsa corresponding message every time it transitions to another phase (for example: start, loop to wait for children termination, allowing its own termination), so that the validation of the correct program operation is feasible. In order to separate the processes, please make sure that every process terminates with a different return code. In this example, one scenario can be: At this point, you may find helpful a number of auxiliary functions for process handling, such as those that: 1) 2) have to do with identifying the circumstances under which a child process terminated (included in your ppt slides). display the process tree starting from the root process (included in the appendix), are related with different ways of recursively traversing a tree once the whole process tree is generated, etc. 3) Questions: 1. What happens if root process A is terminated prematurely, by issuing: kill -KILL pid>? 2. What happens if you display the process tree with root getpid() instead of pid) in main? Which other processes appear in the tree and why . What is the maximum random tree you can generate? Why
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


