Question: In this problem we are going to deal with a type of weighted binary tree in which each node contains one positive integer and has
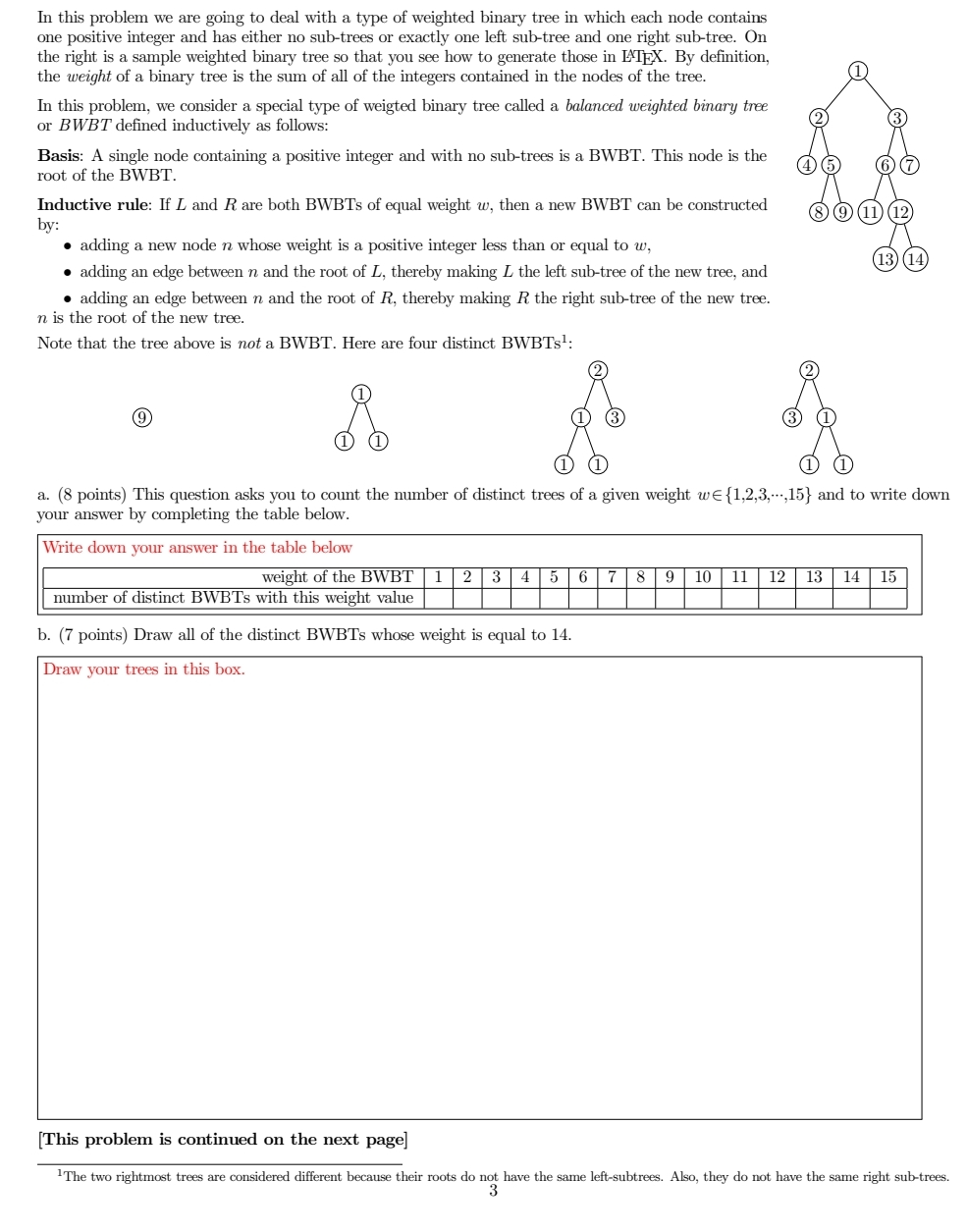
In this problem we are going to deal with a type of weighted binary tree in which each node contains one positive integer and has either no subtrees or exactly one left subtree and one right subtree. On the right is a sample weighted binary tree so that you see how to generate those in By definition, the weight of a binary tree is the sum of all of the integers contained in the nodes of the tree.
In this problem, we consider a special type of weigted binary tree called a balanced weighted binary tree or defined inductively as follows:
Basis: A single node containing a positive integer and with no subtrees is a BWBT This node is the root of the BWBT
Inductive rule: If and are both BWBTs of equal weight then a new BWBT can be constructed by:
adding a new node whose weight is a positive integer less than or equal to
adding an edge between and the root of thereby making the left subtree of the new tree, and
adding an edge between and the root of thereby making the right subtree of the new tree. is the root of the new tree.
a points This question asks you to count the number of distinct trees of a given weight wincdots, and to write down your answer by completing the table below.
Write down your answer in the table below
tableweight of the BWBTnumber of distinct BWBTs with this weight value,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
b points Draw all of the distinct BWBTs whose weight is equal to
Draw your trees in this box.
This problem is continued on the next page
The two rightmost trees are considered different because their roots do not have the same leftsubtrees. Also, they do not have the same right subtrees.
In this problem we are going to deal with a type of weighted binary tree in which each node contains one positive integer and has either no subtrees or exactly one left subtree and one right subtree. On the right is a sample weighted binary tree so that you see how to generate those in By definition, the weight of a binary tree is the sum of all of the integers contained in the nodes of the tree.
In this problem, we consider a special type of weigted binary tree called a balanced weighted binary tree or defined inductively as follows:
Basis: A single node containing a positive integer and with no subtrees is a BWBT This node is the root of the BWBT
Inductive rule: If and are both BWBTs of equal weight then a new BWBT can be constructed by:
adding a new node whose weight is a positive integer less than or equal to
adding an edge between and the root of thereby making the left subtree of the new tree, and
adding an edge between and the root of thereby making the right subtree of the new tree. is the root of the new tree.
a points 'I'his question asks you to count the number of distinct trees of a given weight wincdots, and to write down your answer by completing the table below.
Write down your answer in the table below
tableweight of the BWBTnumber of distinct BWBTs with this weight value,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
b points Draw all of the distinct BWBTs whose weight is equal to
Draw vour trees in this box.
This problem is continued on the next page
The two rightmost trees are considered different because their roots do not have the same leftsubtrees. Also, they do not have the same right subtrees.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


