Question: In this program, you will design a C++ class called myRational to represent rational numbers. As you know, a rational number is represented by a
In this program, you will design a C++ class called myRational to represent rational numbers. As you know, a rational number is represented by a fraction of two numbers such as a/b, where a and b are integers. a is the nominator of the number and b is the denominator of the number. In your myRational class, you will implement 4 basic arithmetic operation, a comparator function, and a print function. Details of the myRational class is given below:
| class myRational | |
| Attributes: | Description |
| int _nom | Nominator of the Rational Number |
| int _denom | Denominator of the Rational Number |
| Member Functions: | Description |
| Constructor(s) | Constructor function(s) for new rational numbers |
| Set/Get Functions | Set and Get function for each attribute |
| R3 = R1 + R2 | Overload + operator to add two rational numbers |
| R3 = R1 R2 | Overload operator to subtract two rational numbers |
| R3 = R1 * R2 | Overload * operator to multiply two rational numbers |
| R3 = R1 / R2 | Overload / operator to divide two rational numbers |
| R1 == R2 | Overload == operator to compare two rational numbers. Return true if they are equal, return false otherwise. |
| cout | Overload |
Please note that addition (and subtraction) of two numbers such as a/b + c/d requires equalizing the denominator. This is a challenge you need to solve. You are not allowed to use float or double variables in this assignment.
In the second part of the homework, you will use the myRational class as a base class and create a derived (child) class called myInteger. This is a new version of Integer numbers. myInteger will be based on myRational. So all myRational member functions will also be available for myInteger. However, the denominator field of myInteger will be always 1. Here are some details of the myInteger class:
| class myInteger: public myRational | |
| Attributes: | Description |
| No extra attribute | |
| Member Functions: | Description |
| Constructor(s) | Constructor function(s) for new rational numbers (tip: Here, you can call the myRational constructor function and set the denominator field as 1) |
| cout | Overload |
| I1 = R1 | Overload = operator to assign a myRational number variable to myInteger variable. This function is necessary to use arithmetic operators of myRational class. |
Your classes must be written as two separate files: myRational.h and myRational.cpp. myRational.h file should include class declarations of myRational and myInteger. myRational.cpp file will include all function implementations of both classes. You will submit only myRational.h and myRational.cpp files.
I will provide a main.cpp, which includes the main function. The main function has several test cases for your classes. You do not need to make any changes on this file. If your class implementations are correct, main.cpp should work just fine, and its output should look like below:
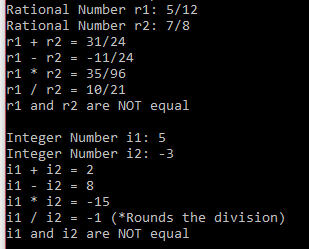
main.cpp
#include#include "myRational.h" using namespace std; int main(){ //Create two myRational numbers myRational r1(-5,-12); myRational r2(7,8); cout Rational Number r1: 5/12 Rational Number r2: 7/8 r1 r231/24 r1 - r2 = -11/24 r1 r2 35/96 r1 r2 10/21 rl and r2 are NOT equal Integer Number i1: 5 Integer Number i2: -3 i1 i22 11-12 = 8 i1 i2 15 11 / 2--1 (*Rounds the division) i1 and i2 are NOT equal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


