Question: #include #include #include using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl; using std::string; using std::vector; int main() { string str; // add declaration for a vector with
#include
#include
#include
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::vector;
int main()
{
string str;
// add declaration for a vector with base type string
while (str != "done")
{
cout
cin >> str;
if (str != "done")
{
// use push_back function to add str to vector
}
}
return 0;
}
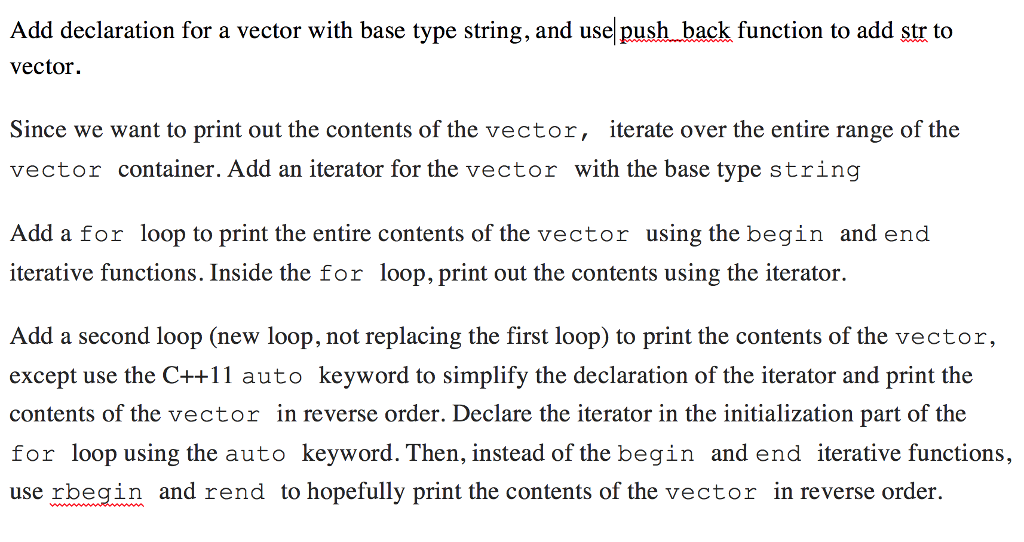
Add declaration for a vector with base type string, and use push back function to add str to Add declaration for a vector with base type string, and usel push back function to add str to vector. Since we want to print out the contents of the vector, iterate over the entire range of the vector container. Add an iterator for the vector with the base type string Add a for loop to print the entire contents of the vector using the begin and end iterative functions. Inside the for loop, print out the contents using the iterator Add a second loop (new loop, not replacing the first loop) to print the contents of the vector, except use the C++1 auto keyword to simplify the declaration of the iterator and print the contents of the vector in reverse order. Declare the iterator in the initialization part of the for loop using the auto keyword. Then, instead of the begin and end iterative functions, use rbegin and rend to hopefully print the contents of the vector in reverse order
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


