Question: In this task, you will redo your Silly Name program from Week 3 and write it in the C programming language. Your program should: terminal_user_input.h:
In this task, you will redo your Silly Name program from Week 3 and write it in the C programming language. Your program should: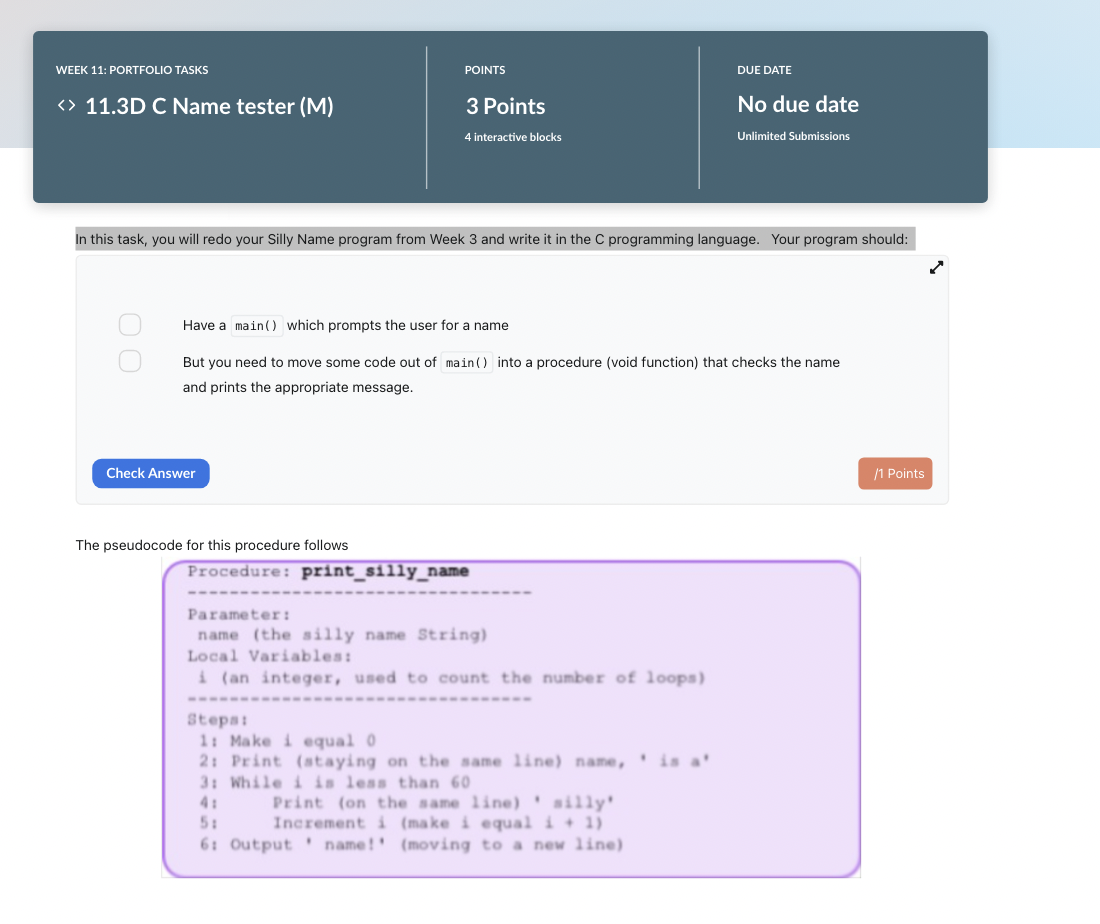
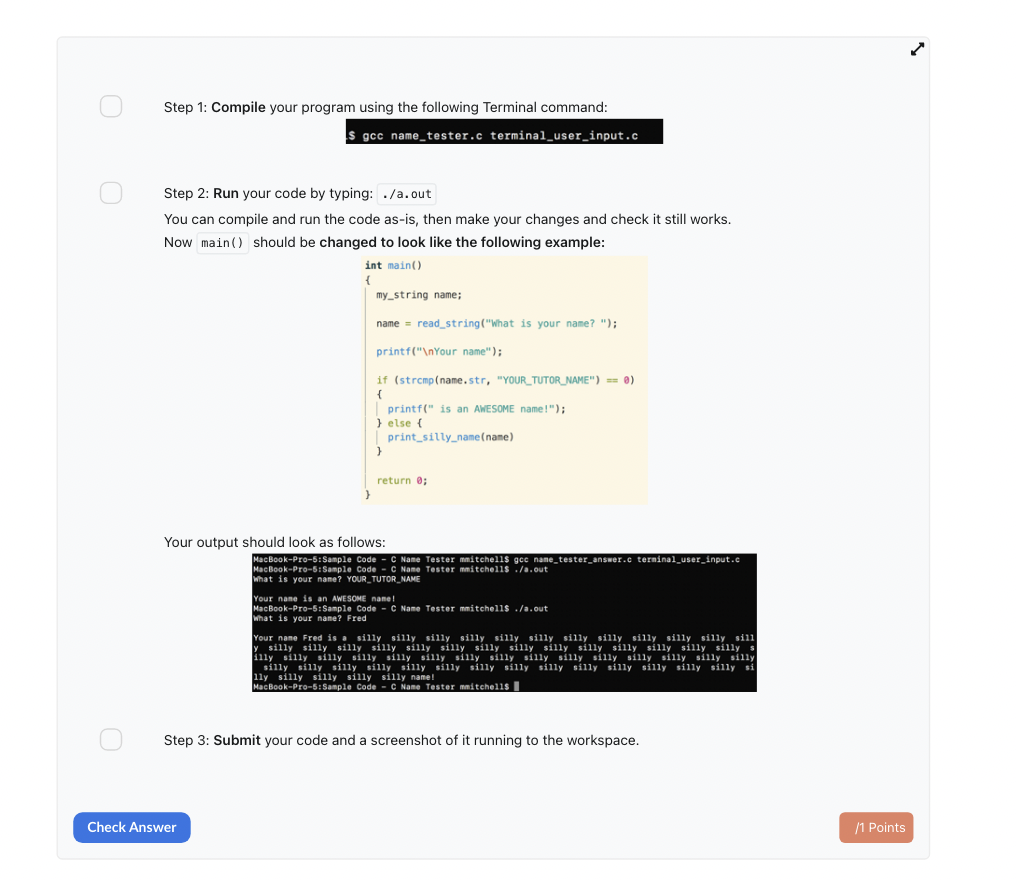
terminal_user_input.h:
// ============================
// = User Input Function in C =
// ============================
//
// This header file contains the types and functions/procedures
// in the Terminal User Input code. You can #include "terminal_user_input.h"
// to access these from your project. Remember to compile both your
// program file and the terminal_user_input.c file.
//
//
// The following code makes sure that you cant accidentally
// include this code twice. It is common to see this kind of
// code at the top of a C/C++ header file.
//
#ifndef TERMINAL_USER_INPUT_H
#define TERMINAL_USER_INPUT_H
//
// The my_string type can be used to represent a "string" in C.
// This needs to be a struct so that it can be returned from
// functions.
//
typedef struct my_string
{
char str[256]; // my string contains an array of 255 characters + null
} my_string;
//
// Reads a string of up to 255 characters + 1 for null
//
my_string read_string(const char* prompt);
//
// Reads a integer from the user.
//
int read_integer(const char* prompt);
//
// Reads a integer from the user in a given range.
//
int read_integer_range(const char* prompt, int min, int max);
//
// Reads a double from the user.
//
double read_double(const char* prompt);
#endif
name tester.c:
#include
#include
#include "terminal_user_input.h"
#define LOOP_COUNT 60
int main()
{
my_string name;
int index;
name = read_string("What is your name? ");
printf("Your name is: %s ", name.str);
// Move the following code into a procedure
// ie: void print_silly_name(my_string name)
for(index=0;index printf(" a silly, "); } printf(" name! "); return 0; } Terminal_user_input.c: // ============================ // = User Input Function in C = // ============================ #include #include "terminal_user_input.h" // // Reads a string of up to 255 characters + 1 for null // my_string read_string(const char* prompt) { my_string