Question: ) (Integral form for Kendall's T) For continuous independent bivariate random vectors (X1, Y1) and (X2, Y2) with the same distribution function, Kendall's 7 can
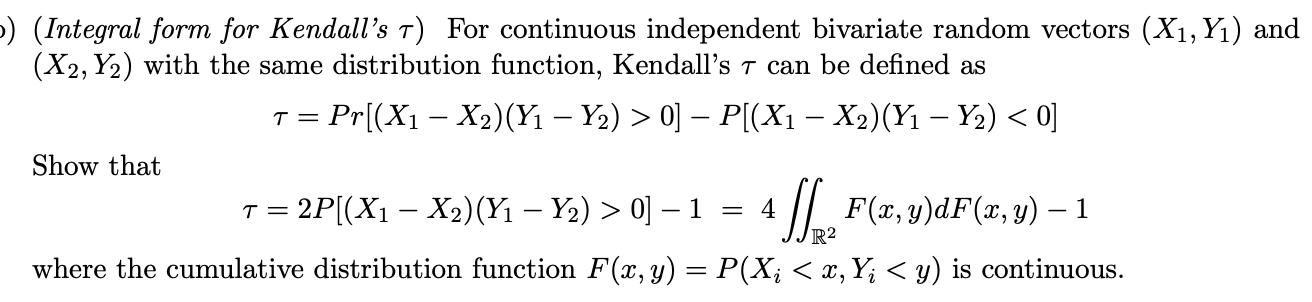
) (Integral form for Kendall's T) For continuous independent bivariate random vectors (X1, Y1) and (X2, Y2) with the same distribution function, Kendall's 7 can be defined as T = Pr[(X1 - X2) (Y1 - Y2) > 0] - P[(X1 - X2) (Y1 - Y2) 0] - 1 = 4 R2 F(x, y)dF(x, y) - 1 where the cumulative distribution function F(x, y) = P(X.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


