Question: In this lab, you will need to develop an application to ask for an input integer number (n) from the user. Then the program should



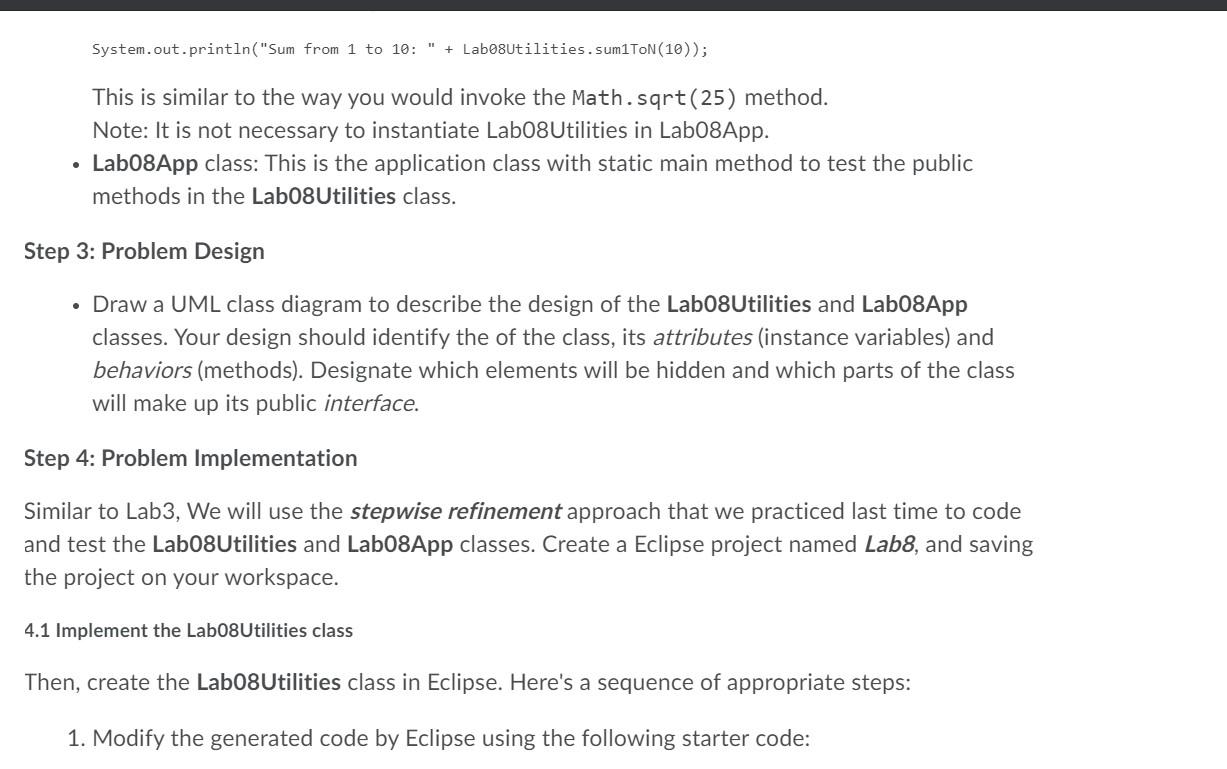


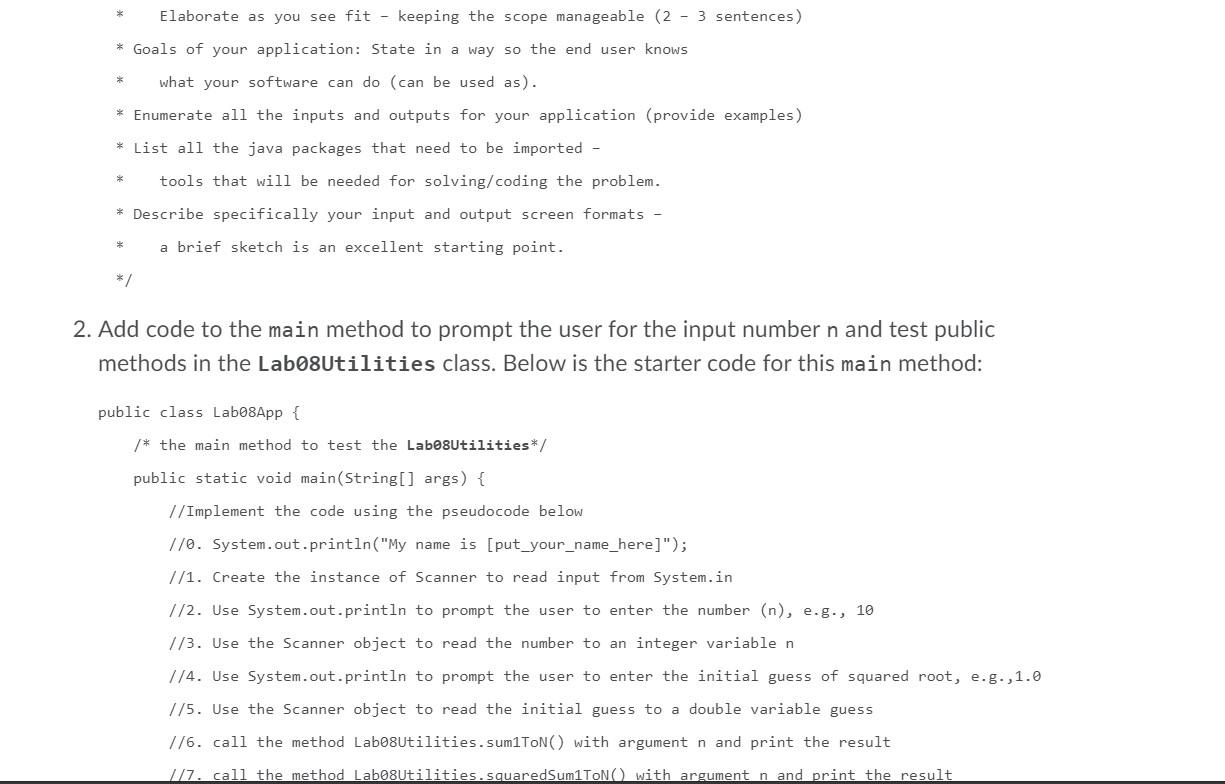
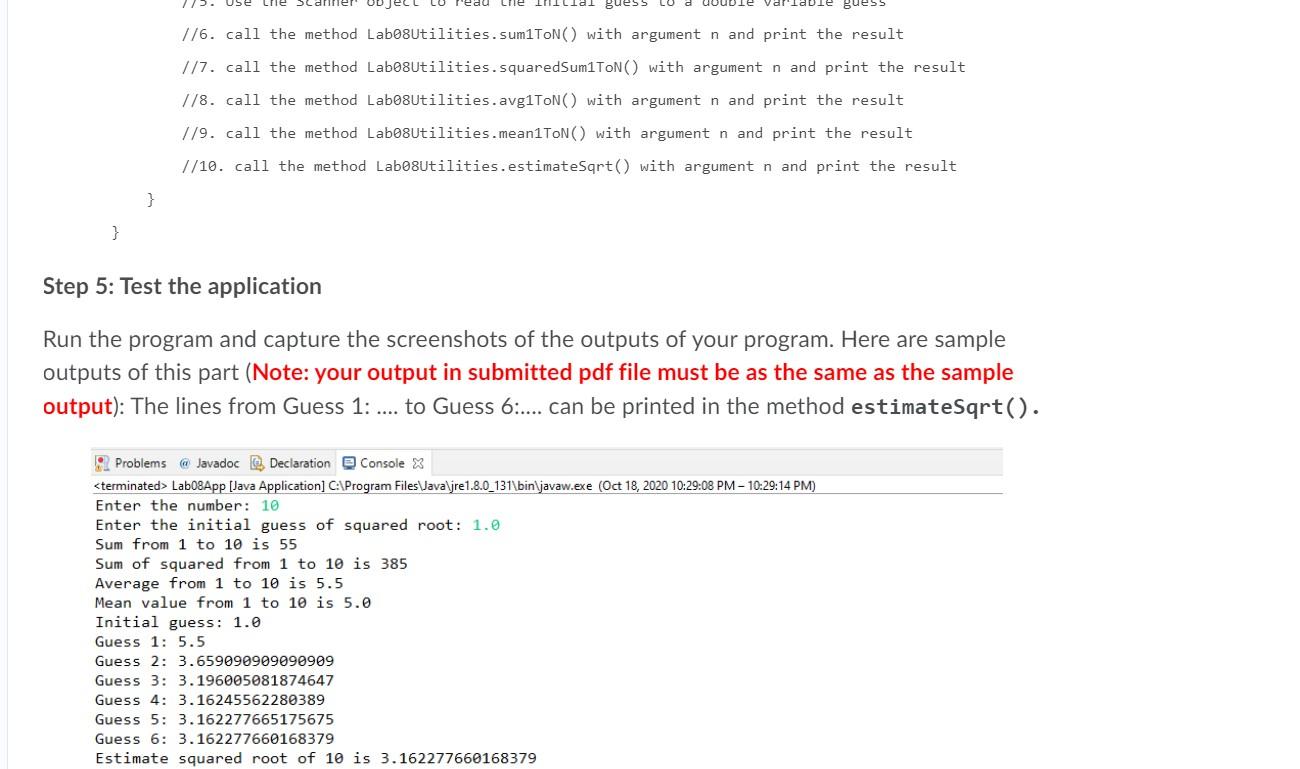
In this lab, you will need to develop an application to ask for an input integer number (n) from the user. Then the program should perform the following tasks: - calculate and print the sum from 1 to the given input number (1 + 2 + + n) - calculate and print the square sum from 1 to the given input number (1^2 + 2^2 + ... + n^2) calculate and print the the average and mean values from 1 to the given input number: avg = (1 + 2 + ... + n) mean = (n+1)/2 if n is odd = n/2 if n is even estimate the square root of n using Newton's method Step 1. Problem Statement You need to develop a Java application to solve the problems described in the previous section. Step 2: Problem Decomposition This program should be broken into two classes: Labo8Utilities and Labo8App. Lab08App will serve as a console user interface. It will prompt the user for the input number n. Then pass that number to static methods in the Labo8Utilities class. You will be provided with incomplete versions of both of these classes. The problem descriptions of this class are described below: Lab08Utilities class: this is an utility class to calculate the sum from 1 to n, squared sum, mean and average, and estimate the square root using Newtons method o The Labo8Utilities class is modeled after the Math class. It is declared final, o o o The Labo8Utilities class is modeled after the Math class. It is declared final, which means that it cannot be extended (subclassed). And its constructor is declared private, which means that this class cannot be instantiated. Also, this class has the following public static methods: public static int sum1ToN(int n): This public static method takes a single int parameter (n) return the sum from 1 to n: 1 + 2 + ... +n o public static int squared Sum1ToN(int n): This public static method takes an int parameters (n) and returns the squared sum from 1 to n: 1^2 + 2^2 + ... + n^2 public static double avg1ToN(int n): This public static method takes an int parameters (n) and returns the average from 1 to n: (1 + 2 + ... + + n) public static double mean1ToN(int n): This public static method takes an int parameters (n) and returns the mean value from 1 to n: n/2 if n is even else (n+1)/2 public static double estimateSqrt(int n, double guess): This public static method takes two parameters (the input n and the initial guess) and returns the estimated squared root of n. Newton's method for calculating the square root of N starts by making a (non zero) guess at the square root. It then uses the original guess to calculate a new guess, according to the following formula: guess = (( NA guess) + guess) / 2; This process of updating 'guess' will repeat until the absolute difference between previous guess and current guess is less than or equal to a threshold value (e.g., 0.00000001). Note you can use Math.abs(double a) method to calculate the absolute value of a. No matter how wild the original guess is, if we repeat this calculation, the algorithm will eventually stop and find the square root of N. o method takes two parameters (the input n and the initial guess) and returns the estimated squared root of n. Newton's