Question: In this project, you will write a program to simulate a few CPU scheduling policies we discussed in class. You will be using C or
In this project, you will write a program to simulate a few CPU scheduling policies we discussed in class. You will be using C or to implement the simulator. The simulator selects a task to run from the ready queue based on the scheduling algorithm. Since the project intends to simulate a CPU scheduler, it does not require any actual process creation or execution. When a task is scheduled, the simulator will simply print out what task is selected to run at a time. Project Descriptions: The selected scheduling algorithms to implement in this project are Shortest Job First.
You will have to give the program read from a text file as the following value
- a SEED for the random number generator
- INIT_TIME
- FIN_TIME
- ARRIVE_MIN
- ARRIVE_MAX
- QUIT_PROB
- NETWORK_PROB
- CPU_MIN
- CPU_MAX
- DISK1_MIN
- DISK1_MAX
- DISK2_MIN
- DISK2_MAX
- NETWORK_MIN
- NETWORK_MAX
The format of the file is up to you, but it could be something as simple as:
INIT_TIME 0 FIN_TIME 10000
The system behaves as follows:
- The system runs from INIT_TIME (usually 0) to FIN_TIME.
- Jobs enter the system with an interarrival time that is uniformly distributed between ARRIVE_MIN and ARRIVE_MAX.
- Once a job has finished a round of processing at the CPU, the probability that it completes and exits the system (instead of doing a disk read or network send, and then further computation) is QUIT_PROB.
- Once a job has been determined to continue executing, a probability function is used to determine whether it will do disk I/O or use the network. This probability is NETWORK_PROB.
- When a job needs to do disk I/O, it uses the disk that's the least busy, i.e., the disk whose queue is the shortest. (This might seem a bit silly, but we can pretend that each disk has the same information.) If the disk queues are of equal length, choose one of the disks at random.
- When jobs reach some component (CPU, disk1, disk2, or network), if that component is free, the job begins service there immediately. If, on the other hand, that component is busy servicing someone else, the job must wait in that component's queue.
- The queue for each system component is FIFO.
- When a job reaches a component (a different job leaves a component or the component is free, and this job is first in the queue), how much time does it spend using the component? This is determined randomly, at runtime, for every component arrival. A job is serviced by a component for an interval of time that is uniformly distributed between some minimum and maximum defined for that component. For example, you'll define: CPU_MIN, CPU_MAX, DISK1_MIN, DISK1_MAX, etc.
- At time FIN_TIME, the entire job simulation terminates. We can ignore the jobs that might be left receiving service or waiting in queue when FIN_TIME is reached.
**Results** **Log File** Your program should write to a log file the values of each of the constants listed above as well as each significant event (e.g., arrival of a new job into the system, the completion of a job at a component, the termination of the simulation, along with the time of the event) **Statistics** Calculate and print: - The average and the maximum size of each queue. - The utilization of each server (component). This would be: time_the_server_is_busy/total_time where total_time = FIN_TIME-INIT_TIME. - The average and maximum response time of each server (response time will be the difference in time between the job arrival at a server and the completion of the job at the server) - The throughput (number of jobs completed per unit of time) of each server. Run the program a number of times with different values for the parameters and random seed. Examine how the utilizations relate to queue sizes. If for a given choice of parameters by changing the random seed we obtain utilization and size values that are stable (i.e., they do dont change much (maybe 10%)), then we have a good simulation. Your program should process a reasonable number of jobs, at least one thousand.
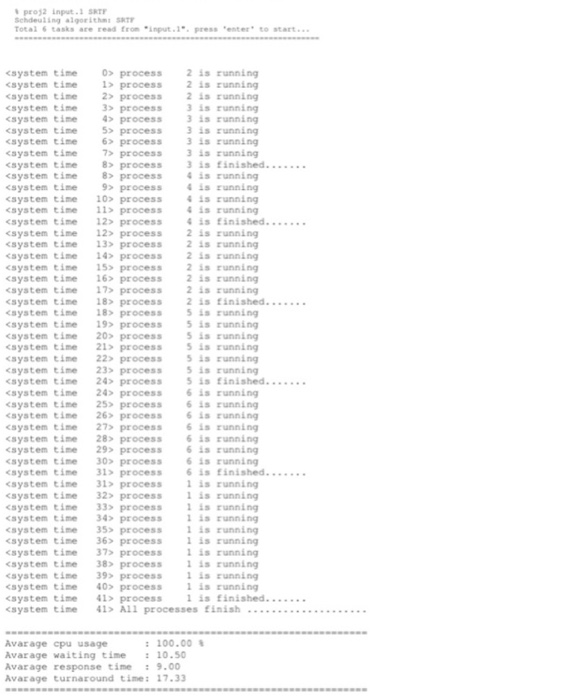
pros2 input. SRT Scheuling algorithm SRTY Total tasks are read from input... press enter to start...
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


