Question: In this project, you will create a command line version of a word guessing game. When the game starts, the game randomly generates 3 game
In this project, you will create a command line version of a word guessing game.
When the game starts, the game randomly generates 3 game levels. Each level is associated with a
secret word. To win the game, the player must pass all 3 levels. The player passes a level by correctly
guessing the secret word associated with that level.
At the start of a level, the levels secret word is displayed to the player as a series of dashes. For
example, if the secret word is CHICAGO, the game would display the word as _ _ _ _ _ _ _.
The player guesses what letters are in the word, one letter at a time. The player has 7 chances to
guess the word.
If the player chooses a letter that is in the word, the relevant dashes are replaced with the selected
letter. If the letter they choose is not in the word, the number of chances is reduced by 1.
For example, assume the secret word is CHICAGO:
First, the player guesses C. Because this letter is in the word, the game will update the
dashes as follows: C _ _ C _ _ _. The player has 7 chances remaining.
Next, the player guesses P. This letter is not in the words, so the game will update the
number of remaining guesses to 6.
Next, the player guesses G. Because this letter is in the word, the game will update the
dashes as follows: C _ _ C _ G _. The player has 6 more chances to guess the word.
If the player correctly guesses the word before running out of chances, the game advances the player
to the next level.
This process repeats until ONE of the following conditions occurs:
1. The player passes all 3 levels
2. The player runs out of chances on any given level (including the first level).
If either of the above conditions occurs, the game is over. At this point, the game must display the
results to the user (you win, you lose).
When the game is over, the game should record:
1. The date and time the game
2. The number of points the person scored. The number of scored points is the total sum of
the players remaining guesses across all 3 levels. That is:
Score = guesses remaining from level 1 +
guesses remaining from level 2 +
guesses remaining from level 3
User interface requirements
1. Asking the user for input
The application must display meaningful prompts whenever it is asking the user for input.
2. Starting the Game
When the player starts the application, you must display a welcome message and menu of choices.
The options for the user are:
Start Game
Results of Previous Games
Exit
Choosing the Start Game option will begin the game.
Choosing Results of Previous Games will display a list of the results of previously played games.
Choosing Exit will display a goodbye message and exit the game
Your app must check whether the user has entered a valid menu option. If an invalid menu option is
detected, then an appropriate error message must be displayed.
3. Level information
While the user is playing the game, the game must always display:
The current level
The number of chances remaining
The current state of the secret word, as dashes. For example, C _ _ C _ G _
For example:
Level 1
Guesses Remaining: 4
Secret Word: C H _ C A _ O
4. Guessing a Letter
The game must provide a prompt that asks the user to enter a letter via the keyboard. You may
assume they will always enter a letter. You are not required to validate if they actually entered a
value between A-Z.
The game must always inform the user about the results of their guess. For example: C is in the
word! or C is not in the word!
5. Game Over
When the game is over, the game must display an explicit WIN or LOSE message. The app should also show the number of points scored.
Object Oriented Design
Your application must adhere to the following object oriented design.
You may include other classes where appropriate.
Description of Classes
You are required to implement the described classes and properties.
You may rename the described. properties and methods to your liking, but they must
perform the operations described.
You are permitted to add any additional properties, methods or classes that you think are
useful.
All classes must enforce encapsulation.
Secret Word
The secret word class is responsible for providing information about the word the person is trying to
guess. The class is responsible for knowing what the secret word is, and the state of the secret word.
For example, assume the secret word is LONDON and the player has guessed L, N, and D correctly. At
this point in time,
The secret word is LONDON
The current state of the word is L _ N D _ N
Mandatory Properties:
actualWord: Represents the word the player is guessing, in plain text. Example: LONDON
Mandatory Methods:
containsLetter(letter): Returns true if letter is in the secret word, and false otherwise
hasLettersRemaining(): Returns true if there are still letters that need to be guessed.
Returns true if all letters were correctly guessed.
toString(): Returns a string that represents the current state of the word. Any unguessed
letters should be represented as _. For example: L _ N D _ N.