method for calculating the square root of N starts by making a (non zero) guess at the square root. It then uses the original guess to calculate a new guess, according to the following formula: guess = (( N/ guess) + guess) / 2; This process of updating 'guess' will repeat until the absolute difference between previous guess and current guess is less than or equal to a threshold value (e.g., 0.00000001). Note you can use Math.abs(double a) method to calculate the absolute value of a. No matter how wild the original guess is, if we repeat this calculation, the algorithm will eventually stop and find the square root of N. Newton's method for calculating the square root of a number requires an initial guess. If we compute sqrt(10), using the not-very-good guess of 1.0 and carrying 8 digits accuracy, the results are as follows. (10.0/1.0 + 1.0)/2 = 5.5 (10.0/5.5 + 5.5)/2 = 3.6590909 (10.0/3.6590909 + 3.6590909)/2 = 3.1960051 (10.0/3.1960051 + 3.1960051)/2 = 3.1624556 (10.0/3.1624556 + 3.1624556)/2 = 3.1622777 (10.0/3.1622777 + 3.1622777)/2 = 3.1622777 The last two results are the same, so we stop. The result is correct to all digits shown. Since all methods in the Labo8Utilities class are defined as static, it is known as a class method (rather than an instance method). It is associated with the Labo8Utilities class itself rather than with any of its instances. Thus, to invoke this method (in a print statement), System.out.println("Sum from 1 to 10: " + Labo8Utilities. sumlToN(10)); This is similar to the way you would invoke the Math.sqrt(25) method. Note: It is not necessary to instantiate Labo8Utilities in Lab08App. Lab08App class: This is the application class with static main method to test the public methods in the Lab08Utilities class. . Step 3: Problem Design . Draw a UML class diagram to describe the design of the Labo8Utilities and Labo8App classes. Your design should identify the of the class, its attributes (instance variables) and behaviors (methods). Designate which elements will be hidden and which parts of the class will make up its public interface. Step 4: Problem Implementation Similar to Lab3, We will use the stepwise refinement approach that we practiced last time to code and test the Lab08Utilities and Lab08App classes. Create a Eclipse project named Labs, and saving the project on your workspace. 4.1 Implement the Lab08Utilities class Then, create the Lab08Utilities class in Eclipse. Here's a sequence of appropriate steps: 1. Modify the generated code by Eclipse using the following starter code: 1. Modify the generated code by Eclipse using the following starter code: public final class Labo8Utilities { // FINAL CLASS CAN'T BE EXTENDED /* this method returns the sum from 1 to n */ public static int sum1ToN(int n) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } /* this method returns the squared sum from 1 to n */ public static int squared SumlToN(int n) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } /* this method returns the average from 1 to n */ public static double avgiToN(int n) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } /* this method returns the mean value from 1 to n */ public static double mean1ToN(int n) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } } /* this method returns the estimate the square root of n using Newton's method */ public static double estimateSqrt(int n, double initial_guess) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } } // end of Labo8Utilities class 2. Type the class design specification in the comment block of this class. 