Question: Instructions The Fibonacci sequence is, by definition, the integer sequence in which every number after the first two is the sum of the two preceding



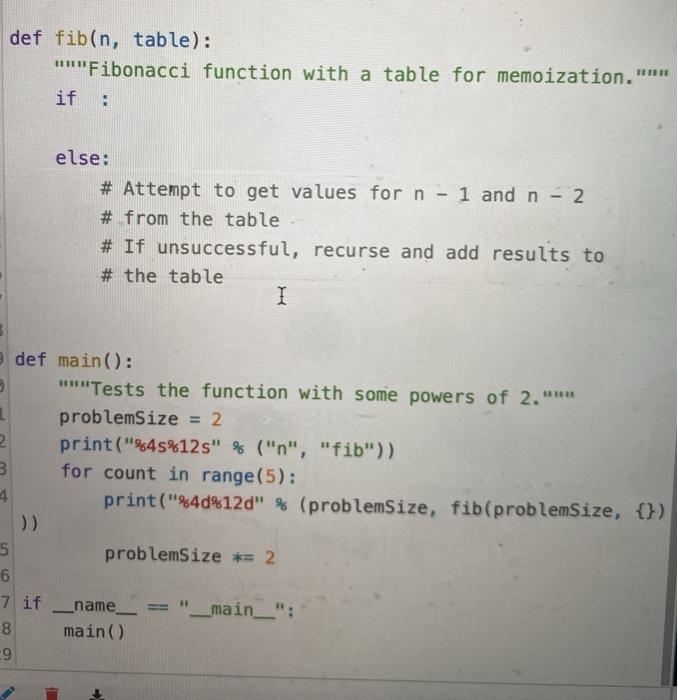
Instructions The Fibonacci sequence is, by definition, the integer sequence in which every number after the first two is the sum of the two preceding numbers. In the fib.py file, complete the following: 1. Modify the recursive Fibonacci function to employ the memoization technique discussed in this chapter. . Form a base case for any number in the sequence, except for the first and second, is the sum of the previous two A base case in a recursive function tells the function when to stop (to avoid going into an infinite loop) The function should expect a dictionary as an additional argument. The top-level call of the function receives an empty o The function should expect a dictionary as an additional argument. The top-level call of the function receives an empty dictionary. o The function's keys and values should be the arguments and values of the recursive calls. o Use the counter object discussed in this chapter to count the number of recursive calls. Counter is already provided in the main() method To test your program run the main() method in the fib.pt file. Your program's output should look like the following: fib 2 1 4 3 8 21 16 987 32 2178309 def fib(n, table): "Fibonacci function with a table for memoization." if else: # Attempt to get values for n - 1 and n - 2 # from the table # If unsuccessful, recurse and add results to # the table I def main(): "Tests the function with some powers of 2. problemSize = 2 2 print("%45%125" % ("n", "fib")) 3 for count in range(5): print("%4d%12d" % (problemSize, fib(problemSize, {}) 4 problemSize *= 2 5 6 7 if 8 -9 name main "__main__
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


