Question: IN VISUAL STUDIO CODE ( C + + ) Deliverable: pointerproblemfunctions.cpp Purpose: Implement the Merge function whose prototype is given in pointerproblemfunctions.h . Read the
IN VISUAL STUDIO CODE C
Deliverable: pointerproblemfunctions.cpp
Purpose: Implement the Merge function whose prototype is given in pointerproblemfunctions.h Read the comments in pointerproblemfunctions.h attached for details about this function.
Specifications: The files for this problem are in the attached problemzip No changes are to be made in the attached pointerproblemfunctions.h file Implement the Merge functions in pointerproblemfunctions.cpp and attach your revised pointerproblemfunctions.cpp file to the assignment. This is the most important file for this problem The function should not create a memory leak or memory leaks The code should compile and link with the command gstdcI pointerproblemfunctions.cpp pointerproblemdriver.cpp to see if your Merge function correctly merges two SortedDynamicArrays
Initial Testing: Randomly generated SortedDynamicArrays are created in pointerproblemdriver.cpp and the Merge function is called to merge the two structures. To test with the file, ou can use command make pointerproblemdriver.
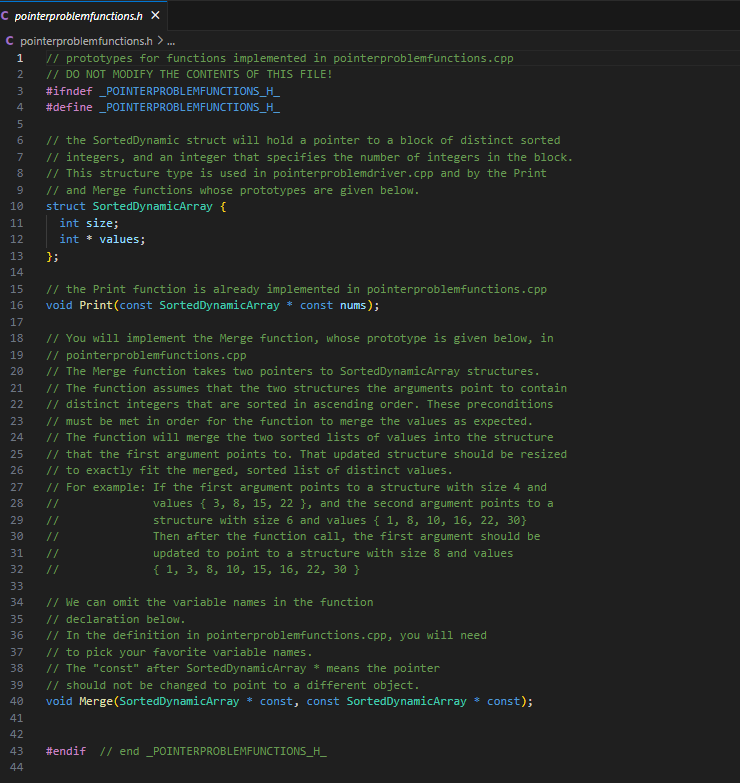
C pointerproblemfunctions.h
prototypes for functions implemented in pointerproblemfunctions.cpp
DO NOT MODIFY THE CONTENTS OF THIS FILE!
#ifndef POINTERPROBLEMFUNCTIONSH
#define POINTERPROBLEMFUNCTIONSH
the SortedDynamic struct will hold a pointer to a block of distinct sorted
integers, and an integer that specifies the number of integers in the block.
This structure type is used in pointerproblemdriver.cpp and by the Print
and Merge functions whose prototypes are given below.
struct SortedDynamicArray
int size;
int values;
;
the Print function is already implemented in pointerproblemfunctions.cpp
void Printconst SortedDynamicArray const nums;
You will implement the Merge function, whose prototype is given below, in
pointerproblemfunctions.cpp
The Merge function takes two pointers to SortedDynamicArray structures.
The function assumes that the two structures the arguments point to contain
distinct integers that are sorted in ascending order. These preconditions
must be met in order for the function to merge the values as expected.
The function will merge the two sorted lists of values into the structure
that the first argument points to That updated structure should be resized
to exactly fit the merged, sorted list of distinct values.
For example: If the first argument points to a structure with size and
values and the second argument points to a
structure with size and values
Then after the function call, the first argument should be
updated to point to a structure with size and values
We can omit the variable names in the function
declaration below.
In the definition in pointerproblemfunctions.cpp you will need
to pick your favorite variable names.
The "const" after SortedDynamicArray means the pointer
should not be changed to point to a different object.
void MergeSortedDynamicArray const, const SortedDynamicArray const;
#endif end POINTERPROBLEMFUNCTIONSH
pointerproblemfunctions.cpp
C pointerproblemfunctions.cpp
#include"pointerproblemfunctions.h
#include
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
#include
using std::setw;
do not modify the implementation of the Print function
void Printconst SortedDynamicArray nums
for int i ; i numssize; i
cout setw numsvaluesi;
cout endl;
implement the Merge function described in pointerproblemfunctions.h here
pointerproblemdriver.cpp
@ pointerproblemdriver.cpp
Initial test driver for the struct pointers dynamic memory allocation
problem on Exam
Your code should compile and link with this UNEDITED file in order to get
compilation points.
You are encouraged to create more rigorous tests.
#include
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
#include
#include
#include
using std::setw;
#include"pointerproblemfunctions.h
int main
seed the random function with the current time
srandtime;
SortedDynamicArray sorted sorted;
randomly generate sizes for two blocks of sorted integers
sortedsize rand;
sortedvalues new intsortedsize;
sortedsize rand;
sortedvalues new intsortedsize;
fill the block of memory sortedl.values points to with a list of distinct
"random" distinct integers sorted from smallest to largest
sortedvalues rand;
for int i ; i sortedsize; i
sortedvaluesi sortedvaluesi rand;
fill the block of memory sortedvalues points to with a list of distinct
"random" distinct integers sorted from smallest to largest
sortedvalues rand;
for int i ; i sortedsize; i
sortedvaluesi sortedvaluesi rand;
print the two lists
cout "Size of sorted sortedsize
V
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