result; // declares a "my_string" variable (contains the array of character) printf("%s", prompt); // output the string from the prompt "%s" defines where to place the string in the output scanf(" %255[^ ]%*c", result.str ); // scan the input looking for upto 255 characters [ that are not newlines ], read this into the string variable return result; // return the my string value } // // Reads a integer from the user. // int read_integer(const char* prompt) { my_string line; int result; // where we will store the result of the function char temp; //used to check nothing comes after the int // Read in the string the user entered. line = read_string(prompt); // scan the string, looking for a number ... followed by nothing // sscanf = string scan format // This will "scan" the array of character in line.str (reads this) // " " = skip any spaces // "%d" = read an integer // " " = skip any spaces // "%c" = read a character // sscanf returns the number of things it read (0 to 2 in this case) // Loop while this is not equal to 1 // 0 = did not read a number at the start // 1 = read a number, but no character followed it // 2 = read a number and a character... like "1 fred" (1 is the number, f is the character) while ( sscanf(line.str, " %d %c", &result, &temp) != 1 ) { // scan found a number followed by something... so its not a whole number printf("Please enter a whole number. "); // read the next "string" and try again line = read_string(prompt); } return result; } int read_integer_range(const char* prompt, int min, int max) { int result = read_integer(prompt); while ( result max ) { printf("Please enter a number between %d and %d ", min, max); result = read_integer(prompt); } return result; } double read_double(const char* prompt) { my_string line; double result; // where we will store the result of the function char temp; //used to check nothing comes after the int // Read in the string the user entered. line = read_string(prompt); while ( sscanf(line.str, " %lf %c", &result, &temp) != 1 ) { // scan found a number followed by something... so its not a whole number printf("Please enter a number. "); // read the next "string" and try again line = read_string(prompt); } return result; }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