4.2 Implement the Lab08App class 1. Type the Labo8App class design specification into a Java comment block at the beginning of the Lab08App.java file. This file will be the file you use for defining the Lab08App class. Here's an example format that you can use: * Class Name: Labo8App * Author: * Date: * * Role: The role/purpose of this class * Problem Description: that defines your application - include name of the project and reason for the development work. Elaborate as you see fit - keeping the scope manageable (2 - 3 sentences) * Goals of your application: State in a way so the end user knows * Elaborate as you see fit keeping the scope manageable (2 - 3 sentences) * Goals of your application: State in a way so the end user knows what your software can do (can be used as). * Enumerate all the inputs and outputs for your application (provide examples) * List all the java packages that need to be imported - tools that will be needed for solving/coding the problem. * Describe specifically your input and output screen formats a brief sketch is an excellent starting point. */ 2. Add code to the main method to prompt the user for the input number n and test public methods in the Labo8Utilities class. Below is the starter code for this main method: public class LaborApp{ /* the main method to test the Labo8Utilities*/ public static void main(String[] args) { //Implement the code using the pseudocode below 7/0. System.out.println("My name is [put_your_name_here]"); //1. Create the instance of Scanner to read input from System.in 1/2. Use System.out.println to prompt the user to enter the number (n), e.g., 10 //3. Use the Scanner object to read the number to an integer variable n 1/4. Use System.out.println to prompt the user to enter the initial guess of squared root, e.g.,1.0 1/5. Use the Scanner object to read the initial guess to a double variable guess 1/6. call the method Labo8Utilities. sumlToN) with argument n and print the result 1/7. call the method Labe8Utilities.squaredSum1TON with argument n and print the result Tal guess Buess 1/6. call the method Labo8Utilities. sumlToN() with argument n and print the result //7. call the method Labo8Utilities.squaredSumlToN() with argument n and print the result 1/8. call the method Labo8Utilities. avg1ToN) with argument n and print the result 1/9. call the method Labo8Utilities.mean1TON) with argument n and print the result //10. call the method Labe8Utilities.estimateSqrt() with argument n and print the result } } Step 5: Test the application Run the program and capture the screenshots of the outputs of your program. Here are sample outputs of this part (Note: your output in submitted pdf file must be as the same as the sample output): The lines from Guess 1: .... to Guess 6.... can be printed in the method estimateSqrt(). Problems @ Javadoc Declaration Console X Lab08App [Java Application] C:\Program Files Java\jre 1.8.0_131\binjavaw.exe (Oct 18, 2020 10:29:08 PM - 10:29:14 PM) Enter the number: 10 Enter the initial guess of squared root: 1.0 Sum from 1 to 10 is 55 Sum of squared from 1 to 10 is 385 Average from 1 to 10 is 5.5 Mean value from 1 to 10 is 5.0 Initial guess: 1.0 Guess 1: 5.5 Guess 2: 3.659090909090909 Guess 3: 3.196005081874647 