Level
The level class is responsible for maintaining information about one (1) level of the game. The class
is responsible for knowing the its level number, the number of chances the player has remaining in
the level, and checking the results of the players guesses.
Mandatory Properties
levelNumber: The level number, for example: 1, 2, 3, 4
chancesRemaining: The number of guesses the player has remaining in the level.
secretWord: An instance of the SecretWord class. This represents the secret word that is
associated with the current level.
debugOn: A boolean variable used to help you debug your application. If debugOn = true,
then the Levels toString() function must output the current secret word, in plain text. If
debugOn = false, then the toString() function will never display the secret word in plain text.
Mandatory Methods
toString(): Returns a string that displays the current level number, the number of guesses
remaining, and the current state of the word, in dashes (eg: L _ N D _ N). If the debugOn
property = true, then the toString() should also display the actual secret word, in plain text.
Example: debugOn = true, toString() outputs:
Level 1, Chances Remaining: 4, Secret Word: L _ N D _ N, Actual Word: LONDON
Example: debugOn = false, toString() outputs:
Level 1, Chances Remaining: 4, Secret Word: L _ N D _ N
checkGuess(guessedLetter): Determines what should happen if guessedLetter is in the
word.
If guessedLetter is in the secret word, update the state of the secret word and return true.
If guessedLetter is not in the secret word, reduce the number of chances remaining and
return false.
isWordGuessed(): Returns true the player has guessed the secret word, and false otherwise.
Previous Game Result
This class models a previously played game.
Mandatory Properties
datePlayed: A String representing the date/time that a game was played. Examples of
obtaining the current date/time: https://www.javatpoint.com/java-get-current-date
points: The number of points scored in the game.
Mandatory Methods
toString(): Outputs the date/time the game was played, and the total number of points
scored in the game.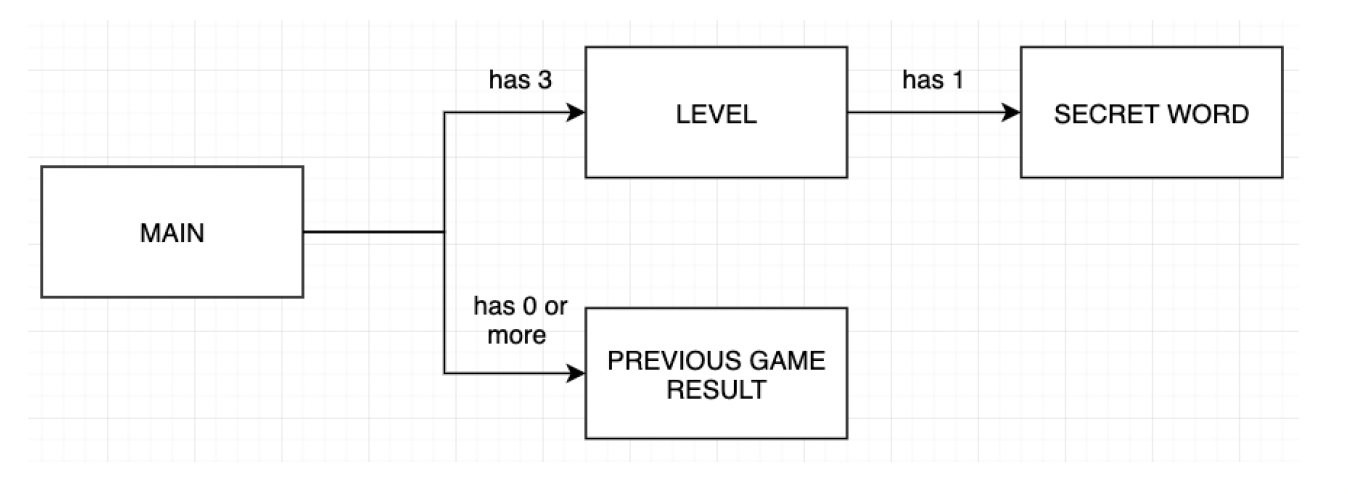
has 3 has 1 LEVEL SECRET WORD MAIN has 0 or more PREVIOUS GAME RESULT
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


