Question: Integer numPoints is read from input, representing the number of floating-point numbers to be read next. Then, the remaining numbers are read and stored
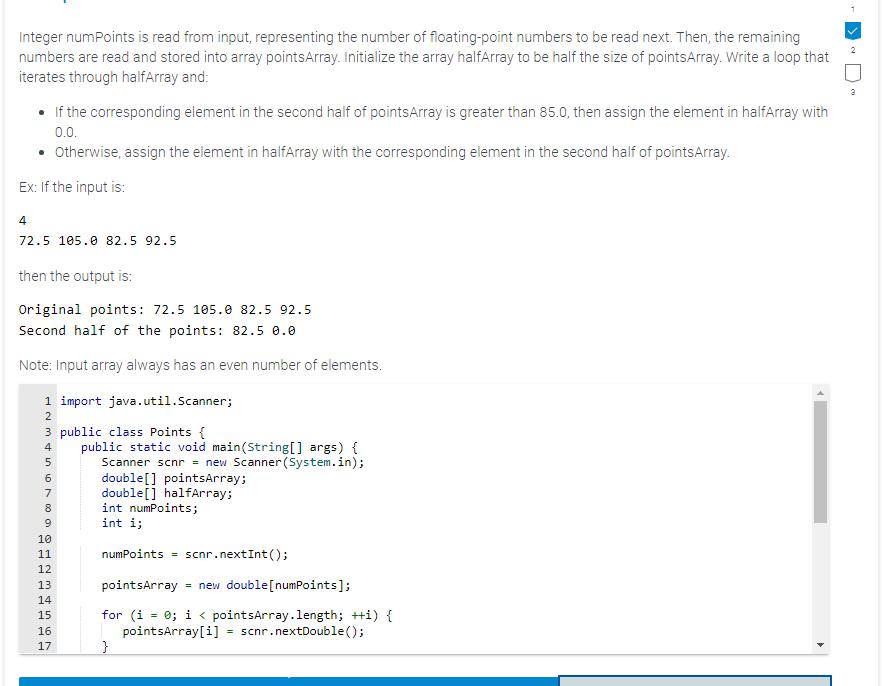

Integer numPoints is read from input, representing the number of floating-point numbers to be read next. Then, the remaining numbers are read and stored into array pointsArray. Initialize the array halfArray to be half the size of pointsArray. Write a loop that iterates through halfArray and: If the corresponding element in the second half of pointsArray is greater than 85.0, then assign the element in halfArray with 0.0. Otherwise, assign the element in halfArray with the corresponding element in the second half of points Array. Ex: If the input is: 4 72.5 105.0 82.5 92.5 then the output is: Original points: 72.5 105.0 82.5 92.5 Second half of the points: 82.5 0.0 Note: Input array always has an even number of elements. 1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Points { 4 5 6789 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 755 public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scnr new Scanner (System.in); double[] pointsArray; double [] halfArray; int numPoints; int i; numPoints scnr.nextInt(); pointsArray = new double [numPoints]; for (i = 0; i < pointsArray.length; ++i) { pointsArray[i] = scnr.nextDouble(); } 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 25 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 26 33 3 } pointsArray[i] = scnr.nextDouble(); } /* Your code goes here */ System.out.print("Original points: "); for (i = 0; i < pointsArray.length; ++i) { System.out.printf("%.1f ", pointsArray[i]); } System.out.println(); System.out.print("Second half of the points: "); for (i = 0; i < halfArray.length; ++i) { System.out.printf("%.1f ", halfArray[i]); } System.out.println(); 4
Step by Step Solution
3.54 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