Guess 4: 3.16245562280389 Guess 5: 3.162277665175675 Guess 6: 3.162277660168379 Estimate squared root of 10 is 3.162277660168379 In this lab, you will need to develop an application to ask for an input integer number (n) from the user. Then the program should perform the following tasks: - calculate and print the sum from 1 to the given input number (1 + 2 + + n) - calculate and print the square sum from 1 to the given input number (1^2 + 2^2 + ... + n^2) calculate and print the the average and mean values from 1 to the given input number: avg = (1 + 2 + ... + n) mean = (n+1)/2 if n is odd = n/2 if n is even estimate the square root of n using Newton's method Step 1. Problem Statement You need to develop a Java application to solve the problems described in the previous section. Step 2: Problem Decomposition This program should be broken into two classes: Labo8Utilities and Labo8App. Lab08App will serve as a console user interface. It will prompt the user for the input number n. Then pass that number to static methods in the Labo8Utilities class. You will be provided with incomplete versions of both of these classes. The problem descriptions of this class are described below: Lab08Utilities class: this is an utility class to calculate the sum from 1 to n, squared sum, mean and average, and estimate the square root using Newtons method o The Labo8Utilities class is modeled after the Math class. It is declared final, o o o The Labo8Utilities class is modeled after the Math class. It is declared final, which means that it cannot be extended (subclassed). And its constructor is declared private, which means that this class cannot be instantiated. Also, this class has the following public static methods: public static int sum1ToN(int n): This public static method takes a single int parameter (n) return the sum from 1 to n: 1 + 2 + ... +n o public static int squared Sum1ToN(int n): This public static method takes an int parameters (n) and returns the squared sum from 1 to n: 1^2 + 2^2 + ... + n^2 public static double avg1ToN(int n): This public static method takes an int parameters (n) and returns the average from 1 to n: (1 + 2 + ... + + n) public static double mean1ToN(int n): This public static method takes an int parameters (n) and returns the mean value from 1 to n: n/2 if n is even else (n+1)/2 public static double estimateSqrt(int n, double guess): This public static method takes two parameters (the input n and the initial guess) and returns the estimated squared root of n. Newton's method for calculating the square root of N starts by making a (non zero) guess at the square root. It then uses the original guess to calculate a new guess, according to the following formula: guess = (( NA guess) + guess) / 2; This process of updating 'guess' will repeat until the absolute difference between previous guess and current guess is less than or equal to a threshold value (e.g., 0.00000001). Note you can use Math.abs(double a) method to calculate the absolute value of a. No matter how wild the original guess is, if we repeat this calculation, the algorithm will eventually stop and find the square root of N. o method takes two parameters (the input n and the initial guess) and returns the estimated squared root of n. Newton's method for calculating the square root of N starts by making a (non zero) guess at the square root. It then uses the original guess to