Question: #include #include using namespace std; class Slacker :public Comparable{ string name; int classesMissed; public: Slacker(int missed, string n): classesMissed(missed), name(n) {} // they don't even
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Slacker :public Comparable{
string name;
int classesMissed;
public:
Slacker(int missed, string n): classesMissed(missed), name(n) {}
// they don't even bother to validate their input!
string toString() const {
return name + " missed " + to_string(classesMissed) + " classes";
}
};
class Workaholic:public Comparable {
int workHours;
// they don't have a name ... work is more important!
public:
Workaholic(int wh) {
assert(wh > 12 && wh
workHours = wh;
}
string toString() const {
return "Workaholic worked " + to_string(workHours) + " hours non-stop!";
}
};
class WorkFamilyBalanced:public Comparable {
string name;
int familyHours;
int workHours;
public:
WorkFamilyBalanced(int fh, int wh, string n): name(n) {
assert(fh >= 0 && wh >= 0);
familyHours = fh;
workHours = wh;
}
string toString() const {
int diff = abs(workHours - familyHours);
return name + " spent " + to_string(workHours) + " hours at work" +
" and " + to_string(familyHours) + " with family " +
"(diff = " + to_string(diff) + ")";
}
};
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
void sort(Comparable * a[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i
for (int j = 0; j
if (a[j]->compareTo(*a[j+1]) == 1)
swap(a[j], a[j+1]);
}
bool all_same(Comparable * a[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i
if (a[i]->compareTo(*a[i+1]) != 0)
return false;
return true;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main() {
cout
Comparable * a[3] = {
new Slacker(81, "Jimmy"),
new Slacker(50, "Tania"),
new Slacker(73, "Josh")
};
sort(a, 3);
for (int i = 0; i
cout (a[i])->toString()
if (all_same(a, 3))
cout
else
cout
if (is_sorted(a, 3))
cout
else
cout
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
cout
Comparable * b[3] = {
new Workaholic(23),
new Workaholic(23),
new Workaholic(23)
};
sort(b, 3);
for (int i = 0; i
cout (b[i])->toString()
if (all_same(b, 3))
cout
else
cout
if (is_sorted(b, 3))
cout
else
cout
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
cout
Comparable * c[3] = {
new WorkFamilyBalanced(8, 8, "Ahmad"),
new WorkFamilyBalanced(7, 12, "Fatima"),
new WorkFamilyBalanced(9, 8, "Salwa")
};
sort(c, 3);
for (int i = 0; i
cout (c[i])->toString()
if (all_same(c, 3))
cout
else
cout
if (is_sorted(c, 3))
cout
else
cout
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
cout
Comparable * d[4] = {
new Slacker(100, "John"),
new Workaholic(24),
new WorkFamilyBalanced(2, 2, "Ahmad")
};
sort(d, 4);
cout 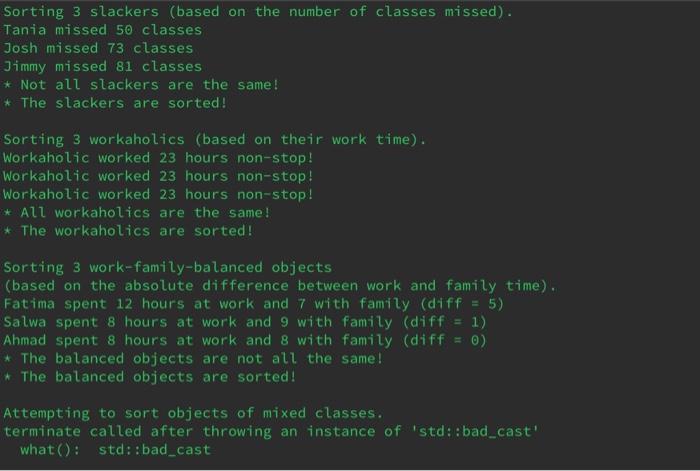 Sorting 3 slackers (based on the number of classes missed). Tania missed 50 classes Josh missed 73 classes Jimmy missed 81 classes * Not all slackers are the same! * The slackers are sorted! Sorting 3 workaholics (based on their work time). Workaholic worked 23 hours non-stop! Workaholic worked 23 hours non-stop! Workaholic worked 23 hours non-stop! * All workaholics are the same! * The workaholics are sorted! Sorting 3 work-family-balanced objects (based on the absolute difference between work and family time). Fatima spent 12 hours at work and 7 with family (diff = 5) Salwa spent 8 hours at work and 9 with family (diff = 1) Ahmad spent 8 hours at work and 8 with family (diff = 0) * The balanced objects are not all the same! * The balanced objects are sorted! Attempting to sort objects of mixed classes. terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::bad_cast' what(): std::bad_cast
Sorting 3 slackers (based on the number of classes missed). Tania missed 50 classes Josh missed 73 classes Jimmy missed 81 classes * Not all slackers are the same! * The slackers are sorted! Sorting 3 workaholics (based on their work time). Workaholic worked 23 hours non-stop! Workaholic worked 23 hours non-stop! Workaholic worked 23 hours non-stop! * All workaholics are the same! * The workaholics are sorted! Sorting 3 work-family-balanced objects (based on the absolute difference between work and family time). Fatima spent 12 hours at work and 7 with family (diff = 5) Salwa spent 8 hours at work and 9 with family (diff = 1) Ahmad spent 8 hours at work and 8 with family (diff = 0) * The balanced objects are not all the same! * The balanced objects are sorted! Attempting to sort objects of mixed classes. terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::bad_cast' what(): std::bad_cast
"REACHING THIS LINE MEANS THAT OBJECTS OF DIFFERENT "
"CLASS HAVE BEEN COMPRED, WHICH IS STRICTLY FORBIDDEN "
"IN OBJECTVILLE!"
return 0;
}
Find errors in this code in C Plus Plus to show the image attached to the question

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


