Question: In this exercise you will implement a shopping cart using the ArrayList class. The file Item.java contains the definition of a class named Item that
In this exercise you will implement a shopping cart using the ArrayList class. The file Item.java contains the definition of a class named Item that models an item one would purchase (this class was used in an earlier lab). An item has a name, price, and quantity (the quantity purchased). The file Shop.java is an incomplete program that models shopping.
1. Complete Shop.java as follows:
a. Declare and instantiate a variable cart to be an empty ArrayList.
b. Fill in the statements in the loop to add an item to the cart and to print the cart contents (using the default toString in the ArrayList class). Comments in the code indicate where these statements go.
c. Compile your program and run it.
2. You should have observed two problems with using the default printing for the cart object: the output doesnt look very good and the total price of the goods in the cart is not computed or printed. Modify the program to correct these problems by replacing the print statement with a loop that does the following:
a. gets each item from the cart and prints the item
b. computes the total price of the items in the cart (you need to use the getPrice and getQuantity methods of the Item
class). The total price should be printed after the loop.
3. Compile and run your program.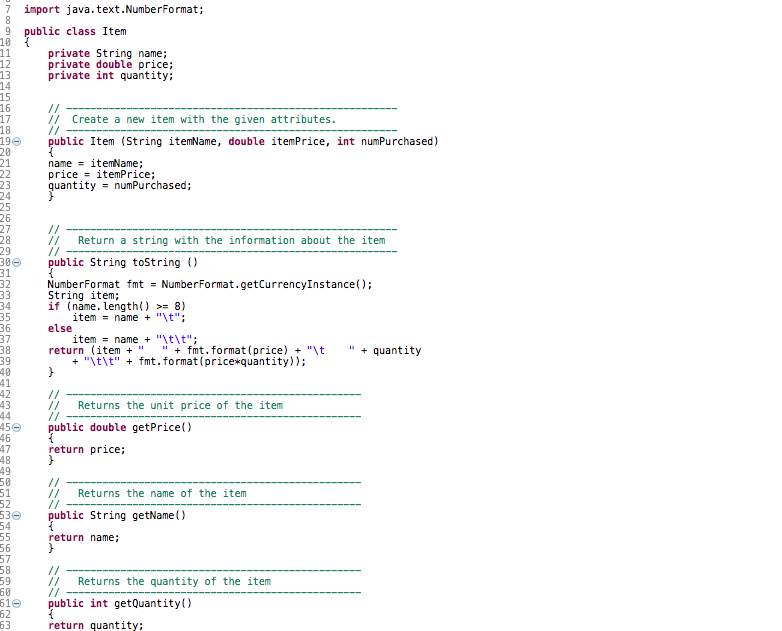
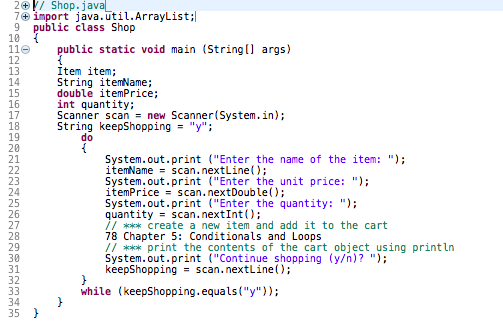
8 18 7 import java.text.Number Format; 9 public class Item 10 { 11 private String name; 12 private double price; 13 private int quantity: 14 15 16 17 11 Create a new item with the given attributes. 19 public Item (String itemName, double itemPrice, int numPurchased) 20 21 name = itemName; 22 price = itemPrice; 23 24 quantity = numPurchased; 25 26 27 28 Return a string with the information about the item 29 300 public String toString() 31 32 Number Format fmt = Number Format.getCurrency Instance(); 33 String item; 34 if (name. length() >= 8) 35 item = name + "\t"; 36 else 37 item = name + "\t\t"; 38 return (item + " " + fmt. format (price) "It + quantity 39 + "\t\t" + fmt.format(price*quantity)); 40 } 41 42 43 Returns the unit price of the item 44 450 public double getPrice) 46 47 return price; 48 } 49 50 51 Returns the name of the item 52 530 public String getName() 54 55 return name; 56 } 57 58 59 Returns the quantity of the item 60 610 public int getQuantity 62 63 return quantity: 2017 Shop,javal 7+ import java.util.ArrayList;/ 9 public class Shop 10 110 public static void main (String[] args) 12 13 Item item; 14 String itemName; 15 double itemPrice; 16 int quantity; 17 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); 18 String keepShopping = "Y"; 19 do 20 { 21 System.out.print ("Enter the name of the item: "); itemName = scan.nextLine(); 23 System.out.print ("Enter the unit price: "); 24 itemPrice = scan.nextDouble(); 25 System.out.print ("Enter the quantity: "); quantity - scan.nextInt(); 27 // *** create a new item and add it to the cart 28 78 Chapter 5: Conditionals and Loops 29 11 *** print the contents of the cart object using println 30 System.out.print ("Continue shopping (y)? "); 31 keepShopping - scan.nextLine(); 32 } 33 while (keepShopping.equals("/")); 34 35 ) 22 26
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