calculate a new guess, according to the following formula: guess = (( N/ guess) + guess) / 2; This process of updating 'guess' will repeat until the absolute difference between previous guess and current guess is less than or equal to a threshold value (e.g., 0.00000001). Note you can use Math.abs(double a) method to calculate the absolute value of a. No matter how wild the original guess is, if we repeat this calculation, the algorithm will eventually stop and find the square root of N. Newton's method for calculating the square root of a number requires an initial guess. If we compute sqrt(10), using the not-very-good guess of 1.0 and carrying 8 digits accuracy, the results are as follows. (10.0/1.0 + 1.0)/2 = 5.5 (10.0/5.5 + 5.5)/2 = 3.6590909 (10.0/3.6590909 + 3.6590909)/2 = 3.1960051 (10.0/3.1960051 + 3.1960051)/2 = 3.1624556 (10.0/3.1624556 + 3.1624556)/2 = 3.1622777 (10.0/3.1622777 + 3.1622777)/2 = 3.1622777 The last two results are the same, so we stop. The result is correct to all digits shown. Since all methods in the Labo8Utilities class are defined as static, it is known as a class method (rather than an instance method). It is associated with the Labo8Utilities class itself rather than with any of its instances. Thus, to invoke this method (in a print statement), System.out.println("Sum from 1 to 10: " + Labo8Utilities. sumlToN(10)); This is similar to the way you would invoke the Math.sqrt(25) method. Note: It is not necessary to instantiate Labo8Utilities in Lab08App. Lab08App class: This is the application class with static main method to test the public methods in the Lab08Utilities class. . Step 3: Problem Design . Draw a UML class diagram to describe the design of the Labo8Utilities and Labo8App classes. Your design should identify the of the class, its attributes (instance variables) and behaviors (methods). Designate which elements will be hidden and which parts of the class will make up its public interface. Step 4: Problem Implementation Similar to Lab3, We will use the stepwise refinement approach that we practiced last time to code and test the Lab08Utilities and Lab08App classes. Create a Eclipse project named Labs, and saving the project on your workspace. 4.1 Implement the Lab08Utilities class Then, create the Lab08Utilities class in Eclipse. Here's a sequence of appropriate steps: 1. Modify the generated code by Eclipse using the following starter code: 1. Modify the generated code by Eclipse using the following starter code: public final class Labo8Utilities { // FINAL CLASS CAN'T BE EXTENDED /* this method returns the sum from 1 to n */ public static int sum1ToN(int n) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } /* this method returns the squared sum from 1 to n */ public static int squared SumlToN(int n) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } /* this method returns the average from 1 to n */ public static double avgiToN(int n) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } /* this method returns the mean value from 1 to n */ public static double mean1ToN(int n) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } } /* this method returns the estimate the square root of n using Newton's method */ public static double estimateSqrt(int n, double initial_guess) { //TODO: Implement the code of this method below } } // end of Labo8Utilities class 2. Type the class design specification in the comment block of this class. 4.2 Implement the Lab08App class 1. Type the Labo8App class design specification into a Java comment block at the beginning of the Lab08App.java file. This file will be the file you use for defining the Lab08App class. Here's an example format that you can use: * Class Name: Labo8App * Author: * Date: * * Role: The role/purpose of this class * Problem Description: that defines your application - include name of the project and reason for the development work. Elaborate as you see fit - keeping the scope manageable (2 - 3 sentences) * Goals of your application: State in a way so the end user knows * Elaborate as you see fit keeping the scope manageable (2 - 3 sentences) * Goals of your application: State in a way so the end user knows what your software can do (can be used as). * Enumerate all the inputs and outputs for your application (provide examples) * List all the java packages that need to be imported - tools that will be needed for solving/coding the problem. * Describe specifically your input and output screen formats a brief sketch is an excellent starting point. */ 2. Add code to the main method to prompt the user for the input number n and test public methods in the Labo8Utilities class. Below is the starter code for this main method: public class LaborApp{ /* the main method to test the Labo8Utilities*/ public static void main(String[] args) { //Implement the code using the pseudocode below 7/0. System.out.println("My name is [put_your_name_here]"); //1. Create the instance of Scanner to read input from System.in 1/2. Use System.out.println to prompt the user to enter the number (n), e.g., 10 //3. Use the Scanner object to read the number to an integer variable n 1/4. Use System.out.println to prompt the user to enter the initial guess of squared root, e.g.,1.0 1/5. Use the Scanner object to read the initial guess to a double variable guess 1/6. call the method Labo8Utilities. sumlToN) with argument n and print the result 1/7. call the method Labe8Utilities.squaredSum1TON with argument n and print the result Tal guess Buess 1/6. call the method Labo8Utilities. sumlToN() with argument n and print the result //7. call the method Labo8Utilities.squaredSumlToN() with argument n and print the result 1/8. call the method Labo8Utilities. avg1ToN) with argument n and print the result 1/9. call the method Labo8Utilities.mean1TON) with argument n and print the result //10. call the method Labe8Utilities.estimateSqrt() with argument n and print the result } } Step 5: Test the application Run the program and capture the screenshots of the outputs of your program. Here are sample outputs of this part (Note: your output in submitted pdf file must be as the same as the sample output): The lines from Guess 1: .... to Guess 6.... can be printed in the method estimateSqrt(). Problems @ Javadoc Declaration Console X Lab08App [Java Application] C:\Program Files Java\jre 1.8.0_131\binjavaw.exe (Oct 18, 2020 10:29:08 PM - 10:29:14 PM) Enter the number: 10 Enter the initial guess of squared root: 1.0 Sum from 1 to 10 is 55 Sum of squared from 1 to 10 is 385 Average from 1 to 10 is 5.5 Mean value from 1 to 10 is 5.0 Initial guess: 1.0 Guess 1: 5.5 Guess 2: 3.659090909090909 Guess 3: 3.196005081874647 Guess 4: 3.16245562280389 Guess 5: 3.162277665175675 Guess 6: 3.162277660168379 Estimate squared root of 10 is 3.162277660168379











